- 数据预处理
- 模型训练
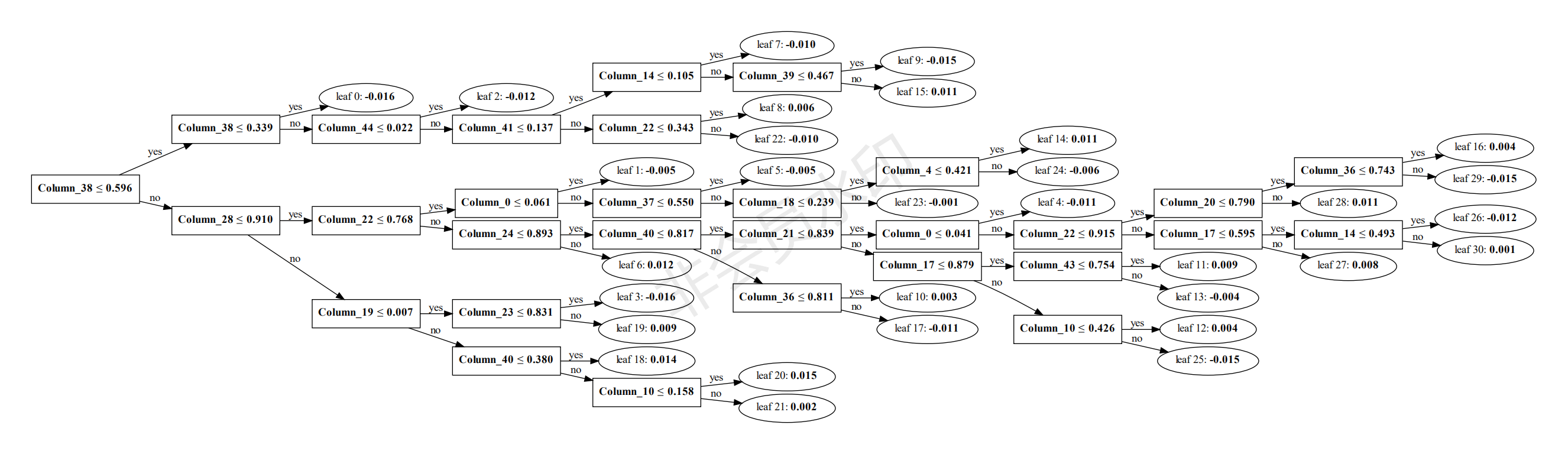
- 模型决策可视化
- 预测
- ndcg评估
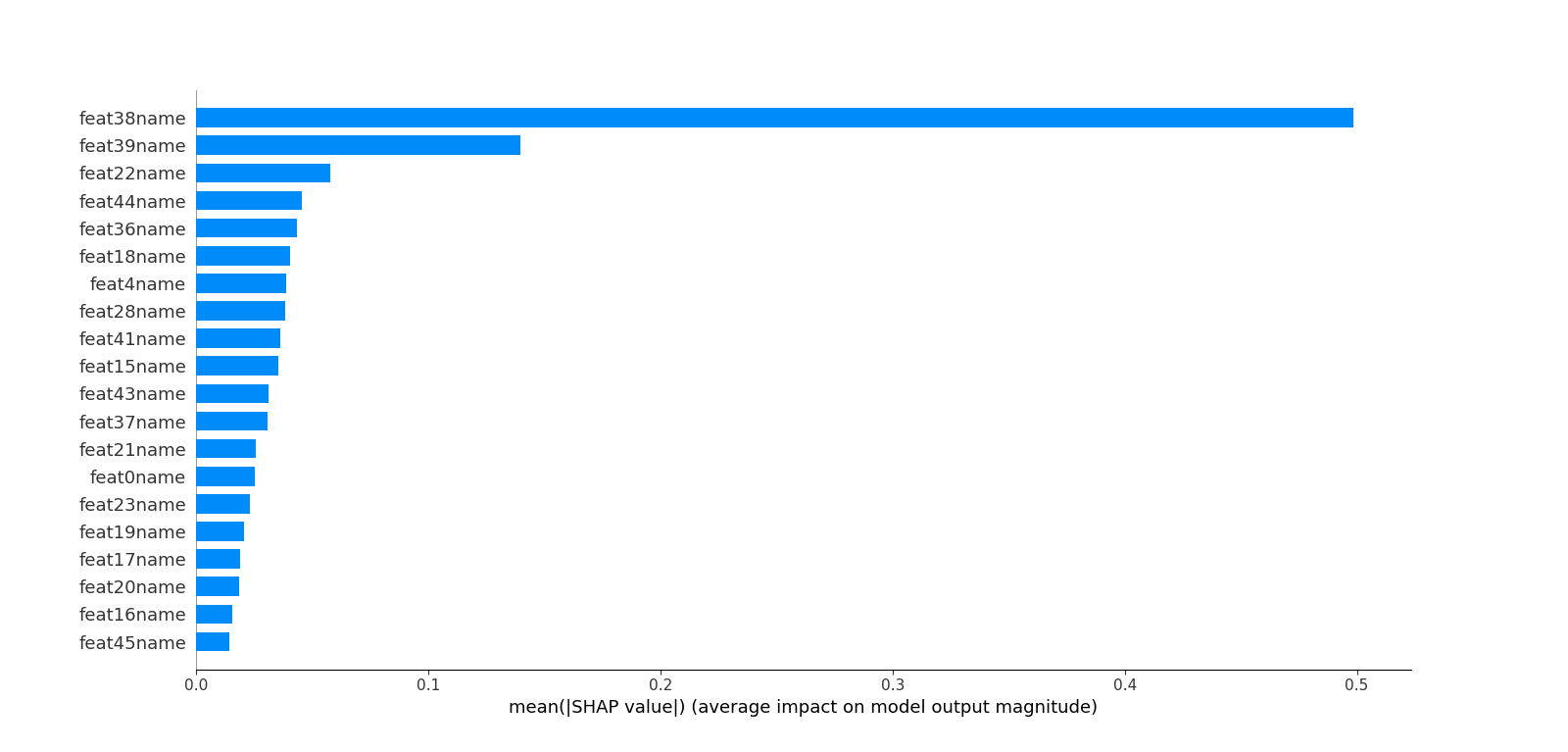
- 特征重要度
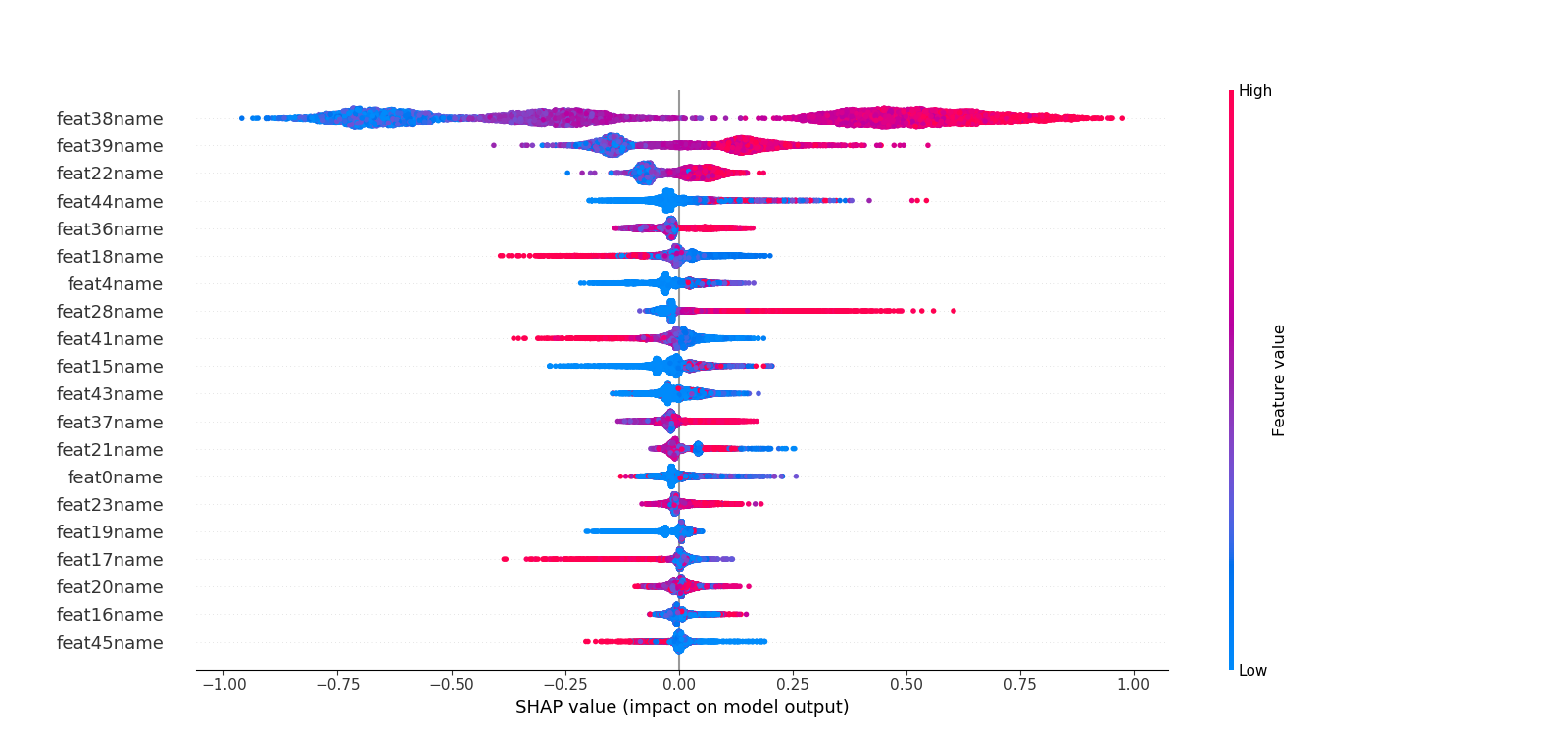
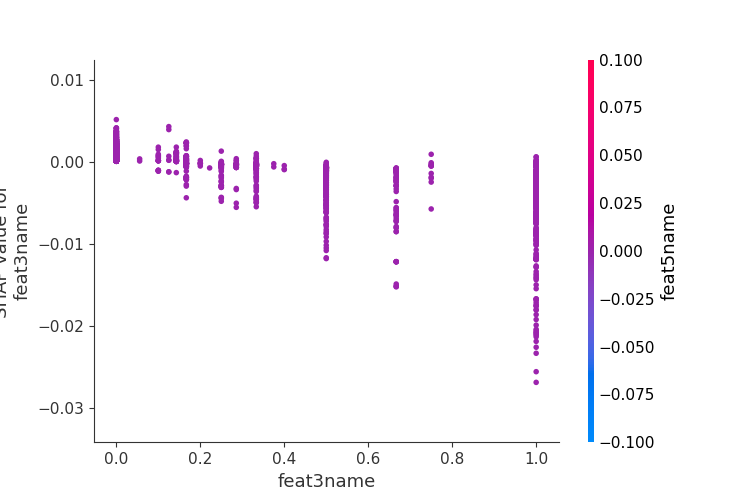
- SHAP特征贡献度解释
- 样本的叶结点输出
(要求安装lightgbm、graphviz、shap等)
0 qid:10002 1:0.007477 2:0.000000 ... 45:0.000000 46:0.007042 #docid = GX008-86-4444840 inc = 1 prob = 0.086622
0 qid:10002 1:0.603738 2:0.000000 ... 45:0.333333 46:1.000000 #docid = GX037-06-11625428 inc = 0.0031586555555558 prob = 0.0897452 ...
0 1:0.007477 2:0.000000 ... 45:0.000000 46:0.007042
0 1:0.603738 2:0.000000 ... 45:0.333333 46:1.000000 ...
8
8
8
8
8
16
8
118
16
8
...
train params = {
'task': 'train', # 执行的任务类型
'boosting_type': 'gbrt', # 基学习器
'objective': 'lambdarank', # 排序任务(目标函数)
'metric': 'ndcg', # 度量的指标(评估函数)
'max_position': 10, # @NDCG 位置优化
'metric_freq': 1, # 每隔多少次输出一次度量结果
'train_metric': True, # 训练时就输出度量结果
'ndcg_at': [10],
'max_bin': 255, # 一个整数,表示最大的桶的数量。默认值为 255。lightgbm 会根据它来自动压缩内存。如max_bin=255 时,则lightgbm 将使用uint8 来表示特征的每一个值。
'num_iterations': 200, # 迭代次数,即生成的树的棵数
'learning_rate': 0.01, # 学习率
'num_leaves': 31, # 叶子数
'max_depth':6,
'tree_learner': 'serial', # 用于并行学习,‘serial’: 单台机器的tree learner
'min_data_in_leaf': 30, # 一个叶子节点上包含的最少样本数量
'verbose': 2 # 显示训练时的信息
}
- docs:7796
- groups:380
- consume time : 4 seconds
- training's ndcg@10: 0.940891
训练时的输出:
- [LightGBM] [Info] Total Bins 9171
- [LightGBM] [Info] Number of data: 7796, number of used features: 40
- [LightGBM] [Debug] Trained a tree with leaves = 31 and max_depth = 9
- [1] training's ndcg@10: 0.791427
- [LightGBM] [Debug] Trained a tree with leaves = 31 and max_depth = 12
- [2] training's ndcg@10: 0.828608
- [LightGBM] [Debug] Trained a tree with leaves = 31 and max_depth = 10
- ...
- ...
- ...
- [198] training's ndcg@10: 0.941018
- [LightGBM] [Debug] Trained a tree with leaves = 31 and max_depth = 11
- [199] training's ndcg@10: 0.941038
- [LightGBM] [Debug] Trained a tree with leaves = 31 and max_depth = 11
- [200] training's ndcg@10: 0.940891
- consume time : 4 seconds
可指定树的索引进行可视化生成,便于分析决策过程。
- ['docid = GX252-32-5579630 inc = 1 prob = 0.190849'
- 'docid = GX108-43-5342284 inc = 0.188670948386237 prob = 0.103576'
- 'docid = GX039-85-6430259 inc = 1 prob = 0.300191' ...,
- 'docid = GX009-50-15026058 inc = 1 prob = 0.082903'
- 'docid = GX065-08-0661325 inc = 0.012907717401617 prob = 0.0312699'
- 'docid = GX012-13-5603768 inc = 1 prob = 0.0961297']
all qids average ndcg: 0.761044123343
模型中的特征是"Column_number",这里打印重要度时可以映射到真实的特征名,比如本测试用例是46个feature
- feat0name : 228 : 0.038
- feat1name : 22 : 0.0036666666666666666
- feat2name : 27 : 0.0045
- feat3name : 11 : 0.0018333333333333333
- feat4name : 198 : 0.033
- feat10name : 160 : 0.02666666666666667
- ...
- ...
- ...
- feat37name : 188 : 0.03133333333333333
- feat38name : 434 : 0.07233333333333333
- feat39name : 286 : 0.04766666666666667
- feat40name : 169 : 0.028166666666666666
- feat41name : 348 : 0.058
- feat43name : 304 : 0.050666666666666665
- feat44name : 283 : 0.04716666666666667
- feat45name : 220 : 0.03666666666666667
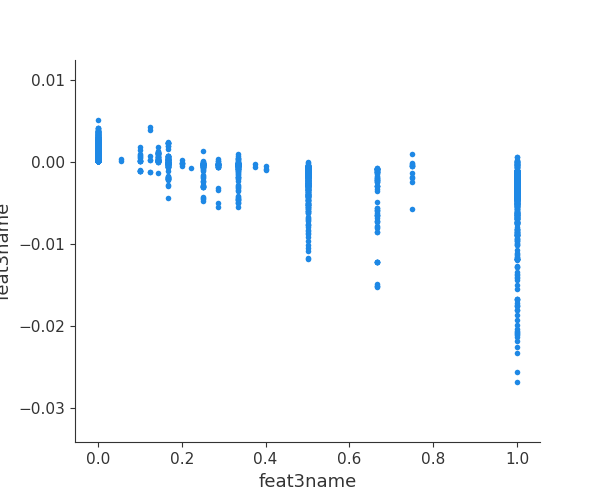
这里不同于六中特征重要度的计算,而是利用博弈论的方法--SHAP(SHapley Additive exPlanations)来解析模型。 利用SHAP可以进行特征总体分析、多维特征交叉分析以及单特征分析等。
这里测试用例是test/leaf.txt 5个样本
[
- [ 0. 1. 0. ..., 0. 0. 1.]
- [ 1. 0. 0. ..., 0. 0. 0.]
- [ 0. 0. 1. ..., 0. 0. 1.]
- [ 0. 1. 0. ..., 0. 1. 0.]
- [ 0. 0. 0. ..., 1. 0. 0.] ]
https://github.com/microsoft/LightGBM
https://github.com/jma127/pyltr
https://github.com/slundberg/shap
如有搜索、推荐、nlp以及大数据挖掘等问题或合作,可联系我:
1、我的github项目介绍:https://github.com/jiangnanboy
2、我的博客园技术博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/little-horse/
3、我的QQ号:2229029156