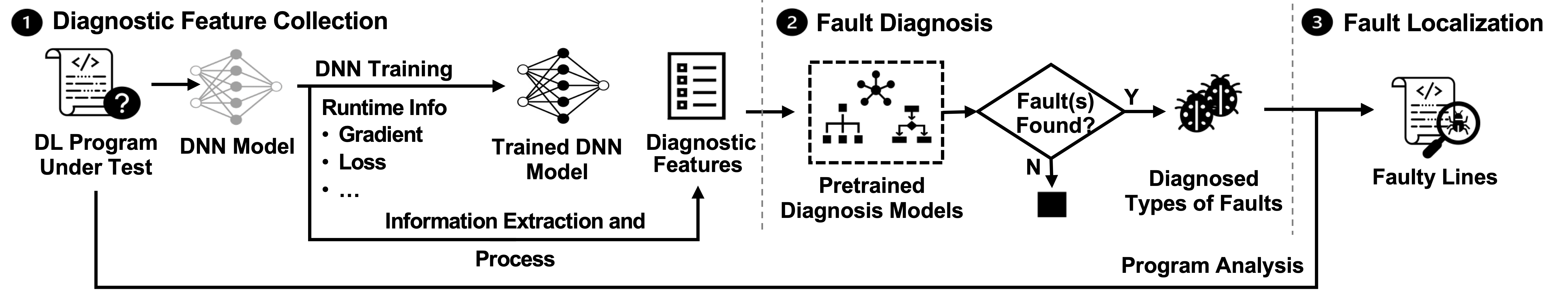
DeepFD, a learning-based fault diagnosis and localization framework which maps the fault localization task to a learning problem.
In particular, it infers the suspicious fault types via monitoring the runtime features extracted during DNN model training, and then locates the diagnosed faults in DL programs.
Given a program, DeepFD constructs a DNN architecture and collects runtime data such as the loss and neurons' information by training the architecture.
After obtaining the diagnostic features, we then infer the possible types of faults that exist in the DL program according to the features. We regard it as a multi-label classification problem, which maps the obtained features into one or more possible labels. Each label corresponds to a fault type.
The classification relies on the predictions made by a set of pre-trained diagnosis models (see below). The diagnosis result is given by the union of the diagnosed faults predicted by each diagnosis model to maximize the number of faults diagnosed.
After acquiring the diagnosed types of faults, DeepFD performs fault localization at the program level. Specifically, the program is first parsed into its abstract syntax tree (AST), and DeepFD goes through the nodes of the parse tree, traverses assignment statement as well as expressions, and then identifies the places (i.e. lines) where the diagnosed types of faults are defined.
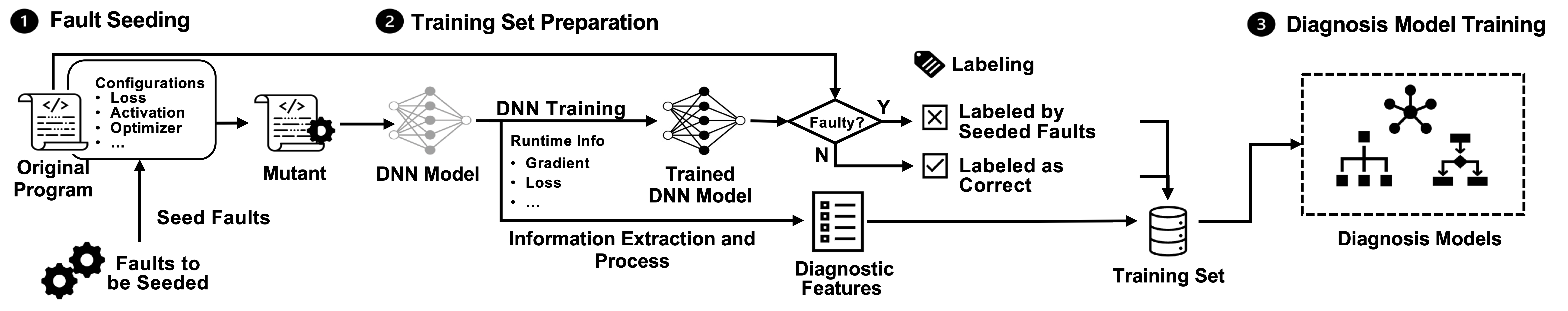
This step is to prepare sufficient training samples for the diagnosis models.
This step prepares the labels and extracting inputs for the training set.
We treat the fault diagnosis as a multi-label classification problem mapping a faulty program to the multiple types of faults that it contains. We construct three diagnosis models using the three widely-used and effective machine learning algorithms (i.e., K-Nearest Neighbors, Decision Tree and Random Forest ) to learn the correlations between diagnostic features and types of faults.
- Python 3.6 +
- Packages:
pip install -r requirements.txt- Run the script
python CodeBook/predict.py- Example output
====================
Working on case:
working on subject: 59282996
The ground truth faults: ['epoch']
Diagnosed / Localized by DeepFD:
Fault 1: [epoch], Lines: [309]
case end
====================
====================
Working on case:
working on subject: 31556268
The ground truth faults: ['lr', 'loss', 'epoch']
Diagnosed / Localized by DeepFD:
Fault 1: [lr], Lines: [17]
Fault 2: [act], Lines: [11, 13]
Fault 3: [loss], Lines: [19]
Fault 4: [epoch], Lines: [34]
case end
====================
-
Under the folder
Benchmark/Subjects, there are two subjects. -
The statistics, patches, detailed information of all benchmarks can be found at
Benchmark/Subjects/Benchmark-with-patches.xlsx -
The evaluation statistics can be found at ``Benchmark/Subjects/Evaluation.xlsx`
-
The entire benchmark with runtime information and extracted features can be downloaded here.
- Script
python CodeBook/feature_extraction.py- Output
summary.csvunder folder (specified by-pd)summary_dict.csvunder folder (specified by-pd)stats.csvin each sub-folder (specified by-ds)
-
Prepare original dataset
- Download from dataset provided here.
- Download into folder
Evaluation, sub-folders inside includingMNIST,CIFAR-10, etc.
-
Generate mutant
python CodeBook/seed_all.py --base Evaluation --dataset MNIST -sf 1 --fault_type loss ----max_fault 2The example seeds 2 faults in type of loss for each DNN model under Evaluation/MNIST.
- Run all the mutants and collect runtime information
python CodeBook/run_all.py --base Evaluation --dataset MNIST --gpu 0 --run 1 --max_iter 1The example runs each generated mutant once, together with original one under Evaluation/MNIST, without using GPU.
- Extract features and labeling
python CodeBook/feature_extraction.pyDeepFD
├── Classifiers # The pretrained diagnosis models
│ └── All
├── CodeBook # code
│ ├── Analyzer
│ ├── Callbacks
│ ├── Config.py
│ ├── MultiLabelClassification
│ ├── SeedFaults
│ ├── Utils
│ ├── feature_extraction.py
│ ├── predict.py
│ ├── run_all.py
│ └── seed_all.py
├── Benchmark # Benchmarks
│ └── Subjects
├── Figures # Figures for README
│ ├── model-prep.png
│ └── workflow.png
├── README.md
└── requirements.txt # requirements to be installed by pip