Feature • Install • Run • Wildcard • License • Discord
shuffleDNS is a wrapper around massdns, written in go, that allows you to enumerate valid subdomains using active bruteforce, as well as resolve subdomains with wildcard handling and easy input-output support.
Based on the work on massdns project by @blechschmidt.
- Simple and modular code base making it easy to contribute.
- Fast And Simple active subdomain scanning.
- Handles wildcard subdomains in a smart manner.
- Optimized for ease of use
- Stdin and stdout support for integrating in workflows
shuffledns -hThis will display help for the tool. Here are all the switches it supports.
shuffleDNS is a wrapper around massdns written in go that allows you to enumerate valid subdomains using active bruteforce as well as resolve subdomains with wildcard handling and easy input-output support.
Usage:
./shuffledns [flags]
Flags:
Flags:
INPUT:
-d, -domain string[] Domain to find or resolve subdomains for
-l, -list string File containing list of subdomains to resolve
-w, -wordlist string File containing words to bruteforce for domain
-r, -resolver string File containing list of resolvers for enumeration
-tr, -trusted-resolver string File containing list of trusted resolvers
-ri, -raw-input string Validate raw full massdns output
-mode string Execution mode (bruteforce, resolve, filter)
RATE-LIMIT:
-t int Number of concurrent massdns resolves (default 10000)
UPDATE:
-up, -update update shuffledns to latest version
-duc, -disable-update-check disable automatic shuffledns update check
OUTPUT:
-o, -output string File to write output to (optional)
-j, -json Make output format as ndjson
-wo, -wildcard-output string Dump wildcard ips to output file
CONFIGURATIONS:
-m, -massdns string Path to the massdns binary
-mcmd, -massdns-cmd string Optional massdns commands to run (example '-i 10')
-directory string Temporary directory for enumeration
OPTIMIZATIONS:
-retries int Number of retries for dns enumeration (default 5)
-sw, -strict-wildcard Perform wildcard check on all found subdomains
-wt int Number of concurrent wildcard checks (default 250)
DEBUG:
-silent Show only subdomains in output
-version Show version of shuffledns
-v Show Verbose output
-nc, -no-color Don't Use colors in output|
The tool also needs a list of valid resolvers. The dnsvalidator project can be used to generate these lists. You also need to provide wordlist, you can use a custom wordlist or use the commonspeak2-wordlist. |
shuffledns requires go1.21+ to install successfully. Run the following command to install the latest version:
go install -v github.com/projectdiscovery/shuffledns/cmd/shuffledns@latestshuffledns supports two types of operations:
Subdomain resolving
To resolve a list of subdomains, you can pass the list of subdomains via the -list option.
shuffledns -d example.com -list example-subdomains.txt -r resolvers.txt -mode resolveThis will run the tool against subdomains in example-subdomains.txt and returns the results. The tool uses the resolvers specified with -r flag to do the resolving.
You can also pass the list of subdomains at standard input (STDIN). This allows for easy integration in automation pipelines.
subfinder -d example.com | shuffledns -d example.com -r resolvers.txt -mode resolveThis uses the subdomains found passively by subfinder and resolves them with shuffledns returning only the unique and valid subdomains.
Subdomain Bruteforcing
shuffledns also supports bruteforce of a target with a given wordlist. You can use the w flag to pass a wordlist which will be used to generate permutations that will be resolved using massdns.
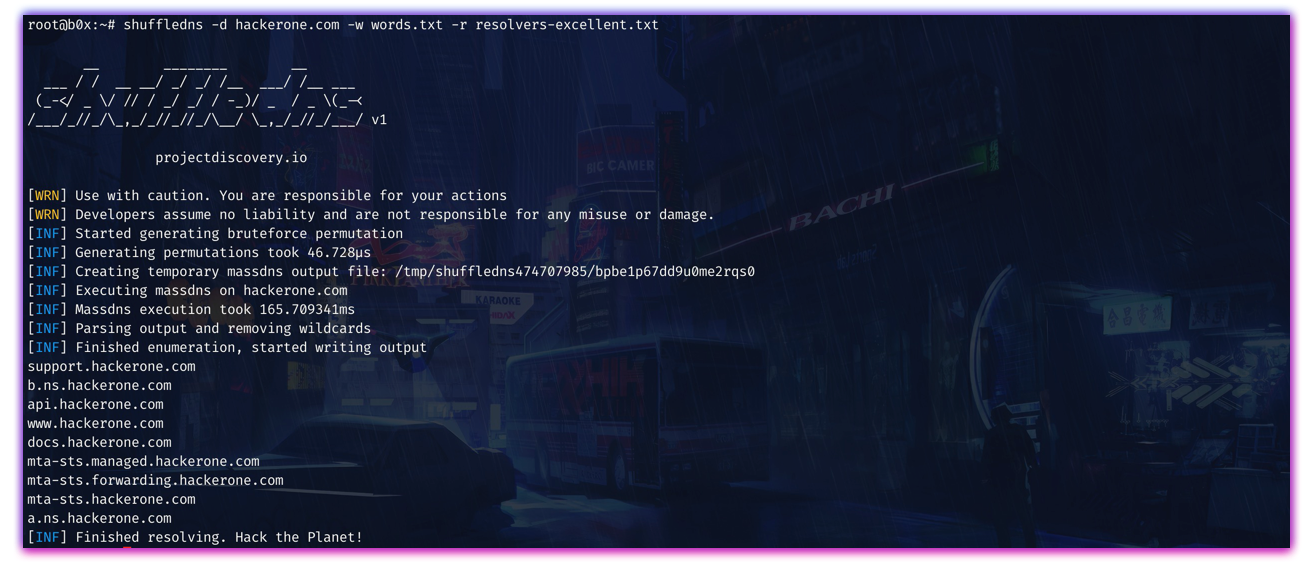
shuffledns -d hackerone.com -w wordlist.txt -r resolvers.txt -mode bruteforceThis will run the tool against hackerone.com with the wordlist wordlist.txt. The domain bruteforce can also be done with standard input as in previous example for resolving the subdomains.
echo hackerone.com | shuffledns -w wordlist.txt -r resolvers.txt -mode bruteforce|
A special feature of |
- Wildcard filter feature works with domain (
-d) input only. - Resolving or Brute-forcing only one operation can be done at a time.
shuffledns is distributed under GPL v3 License