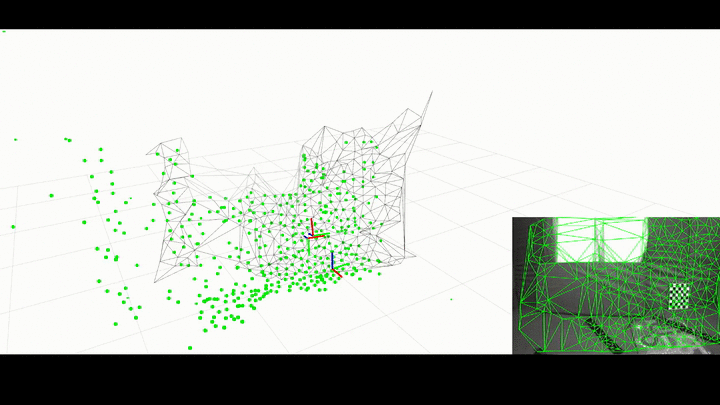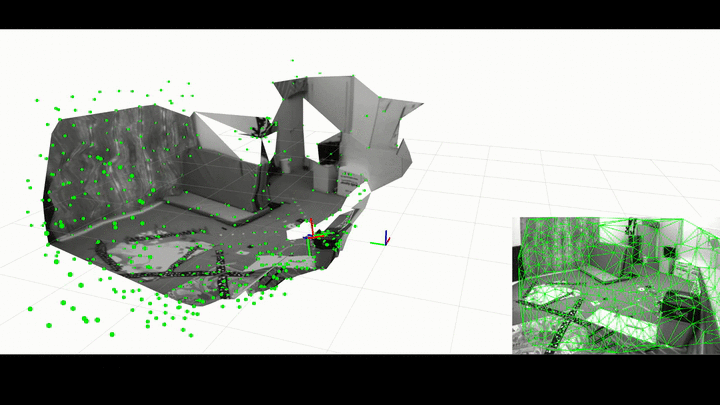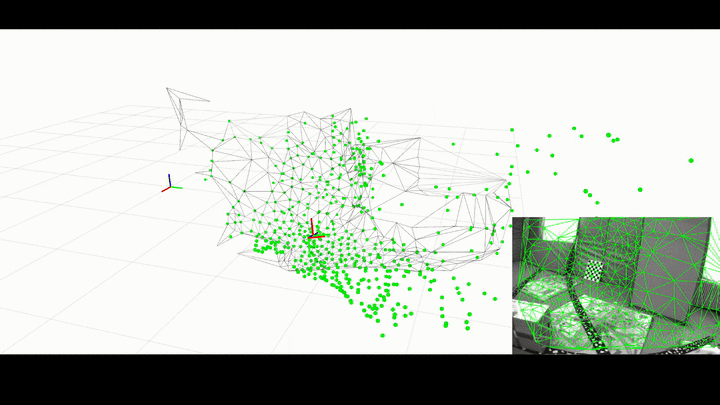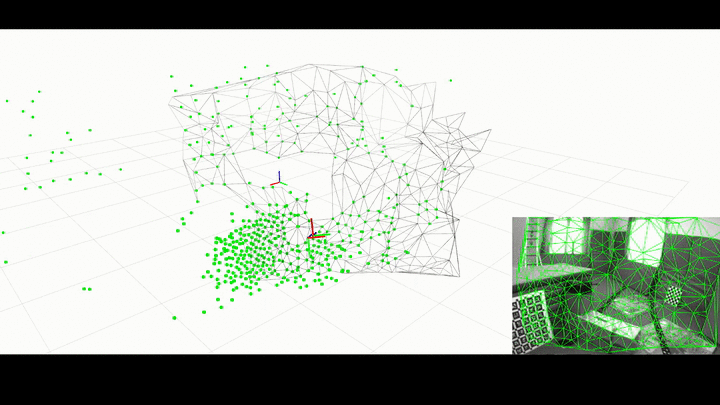
ROS Wrapper for Kimera.
We kindly ask to cite our paper if you find this library useful:
- A. Rosinol, M. Abate, Y. Chang, L. Carlone, Kimera: an Open-Source Library for Real-Time Metric-Semantic Localization and Mapping. IEEE Intl. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2020. arXiv:1910.02490.
@InProceedings{Rosinol20icra-Kimera,
title = {Kimera: an Open-Source Library for Real-Time Metric-Semantic Localization and Mapping},
author = {Rosinol, Antoni and Abate, Marcus and Chang, Yun and Carlone, Luca},
year = {2020},
booktitle = {IEEE Intl. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)},
url = {https://github.com/MIT-SPARK/Kimera},
pdf = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.02490.pdf}
}-
Install ROS by following our reference, or the official ROS website.
-
ROS non-default dependencies for mesh_rviz_plugins (change
noeticfor your ROS distribution):
sudo apt-get install ros-noetic-image-geometry ros-noetic-pcl-ros ros-noetic-cv-bridge- System dependencies:
First, update package list:
sudo apt-get update
# For 20.04 (noetic)
sudo apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends apt-utils
sudo apt-get install -y \
cmake build-essential unzip pkg-config autoconf \
libboost-all-dev \
libjpeg-dev libpng-dev libtiff-dev \
# Use libvtk5-dev, libgtk2.0-dev in ubuntu 16.04 \
libvtk7-dev libgtk-3-dev \
libatlas-base-dev gfortran \
libparmetis-dev \
python3-wstool python3-catkin-tools \- GTSAM's Optional dependencies (highly recommended for speed)
Install Intel Threaded Building Blocks (TBB):
sudo apt-get install libtbb-dev
# Setup catkin workspace
mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src
cd ~/catkin_ws/
catkin init
catkin config --cmake-args -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DGTSAM_TANGENT_PREINTEGRATION=OFF
# On Ubuntu 16.04:
# catkin config --cmake-args -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DGTSAM_USE_SYSTEM_EIGEN=ON -DGTSAM_TANGENT_PREINTEGRATION=OFF
catkin config --merge-devel
# Add workspace to bashrc for automatic sourcing of workspace.
echo 'source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash' >> ~/.bashrc
# Clone repo
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
# For ssh:
git clone git@github.com:MIT-SPARK/Kimera-VIO-ROS.git
# For https:
# git clone https://github.com/MIT-SPARK/Kimera-VIO-ROS.git
# Install dependencies from rosinstall file using wstool
wstool init # Use unless wstool is already initialized
# For ssh:
wstool merge Kimera-VIO-ROS/install/kimera_vio_ros_ssh.rosinstall
# For https
# wstool merge Kimera-VIO-ROS/install/kimera_vio_ros_https.rosinstall
# download and update repos:
wstool update
# Optionally install all dependencies that you might have missed:
# Some packages may report errors, this is expected
# rosdep install --from-paths . --ignore-src -r -yFinally, compile:
# Compile code
catkin build
# Refresh workspace
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bashDownload a Euroc rosbag: for example V1_01_easy.
-
As a general good practice, open a new terminal and run:
roscore -
In another terminal, launch KimeraVIO ROS wrapper:
roslaunch kimera_vio_ros kimera_vio_ros_euroc.launch- In another terminal, launch rviz for visualization:
rviz -d $(rospack find kimera_vio_ros)/rviz/kimera_vio_euroc.rvizNote: this rviz configuration makes use of a rviz plugin: mesh_rviz_plugins. To visualize the textured 3D mesh, clone this plugin to your catkin workspace and catkin build it (note that this should be done automatically via
wstool).
- Finally, in another terminal, launch the downloaded Euroc rosbag:
rosbag play --clock /PATH/TO/EUROC_ROSBAGNote that you will need to both source ROS and your
catkin_wsfor each new terminal unless you added the following lines to your~/.bashrcfile:source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash # Change `noetic` for your ROS distribution. source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash # Change `bash` to the shell you use.
In this mode, the provided rosbag will be first parsed and then sent to the VIO for processing. This is particularly useful when debugging to avoid potential ROS networking issues.
- To run, launch the KimeraVIO ROS wrapper with the
onlineparameter set tofalseand specify the rosbag's path:
roslaunch kimera_vio_ros kimera_vio_ros_euroc.launch online:=false rosbag_path:="PATH/TO/ROSBAG"To run unit tests using catkin for this specific package, call (after building the package and sourcing the workspace):
catkin run_tests --no-deps --thisIt is sometimes convenient to use the camera_info topics to parse the camera's parameters.
There is currently only one way to use these topics:
- Offline: using the launch file
launch/cam_info_yamlizer.launchwhich will generate yaml files out of the topics. You need to make sure that theframe_ids and the ROS topics are correctly set. Also, mind that the left/right cam frame ids are typically set as static tfs in a rosbag, therefore, first launch the node, and then run the rosbag (in case you see an exception bcs of a missing frame_id).
The typical use case is that you have multiple rosbags and you don't want to be killing Kimera-VIO(-ROS) each time. If this is your case, then we provide a rosservice to restart Kimera-VIO (it will do a hard restart, meaning the whole pipeline and data provider will be destructed and constructed again).
rosservice call /kimera_vio_ros/kimera_vio_ros_node/restart_kimera_vioNote that Kimera-VIO will complain if timestamps are not strictly increasing. Therefore, one must follow these steps:
- Start Kimera-VIO and rosbag
- Stop rosbag
- Call rosservice to restart VIO
- Start another rosbag
This will run OpenCV's StereoBM algorithm, more info can be found here (also checkout this to choose good parameters):
roslaunch kimera_vio_ros kimera_vio_ros_euroc run_stereo_dense:=1This will publish a /stereo_gray/points2 topic, which you can visualize in Rviz as a 3D pointcloud.
Alternatively, if you want to visualize the depth image, since Rviz does not provide a plugin to
visualize a disparity image, we also run a disparity_image_proc nodelet that will publish the depth image to /stereo_gray/disparity_image_proc/depth/image_raw.
See the documentation on hardware setup for instructions on running KimeraROS on supported hardware platforms, as well as guides on how to develop for other platforms.
KimeraVIO ROS wrapper is open source under the BSD license, see the LICENSE.BSD file.