This repository contains source code (MuViTaNet) for paper "Cardiac Complication Risk Profiling for Cancer Survivors via Multi-View Multi-Task Learning" (ICDM 2021).
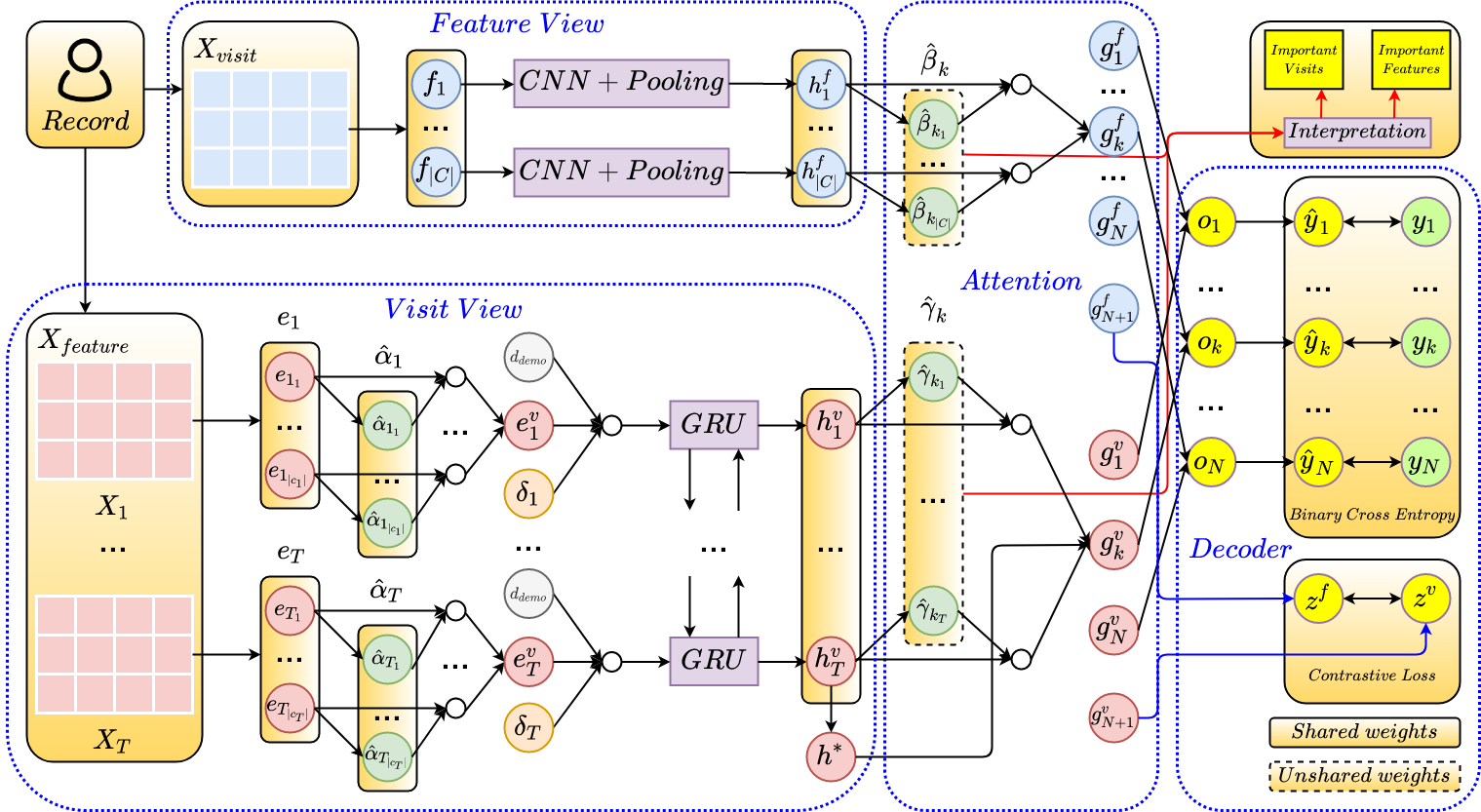
MuViTaNet is a Python implementation of the multi-view multi-task network for predicting the onset of multiple complications. In particular, MuViTaNet complements patient representation by using a multi-view encoder to effectively extract information by considering clinical data as both sequences of clinical visits and sets of clinical features. In addition, it leverages additional information from both related labeled and unlabeled datasets to generate more generalized representations by using a new multi-task learning scheme for making more accurate predictions.
The experimental results show that MuViTaNet outperforms existing methods for profiling the development of cardiac complications in breast cancer survivors. Furthermore, thanks to its multi-view multi-task architecture, MuViTaNet also provides an effective mechanism for interpreting its predictions in multiple perspectives, thereby helping clinicians discover the underlying mechanism triggering the onset and for making better clinical treatments in real-world scenarios.
Figure 1: Overall architecture of MuViTaNet
MuViTaNet depends on Numpy, tqdm, scikit-learn, and PyTorch (CUDA toolkit if use GPU). You must have them installed before using MuViTaNet.
The simple way to install them is using conda:
$ conda install numpy tqdm scikit-learn pytorchWe do not provide the insurance claim data itself due to copyright issue.
The training script for MuViTaNet is located at the main folder.
$ python muvitanet_main.py Arguments in this scripts:
--fold: data fold in cross-validation setting--batch_size: batch size used for training--max_epoch: maximum number of training iterations--model_name: name of model--gpu: gpu id--warm_start: train model from pretrained weights--inference: use model in inference stage