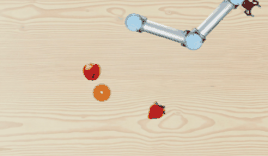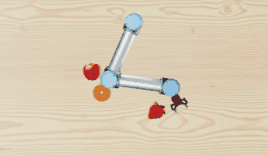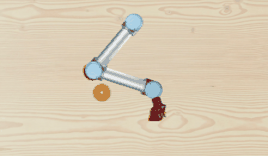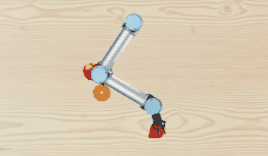
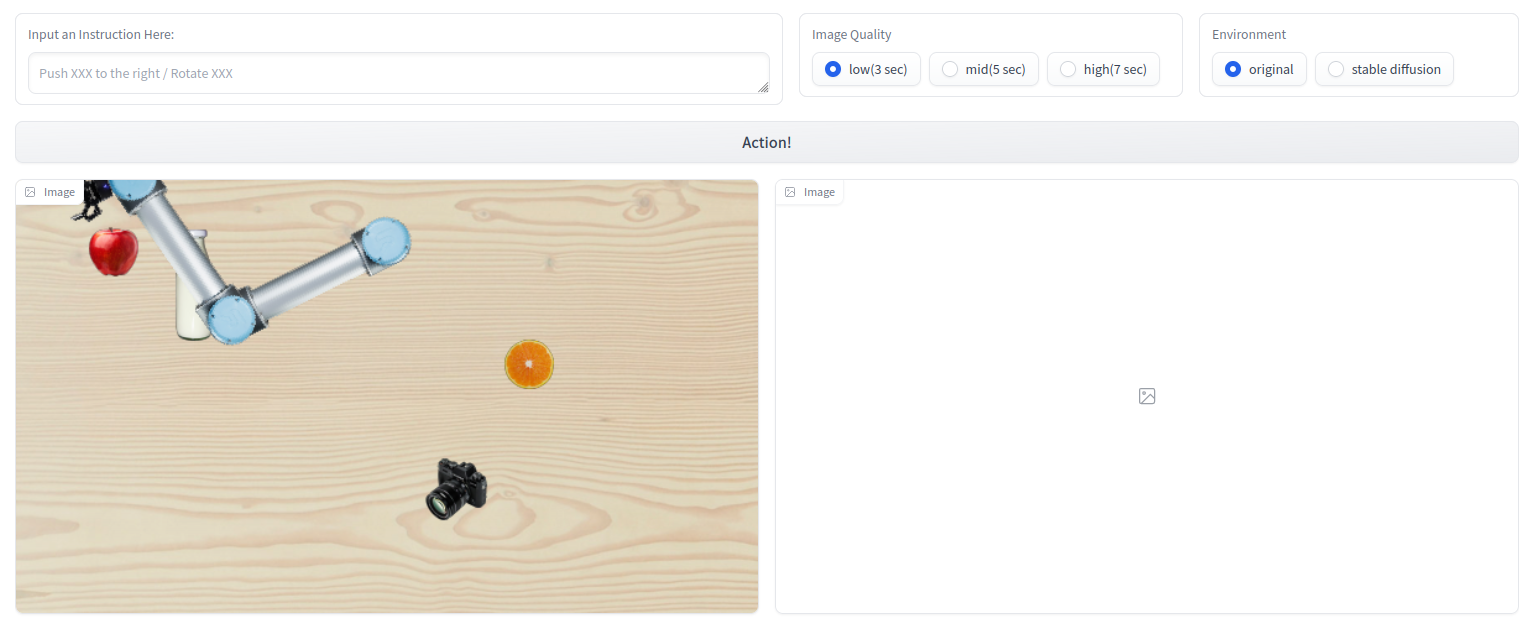
A light-weighted, open-box 2D robot manipulation simulator.
An interactive demonstration here.
This repo majorly includes 2 parts:
- A lighted-weighted simulator (class
TinyRobotEnv) powered by pygame and openai gym. This is a 2D simulator, featuring the visual appearance of a UR5 robot. Inverse kinematics API is implemented as well. - Data collection toolkit for collecting language-conditioned imitation
learning datasets. In this toolkit, there includes the following items:
- A rule-based planner (class
Planner) that generates actions to perform, according to users' rules, such as go to specific position and close the gripper. - A recorder (class
Recorder) that records the image, states, sentence and all useful information to files.
- A rule-based planner (class
git clone https://github.com/ir-lab/TinyLanguageRobots.git
pip install -r requirements.txt
python collect_data.py
In collect_data.py, some sample tasks are defined.
This command will automatically start collecting demonstrations under the current directory.
Please use this file as a reference for constructing your own tasks and dataset.
configis a dictionModularity through Attention: Efficient Training and Transfer of Language-Conditioned Policies for Robot Manipulationary indicating the initialization setups of the environment. An example is at./config.yaml. It defines the background scale in pixels (desk_width,desk_heightandscale). It also defines the robot (robot) and all the objects to be displayed (objects). Inobjects, all the objects with apositionproperty will be moveable.render_modedefines how to visualize the environment. Whenrender_mode == human, it will visualize it in a window. Whenrender_mode == rgb_array, the simulator will return an image instead of showing it in the window when rendering.
actionis an array with shape (4,), where each entry represents the action for each joint of the robot, starting from the shoulder.eef_zrepresents the target height of the z axis.
render_modehas been implemented forhumanandrgb_arrayoptions.
This function calculates the inverse kinematics for a given target eef position.
xyois the given eef position, an array of [x, y, orientation]
In this class, users can write the code to define different tasks, and generate actions for a given task.
In this function, users can write code to define the action of each task. Please
refer to the code ./planner.py for an example of how to do it.
taskis a dictionary and should be aligned with the definition in_generate_plan_().generate_action()returns the current action to take. The return value is ready to input toTinyRobotEnv.step(...).ends()returns a boolean value of whether the plan has ended.
This class provides a solution to store the whole episode to files. For an episode, a folder will be created. Images of each of the timesteps will be stored. The states, task information and all other information will be logged as in a json file under that folder.
data_folderis a string indicating the folder of the target data storage location.
stepis an integer indicating the current timestep.imgis an array of representing the current img.stateis a dictionary of current state. It will be logged in a json file.sentenceis a string which is the language instruction to the task.actionis an array showing the current action taken.taskis a dictionary depicting the task the demonstration is currently executing.
All the informations will be stored to the local json file when this function is called.