Official code for Out-of-Sample Testing for GANs by Pablo Sánchez-Martín, Pablo M. Olmos and Fernando Perez-Cruz. For any question or help to run the code please feel free to contact us at psanch@tsc.uc3m.es
git clone https://github.com/psanch21/EvalGAN
cd EvalGAN
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
Throughout this document we will refer to the generator network as G
Here you may find a description of the parameters of the EvalGAN object:
input_G_name: Placeholder's name of the input noise to G.output_G_name: Name of the tensor in G holding the generated data.batch_size: Batch size of the trained GAN.z_dim: Dimension of the noise vector.z_init: Initialization for the noise vector.constraint: Select constraint to be applied during optimization (Optional)learning_rate: Initialization for the noise vector.checkpoint_dir: Path to the trained GAN checkpoint and meta data.output_dir: Folder to save results.model_name: Name of the model evaluated using EvalGAN
Here you will find the methods you may need to modify in order to fit your data type. All these methods can be found in evalGAN.py
Be sure that after normalization your data match the format of the output of G.
def normalize_data(self, data):
return data
def denormalize_data(self, data):
if(data.max()< 1.01 and data.min() < -0.01):
data = (data+1.)*127.5
elif(data.max()< 1.01 and data.min() > -0.01):
data = (data)*255.
if(data.shape[-1]>3):
data = np.transpose(data,(0,2,3,1))
return data.astype(int)
Metric to measure how similar are two samples of your dataset. In this example we show the Peak SNR (PSNR) that can be used for images. Please notice this method receives two arrays with shape [n_samples,...]
def dist(self, x_test, x_recons):
mse = np.mean((x_test-x_recons)**2, (1,2,3))
return 10*np.log10(255**2/mse)
The following method select the loss function to use during optimization. Notice it receives two tensors.
def loss_function(self, x_real, x_recons):
return tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(x_real - x_recons),[1,2,3]))
NOTE: the use of GPU is recommended.
First you need to load your n samples in a numpy array
x_test = get_your_data() # shape: [n,h,w,c]
Then, fill the necessary parameters to locate your trained GAN, identify the input (plus its dimension) and output tensors of G,... This is a possible configuration
z_dim=256
evalGAN = EvalGAN(input_G_name='z',
output_G_name='generator/out:0',
batch_size=64,
z_dim=z_dim,
z_init=tf.initializers.random_normal(0.,1.),
constraint=lambda t: tf.clip_by_norm(t, np.sqrt(z_dim)),
learning_rate=5e-3,
beta1=0.9,
checkpoint_dir='./checkpoint_folder',
output_dir='./result_folder',
model_name='GAN')
Then load the samples in which you want to evaluate the GAN and set any additional placeholder your network may need
evalGAN.set_data(x_test)
evalGAN.add_placeholder('Placeholder1', False)
evalGAN.add_placeholder('Placeholder2', 0.5)
Now, we are ready to solve the optimization problem to find the best reconstruction and its associated input vector. Be aware this is an optimization per sample.
evalGAN.fit(epochs=3, early_stopping=1, restore=1)
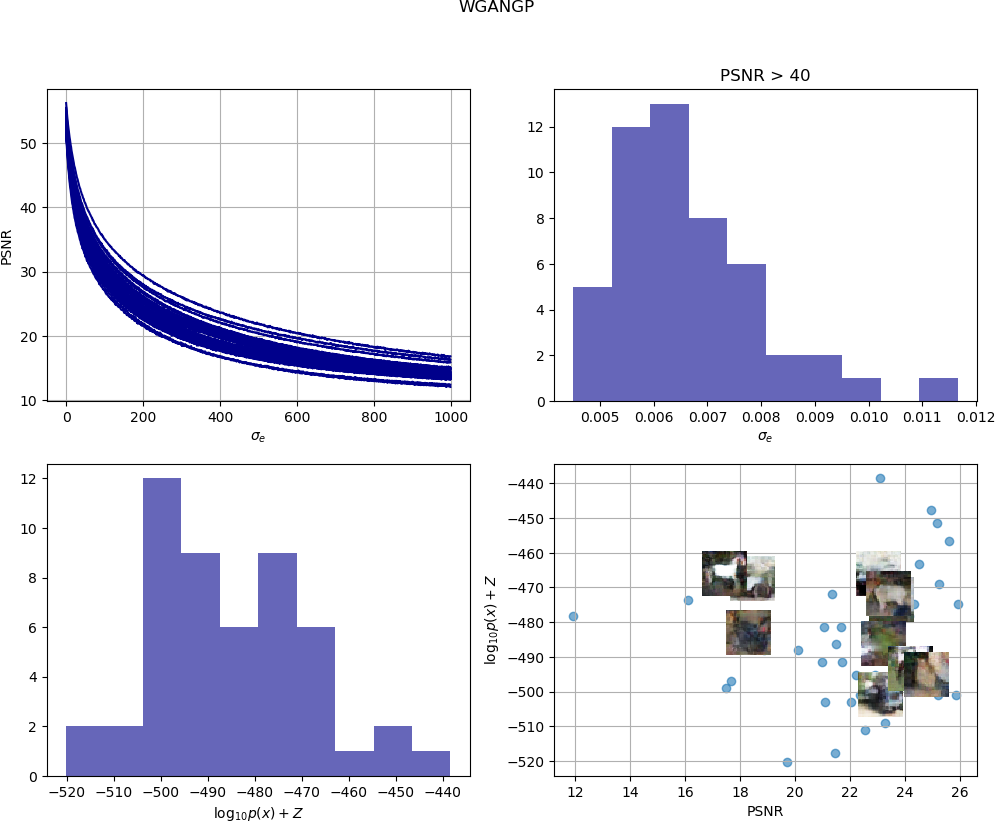
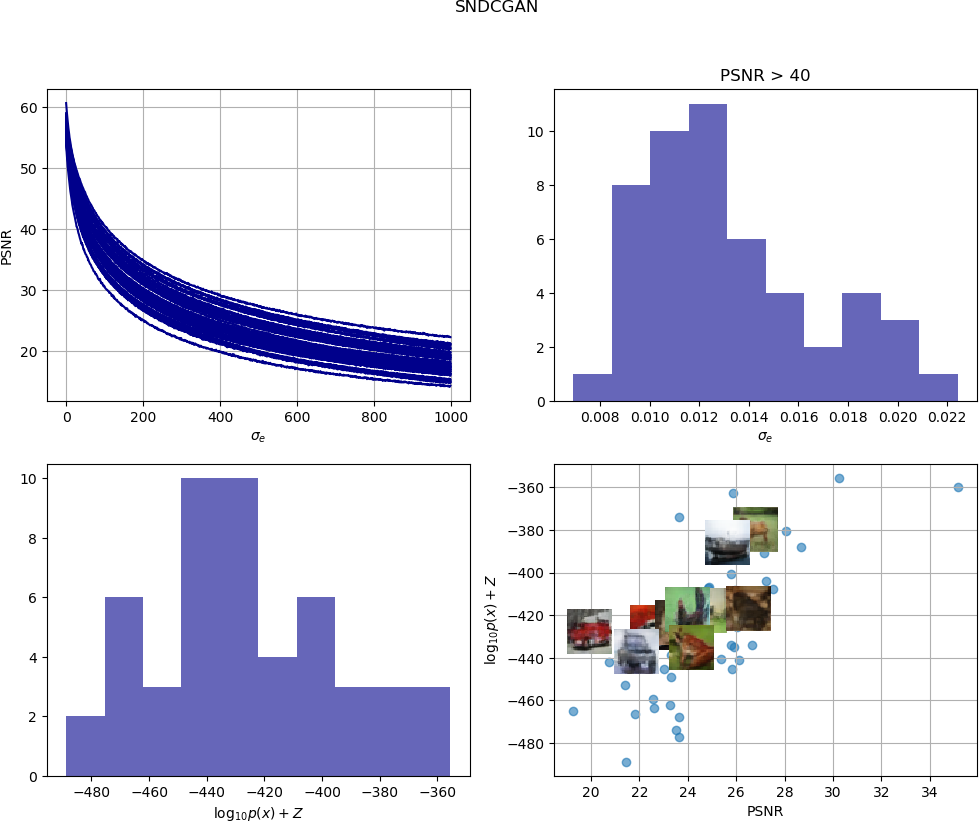
To obtain the estimated sample loglikelihood, select the range of sigma, that is the region around the inferred input noise, you would like to explore. For the non-isotropic approximation select the maximum number of noise samples to consider and choose a threshold to ensure that two samples are indistinguishable. In this example, we select as T a PSNR=40.
sigma_list = np.linspace(0.001,0.2,100)
evalGAN.analysis_isotropic(sigma_list, N=128)
evalGAN.analysis_non_isotropic( sigma_list, N=1000,N_max=10000, T=40)
We get the results with
evalGAN.print_results() # Returns the PSNR and ll per sample
f = evalGAN_SN.plot()
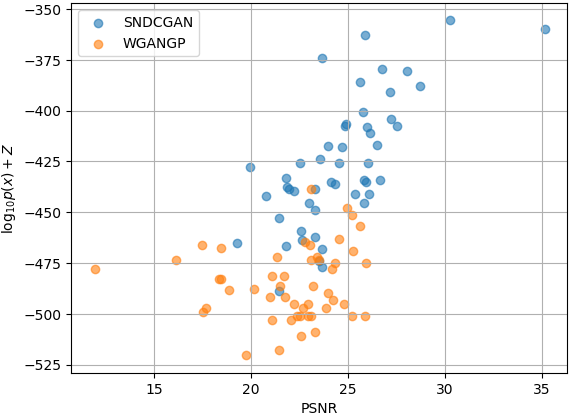
We can compare the EvalGAN scatter plot of several models as follows
data_SN = evalGAN_SN.get_scatter_data()
data_GP = evalGAN_GP.get_scatter_data()
utils.plot_scatter(data_SN, ax, label=evalGAN_SN.model_name)
utils.plot_scatter(data_GP, ax, label=evalGAN_GP.model_name)
utils.save_fig(f,'evalGAN_scatter.png', latex=False)
We have trained the SNDCGAN and WGANGP with CIFAR10 and used 50 test samples with EvalGAN.
SNDCGAN
--------------------------------
Samples | PSNR | LL(x)
Sample(0/50) | 22.0 | -459.97
Sample(1/50) | 23.3 | -486.07
Sample(2/50) | 25.9 | -432.07
Sample(3/50) | 24.9 | -428.88
Sample(4/50) | 23.3 | -471.4
Sample(5/50) | 26.1 | -434.18
- TensorFlow - Open source software library for numerical computation using data-flow graphs
- Python 3.6.4 - Dependency Management