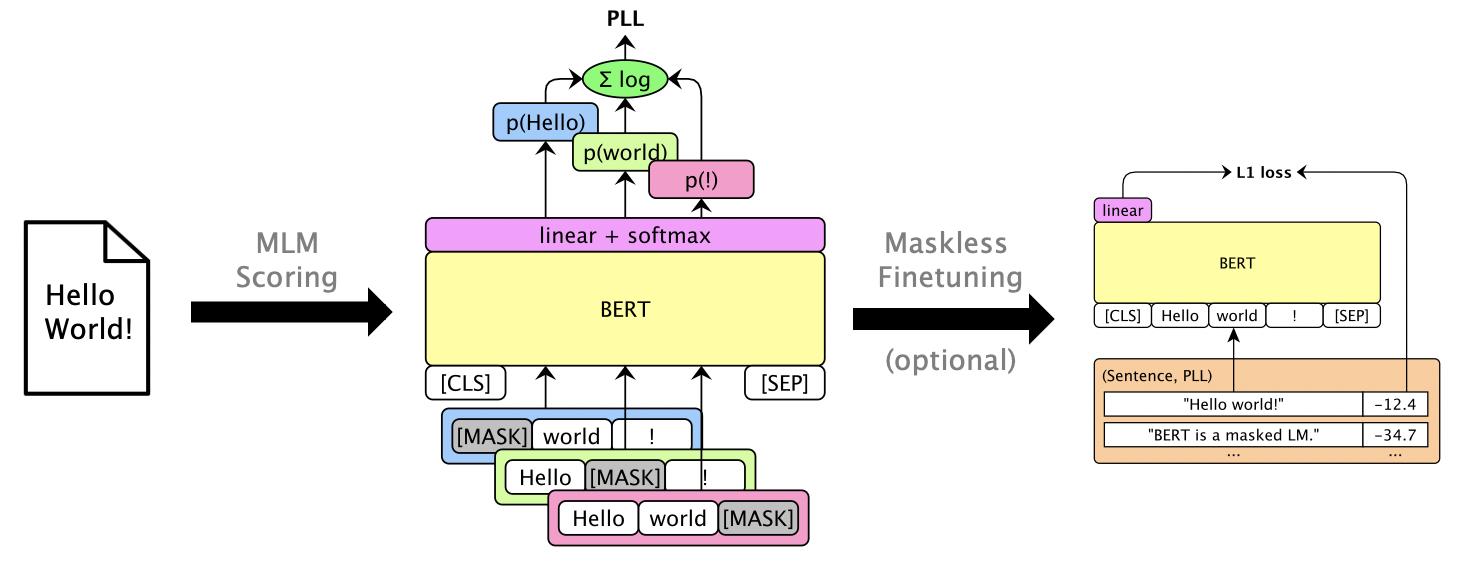
This package uses masked LMs like BERT, RoBERTa, and XLM to score sentences and rescore n-best lists via pseudo-log-likelihood scores, which are computed by masking individual words. We also support autoregressive LMs like GPT-2. Example uses include:
- Speech Recognition: Rescoring an ESPnet LAS model (LibriSpeech)
- Machine Translation: Rescoring a Transformer NMT model (IWSLT'15 en-vi)
- Linguistic Acceptability: Unsupervised ranking within linguistic minimal pairs (BLiMP)
Paper: Julian Salazar, Davis Liang, Toan Q. Nguyen, Katrin Kirchhoff. "Masked Language Model Scoring", ACL 2020.
Python 3.6+ is required. Clone this repository and install:
pip install -e .
pip install torch mxnet-cu102mkl # Replace w/ your CUDA version; mxnet-mkl if CPU only.Some models are via GluonNLP and others are via 🤗 Transformers, so for now we require both MXNet and PyTorch. You can now import the library directly:
from mlm.scorers import MLMScorer, MLMScorerPT, LMScorer
from mlm.models import get_pretrained
import mxnet as mx
ctxs = [mx.cpu()] # or, e.g., [mx.gpu(0), mx.gpu(1)]
# MXNet MLMs (use names from mlm.models.SUPPORTED_MLMS)
model, vocab, tokenizer = get_pretrained(ctxs, 'bert-base-en-cased')
scorer = MLMScorer(model, vocab, tokenizer, ctxs)
print(scorer.score_sentences(["Hello world!"]))
# >> [-12.410664200782776]
print(scorer.score_sentences(["Hello world!"], per_token=True))
# >> [[None, -6.126736640930176, -5.501412391662598, -0.7825151681900024, None]]
# EXPERIMENTAL: PyTorch MLMs (use names from https://huggingface.co/transformers/pretrained_models.html)
model, vocab, tokenizer = get_pretrained(ctxs, 'bert-base-cased')
scorer = MLMScorerPT(model, vocab, tokenizer, ctxs)
print(scorer.score_sentences(["Hello world!"]))
# >> [-12.411025047302246]
print(scorer.score_sentences(["Hello world!"], per_token=True))
# >> [[None, -6.126738548278809, -5.501765727996826, -0.782496988773346, None]]
# MXNet LMs (use names from mlm.models.SUPPORTED_LMS)
model, vocab, tokenizer = get_pretrained(ctxs, 'gpt2-117m-en-cased')
scorer = LMScorer(model, vocab, tokenizer, ctxs)
print(scorer.score_sentences(["Hello world!"]))
# >> [-15.995375633239746]
print(scorer.score_sentences(["Hello world!"], per_token=True))
# >> [[-8.293947219848633, -6.387561798095703, -1.3138668537139893]](MXNet and PyTorch interfaces will be unified soon!)
Run mlm score --help to see supported models, etc. See examples/demo/format.json for the file format. For inputs, "score" is optional. Outputs will add "score" fields containing PLL scores.
There are three score types, depending on the model:
- Pseudo-log-likelihood score (PLL): BERT, RoBERTa, multilingual BERT, XLM, ALBERT, DistilBERT
- Maskless PLL score: same (add
--no-mask) - Log-probability score: GPT-2
We score hypotheses for 3 utterances of LibriSpeech dev-other on GPU 0 using BERT base (uncased):
mlm score \
--mode hyp \
--model bert-base-en-uncased \
--max-utts 3 \
--gpus 0 \
examples/asr-librispeech-espnet/data/dev-other.am.json \
> examples/demo/dev-other-3.lm.jsonOne can rescore n-best lists via log-linear interpolation. Run mlm rescore --help to see all options. Input one is a file with original scores; input two are scores from mlm score.
We rescore acoustic scores (from dev-other.am.json) using BERT's scores (from previous section), under different LM weights:
for weight in 0 0.5 ; do
echo "lambda=${weight}"; \
mlm rescore \
--model bert-base-en-uncased \
--weight ${weight} \
examples/asr-librispeech-espnet/data/dev-other.am.json \
examples/demo/dev-other-3.lm.json \
> examples/demo/dev-other-3.lambda-${weight}.json
doneThe original WER is 12.2% while the rescored WER is 8.5%.
One can finetune masked LMs to give usable PLL scores without masking. See LibriSpeech maskless finetuning.
Run pip install -e .[dev] to install extra testing packages. Then:
- To run unit tests and coverage, run
pytest --cov=src/mlmin the root directory.