Ardb is a BSD licensed, redis-protocol compatible persistent nosql, it support multiple storage engines as backend like Google's LevelDB, Facebook's RocksDB, OpenLDAP's LMDB, WiredTiger, PerconaFT, the default backend is Facebook's RocksDB.
Rocksdb is the default storage engine, to compile with rocksdb, just type make to compile server & lib & tests.
To use LMDB or LevelDB or WiredTiger as storage engine, you should set env storage_engine first.
storage_engine=lmdb make
storage_engine=leveldb make
storage_engine=wiredtiger make
storage_engine=perconaft make
storage_engine=forestdb make
It should compile to several executables in src directory, such as ardb-server, ardb-test etc.
- Full redis-protocol compatibility
- 2d spatial index supported. Spatial Index
- Redis 3.2 geo commands support
- Most redis commands supported, and a few new commands.
- Replication compatible with Redis 2.6/2.8
- Ardb instance work as slave of Redis 2.6/2.8+ instance
- Ardb instance work as master of Redis 2.6/2.8+ instance
- Ardb instance work as slave of Ardb instance
- Auto failover support by redis-sentinel
- Lua Scripting support
- Backup data online
- Use 'save/bgsave' to backup data
- Use 'import' to import backup data
Since ardb is a full redis-protocol compatible server, you can use most existed redis client to connect it without any problem. Here lists all redis clients. http://www.redis.io/clients
-
Known Issues:
- For Node.js, the recommand client node_redis would try to parse
redis_version:x.y.zfrominfocommand's output, Ardb users should configureredis-compatible-versionin ardb.conf to makesure thatredis_version:x.y.zexists ininfocommand's output. There is an online redis GUI admin service redsmin build on node_redis, users can test ardb's redis protocol conformance by a visual way.
- For Node.js, the recommand client node_redis would try to parse
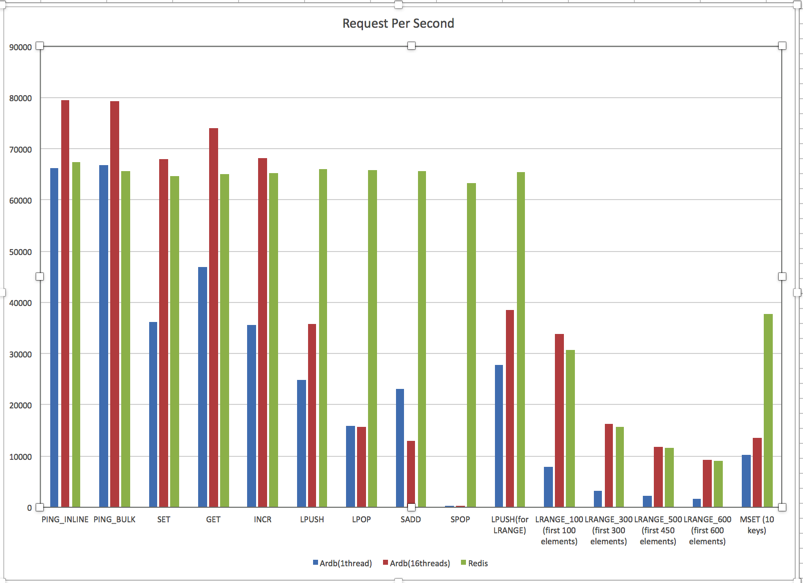
Benchmarks were all performed on a four-core Intel(R) Xeon(R) CPU E5520@2.27GHz, with 64 GB of DDR3 RAM, 500 GB of SCSI disk
The benchmark tool is 'redis-benchmark' from redis,50 parallel clients, 10000000 requests, 1000000 random keys each test case.
GCC Version:4.8.3
OS Version: Red Hat Enterprise Linux AS release 4 (Nahant Update 3)
Kernel Version: 2.6.32_1-10-6-0
Redis Version: 2.8.9
Ardb Version: 0.9.0(RocksDB4.3.1), 1 thread(thread-pool-size configured 1)
RocksDB Options:
write_buffer_size=128M;max_write_buffer_number=16;compression=kSnappyCompression;
block_based_table_factory={block_cache=512M;block_size=4;filter_policy=bloomfilter:10:true};
create_if_missing=true;max_open_files=-1;rate_limiter_bytes_per_sec=50M
Becnhmark data(./redis-benchmark -r 10000000 -n 10000000):
RocksDB Redis
PING_INLINE 66313.01 67294.75
PING_BULK 66844.91 65703.02
SET 36238.45 64574.45
GET 46979.24 65112.64
INCR 35522.72 65274.15
LPUSH 24789.29 66093.85
LPOP 15812.53 65832.78
SADD 23033.51 65573.77
SPOP 9701.3 63291.14
LPUSH(for LRANGE) 27693.16 65487.89
LRANGE_100 (first 100 elements) 7857.93 30797.66
LRANGE_300 (first 300 elements) 3176.16 15710.92
LRANGE_500 (first 450 elements) 2156.1 11504.83
LRANGE_600 (first 600 elements) 1647.88 9094.22
MSET (10 keys) 10217.64 37678.97
Note:
- Ardb uses 1 threads in this benchmark test, since redis is single threaded application. But ardb is actually a multithreaded applcation, you can start the server with more threads by setting 'thread-pool-size' to 2 or higher to increase the read/write performance.
- Join the mailing list(Subscribe via email)