Simple and efficient use for yolov8
This is an unofficial repository maintained by independent developers for learning and communication based on the ultralytics v8 Weights and ultralytics Project. If you have more questions and ideas, please feel free to discuss them together. In addition, ultralytics has released the latest ultralytics repository, and it is recommended to use the official one first.
This project is based on ultralytics and yolov5 for comprehensive reference, and is committed to making the yolo series more efficient and easy to use.
Currently doing the following work:
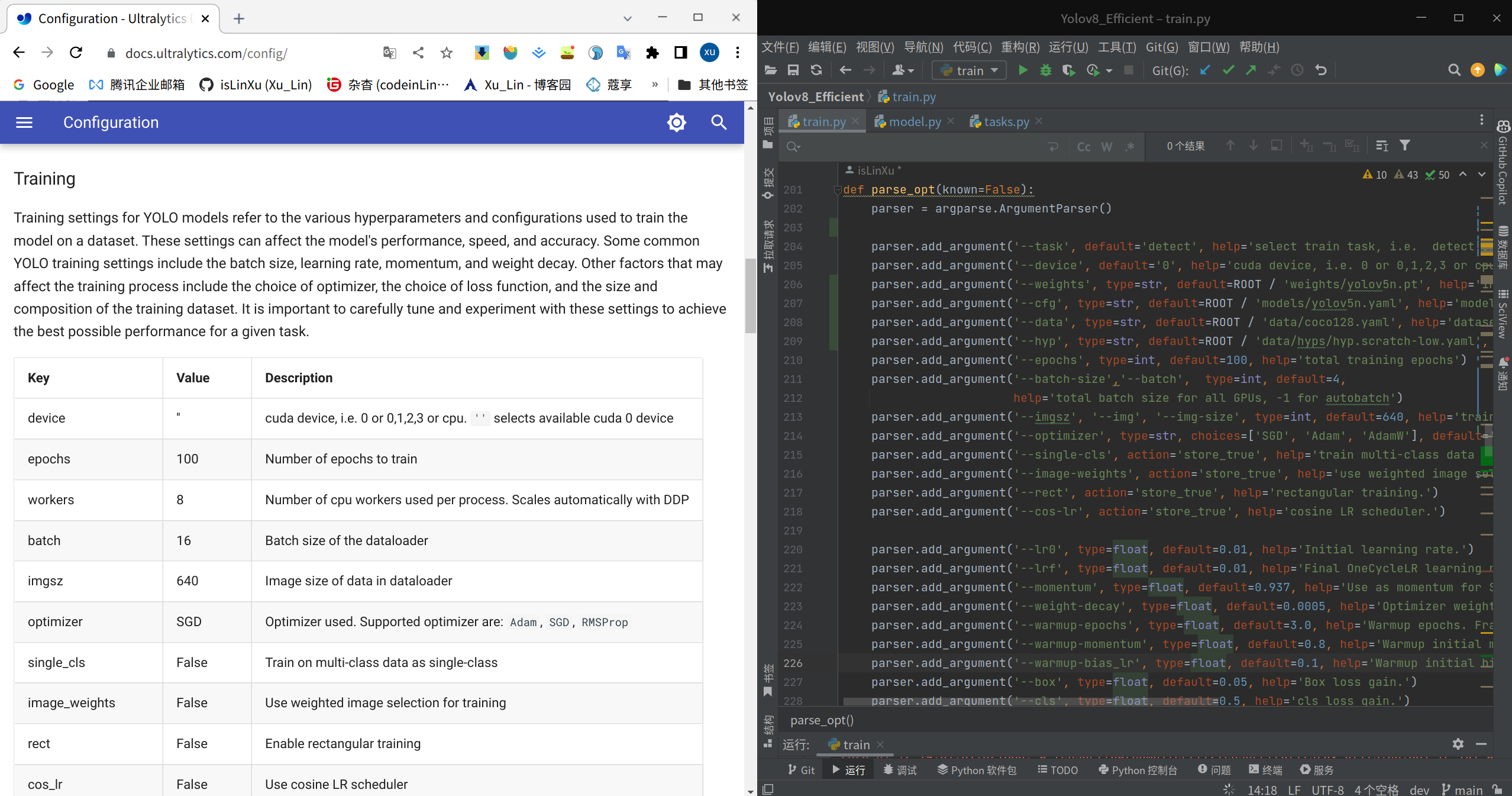
- Referring to the Configuration parameters in https://docs.ultralytics.com/config/, the configuration alignment of corresponding parameters has been made for train.py, detect.py, val.py, etc.
- Combined with yolov5's usage habits and code structure, it is compatible and optimized
-
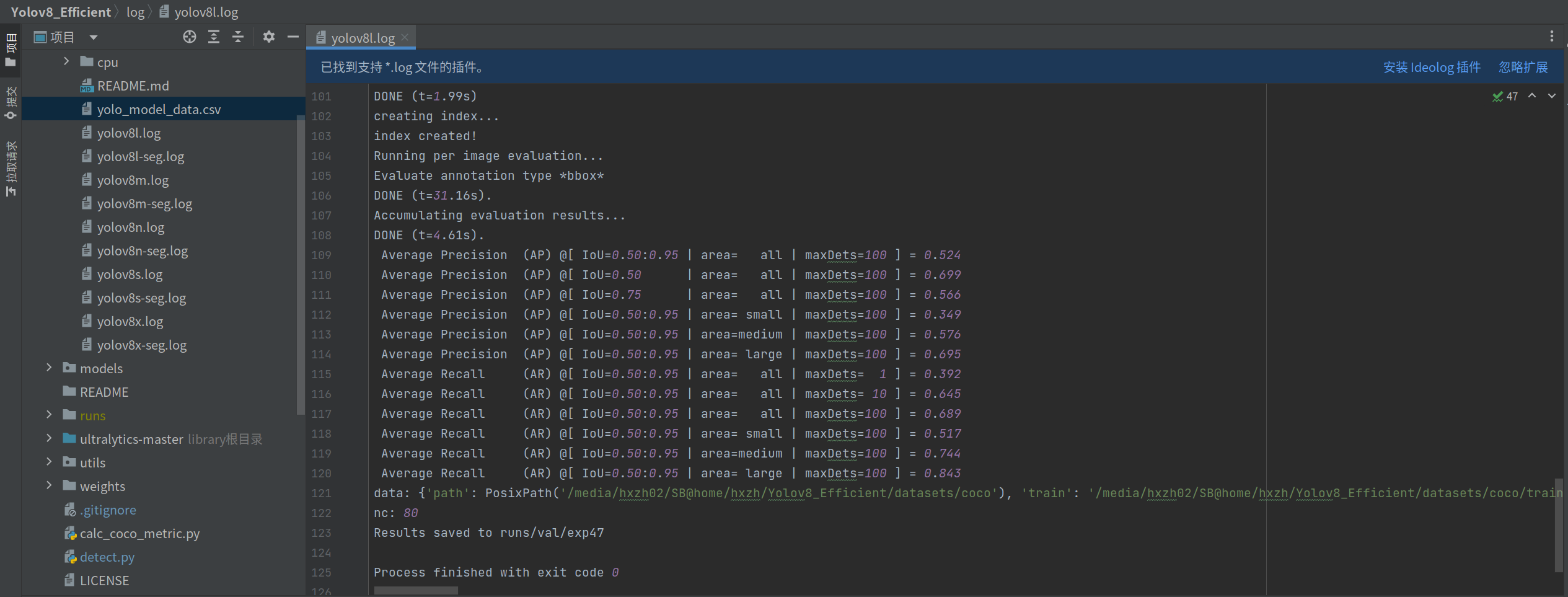
By verifying and calculating the weights of the index parameters on the coco dataset on their own machine, experimental records are stored:https://github.com/isLinXu/YOLOv8_Efficient/tree/main/log.
-
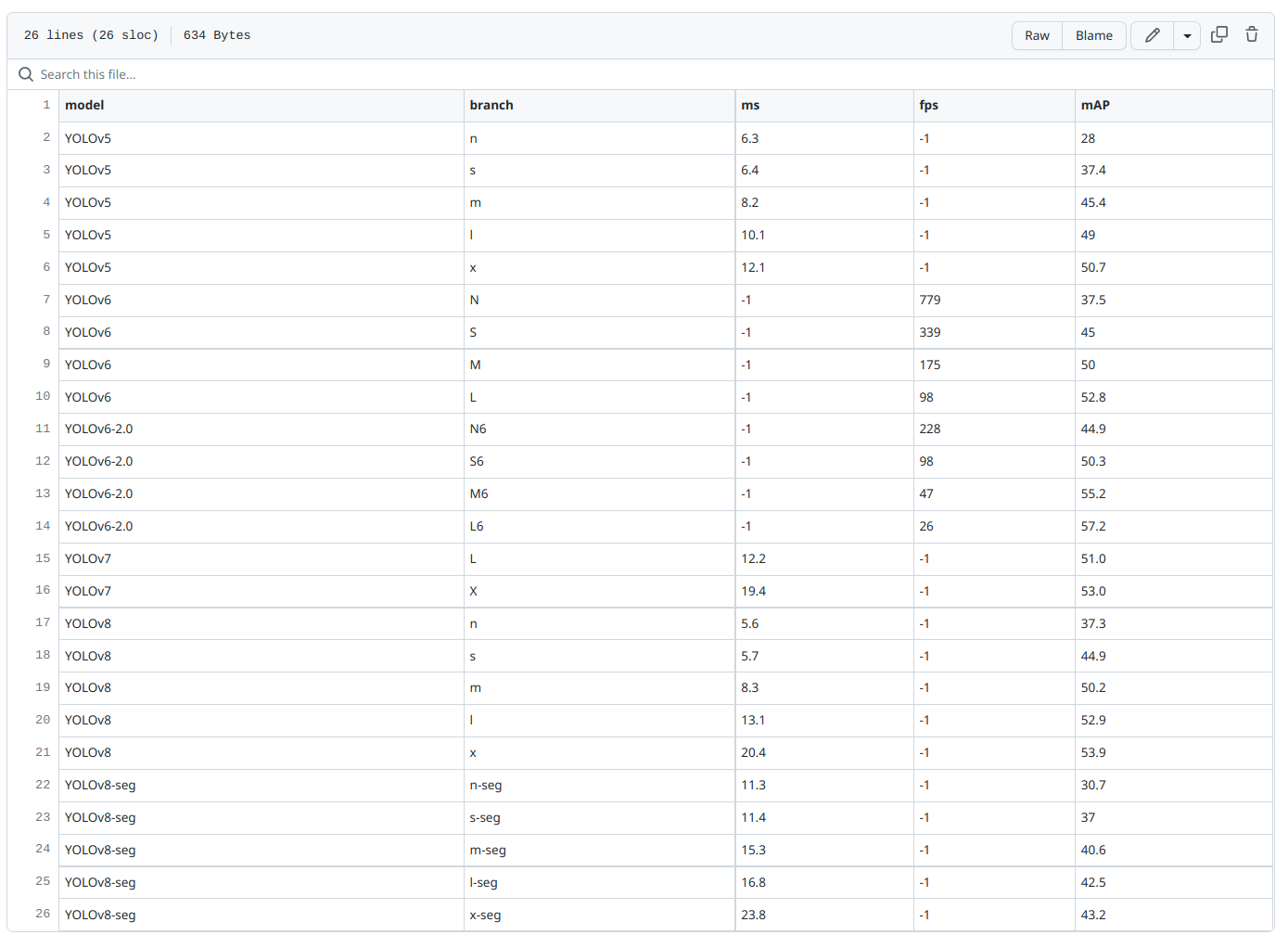
Experimental data are recorded in:https://github.com/isLinXu/YOLOv8_Efficient/blob/main/log/yolo_model_data.csv
-
According to the calculated results, the corresponding index parameter comparison chart is drawn, this drawing program is also open source:https://github.com/isLinXu/model-metrics-plot。
-
integration and configuration with other network model structures is in progress...
Thanks to jizhishutong for providing model structure diagrams for this project.
- ... ...
- 2023/01/10 - add yolov8 metrics and logs
- 2023/01/09 - add val.py and fix some error
- 2023/01/07 - fix some error and warning
- 2023/01/06 - add train.py, detect.py and README.md
- 2023/01/06 - Create and Init a new repository
- Model testing and validation in progress
- [ ]
-
Documentation
To simply use the latest Ultralytics YOLO models
yolo task=detect mode=train model=yolov8n.yaml args=...
classify predict yolov8n-cls.yaml args=...
segment val yolov8n-seg.yaml args=...
export yolov8n.pt format=onnxTo use pythonic interface of Ultralytics YOLO model
from ultralytics import YOLO
model = YOLO("yolov8n.yaml") # create a new model from scratch
model = YOLO(
"yolov8n.pt"
) # load a pretrained model (recommended for best training results)
results = model.train(data="coco128.yaml", epochs=100, imgsz=640, ...)
results = model.val()
results = model.predict(source="bus.jpg")
success = model.export(format="onnx")If you're looking to modify YOLO for R&D or to build on top of it, refer to https://docs.ultralytics.com/.
Here take coco128 as an example:
-
1.To make data sets in YOLO format, you can divide and transform data sets by
prepare_data.pyin the project directory. -
2.Modify the
.yamlof the corresponding model weight inconfig, configure its data set path, and read the data loader. -
3.To modify the corresponding parameters in the model, it is mainly to modify the number of categories and network structure parameters. If it is only a simple application, it is not recommended to modify the following network structure parameters, but only the number of nc categories
-
4.Run
train.py, this step can be modified under the corresponding variable inparse_opt, which needs to be configured according to equipment and training needs, includingdevice,task,data,weights,epochs,batch_size, etc. If this parameter is not specified, the default parameter is used.
| Model | size (pixels) | mAPval 50-95 | mAPval 50 | Speed CPU b1 (ms) | Speed RTX 3080 b1(ms) | layers | params (M) | FLOPs @640 (B) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| yolov8n | 640 | 37.2 | 53.2 | 47.2 | 5.6 | 168 | 3.15 | 8.7 |
| yolov8n-seg | 640 | 30.7 | 50.0 | 59.3 | 11.3 | 195 | 3.40 | 12.6 |
| yolov8s | 640 | 44.7 | 62.2 | 87.9 | 5.7 | 168 | 11.15 | 28.6 |
| yolov8s-seg | 640 | 37.0 | 58.8 | 107.6 | 11.4 | 195 | 11.81 | 42.6 |
| yolov8m | 640 | 49.9 | 67.4 | 185.6 | 8.3 | 218 | 25.89 | 78.9 |
| yolov8m-seg | 640 | 40.6 | 63.5 | 207.7 | 15.3 | 245 | 27.27 | 110.2 |
| yolov8l | 640 | 52.4 | 69.9 | 319.6 | 13.1 | 268 | 43.67 | 165.2 |
| yolov8l-seg | 640 | 42.5 | 66.1 | 296.9 | 16.8 | 295 | 45.97 | 220.5 |
| yolov8x | 640 | 53.5 | 70.9 | 334.6 | 20.4 | 268 | 68.20 | 257.8 |
| yolov8x-seg | 640 | 43.2 | 67.1 | 418.8 | 23.8 | 295 | 71.80 | 344.1 |
Table Notes The above data is generated by running tests in the following configured environment. See below for details.
- GPU: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080/PCIe/SSE2
- CPU: Intel® Core™ i9-10900K CPU @ 3.70GHz × 20
- Memory: 31.3 GiB
- System: Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
- (ms): The statistical speed here is inference speed
pip install ultralyticsgit clone git@github.com:isLinXu/YOLOv8_Efficient.git
cd YOLOv8_Efficient
cd ultralytics-master
pip install -e .- Single-GPU training:
python train.py --data coco128.yaml --weights weights/yolov8ns.pt --img 640 # from pretrained (recommended)python train.py --data coco128.yaml --weights '' --cfg yolov8ns.yaml --img 640 # from scratchUse IDE Pycharm
- Multi-GPU DDP training:
python -m torch.distributed.run --nproc_per_node 4 --master_port 1 train.py --data coco128.yaml --weights yolov8ns.pt --img 640 --device 0,1,2,3
python detect.py --weights yolov8s.pt --source 0 # webcam
img.jpg # image
vid.mp4 # video
screen # screenshot
path/ # directory
list.txt # list of images
list.streams # list of streams
'path/*.jpg' # glob
'https://youtu.be/Zgi9g1ksQHc' # YouTube
'rtsp://example.com/media.mp4' # RTSP, RTMP, HTTP streamUse IDE Pycharm
- i.e coco128:
python val.py --weights yolov8n.pt --data coco128.yaml --img 640python val.py --weights yolov8s.pt # PyTorch
yolov8s.torchscript # TorchScript
yolov8s.onnx # ONNX Runtime or OpenCV DNN with --dnn
yolov8s_openvino_model # OpenVINO
yolov8s.engine # TensorRT
yolov8s.mlmodel # CoreML (macOS-only)
yolov8s_saved_model # TensorFlow SavedModel
yolov8s.pb # TensorFlow GraphDef
yolov8s.tflite # TensorFlow Lite
yolov8s_edgetpu.tflite # TensorFlow Edge TPU
yolov8s_paddle_model # PaddlePaddle