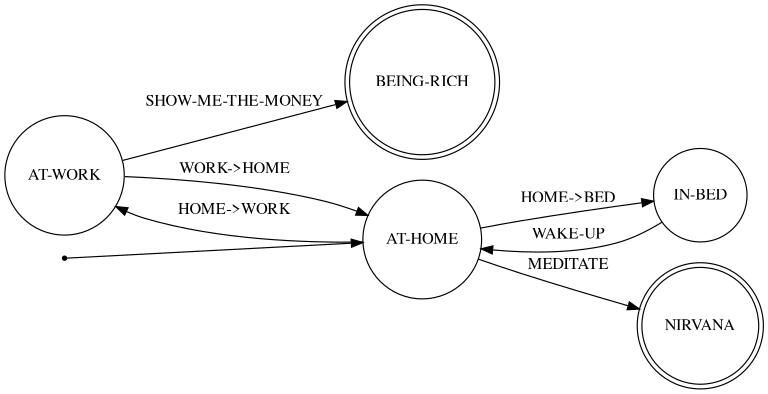
Simple state machine DSL/library for CommonLisp.
- Define state machines in DSL.
- Wire with external object by attaching hook functions.
git clone git@github.com:ageldama/cl-state-machine.git
..And then:
;;; Load this system. (You need Quicklisp and up to date ASDF v3.3+)
;;; - in case no idea how ASDF finds `cl-state-machine.asd' file on your disk:
;;; https://common-lisp.net/project/asdf/asdf/Configuring-ASDF-to-find-your-systems.html
;;;
(ql:quickload :cl-state-machine)
;;; (Optional, Run tests)
;;;
(asdf:test-system :cl-state-machine)
;;; (Optional, Run example program)
;;;
(asdf:load-system :cl-state-machine-examples)
(cl-state-machine-examples/tamagochi:run)- I will omit the package name
cl-state-machine:in every example codes below. (Consider every external symbol has been imported to your working package)
;;; Using `state-machine-of' DSL macro:
;;;
(state-machine-of `(:current-state :HOME)
(`(:state :HOME)
`(:state :FIN :terminal t)
`(:state :WORK))
(`(:from :START :to :WORK
:event :HOME->WORK)
`(:from :WORK :to :HOME
:event :WORK->HOME)
`(:from :HOME :to :FIN
:event :HOME->FIN)))
;;; Or without using DSL:
;;;
(let* (;; states
(state-home (make-instance 'state-definition :state :HOME))
(state-work (make-instance 'state-definition :state :WORK))
(state-fin (make-instance 'state-definition :state :FIN :terminal t))
;; events
(event-home->work (make-instance 'transition-definition
:from :HOME :to :WORK
:event :HOME->WORK))
(event-work->home (make-instance 'transition-definition
:from :WORK :to :HOME
:event :WORK->HOME))
(event-home->fin (make-instance 'transition-definition
:from :HOME :to :FIN
:event :HOME->FIN))
;; state-machine
(a-state-machine (make-instance 'state-machine
:state-definitions (list state-home
state-work
state-fin)
:transition-definitions (list event-home->work
event-work->home
event-home->fin)
:current-state :HOME)))
;; ...Your code here...
nil)
;;; ...Exactly equivalent definitionsHook functions can be attached to:
- state machine instance
- state definition
- transition definition
And those will be invoked when attached state-machine/state/transition’s getting activation, on the before and the after.
;;; Both does not return any value,
;;;
;;; And take `state-transition' of current event.
;;;
;;; Also can take auxiliary values by `&rest t' which has been passed
;;; by event initiator.
;;;
(deftype before-hook-function ()
`(function (state-transition &rest t) null))
(deftype after-hook-function ()
`(function (state-transition &rest t) null))
;;; Thus, it would look like:
(flet ((a-before-hook (a-state-definition &rest args) nil)
(an-after-hook (a-state-definition &rest args) nil))
nil)The order of evaluations of hook functions are:
- before hooks of
state-machine - before hooks of
state-definition - before hooks of
transition-definition - after hooks of
transition-definition - after hooks of
state-definition - after hooks of
state-machine
(make-instance 'state-definition
:state :FIN ; Name of this state
:terminal t ; Is a terminal state? Optional, Default: false.
:description "foo????" ; Simple descriptive string. Optional.
;; Hook function slots are list of functions:
;; (Read above `Hook functions' section)
;;
;; Optional.
:before-hooks (list #'a-before-hook-fn)
:after-hooks (list #'a-after-hook-fn
#'another-after-hook-fn));;; Can express a list of `state-definition's easily:
(state-definitions-of
'(:state :a) ; simply `initarg' of `state-definition'.
`(:state :b
:terminal t
:before-hooks (,#'a-before-hook-fn))) ; Use of quasiquotes
;; => list of `state-definition'(make-instance 'transition-definition
:from :STARTING-STATE :to :END-STATE
:event :END-IT ; the `transition-definition' triggered by this `:event'-keyword
:description "Hasta la vista, baby." ; Optional
:before-hooks (list #'a-before-hook-fn
#'another-before-hook-fn)
:after-hooks '())(transition-definitions-of
'(:from :A :to :B :event :A->B)
'(:from :B :to :A :event :B->A)
`(:from :A :to :C :event :A->C
:description "yet another foobar????"
:before-hooks (,#'a-before-hook-fn)))
;; => list of `transition-definition'Can use of (make-instance 'state-machine ...) with following
initarg s:
:state-definitions: list ofstate-definition:transition-definitions: list oftransition-definition:current-state: starting point, startingstate-definition’s keyword.:before-hooksand:after-hooks: list of hook functions:datum: Auxilary value slot that want to be exposed to hook functions.
(state-machine-of `(:current-state :HOME
:datum "foobar here")
(`(:state :HOME)
`(:state :FIN :terminal t)
`(:state :WORK))
(`(:from :START :to :WORK
:event :HOME->WORK)
`(:from :WORK :to :HOME
:event :WORK->HOME)
`(:from :HOME :to :FIN
:event :HOME->FIN)))
;; => a `state-machine' instance(current-state a-state-machine) ; => `:AT-HOME'
(can? a-state-machine :HOME->WORK)
;; => T
;;
;; if currently at `:AT-HOME' state and a transition-definition of
;; `:HOME->WORK' is defined.
(can? a-state-machine :HOME->WORK :AT-WORK) ; Specified ``state'',
; not current state.
;; => NIL
;;
;; because we're at `:AT-WORK' state which can be assumed it isn't
;; `:from' of `:HOME->WORK''s `transition-definition'.(current-state a-state-machine) ; => `:AT-HOME'
(terminated? a-state-machine) ; => NIL
;; Because `:AT-HOME' state isn't a terminal state.
;; Can specify a state, not just using current state.
(terminated? a-state-machine :FIN) ; => T
;; `:FIN' state is defined as `:terminal = T'.;;; Where:
(defvar a-state-machine (state-machine-of '(:current-state :A)
('(:state :A)
'(:state :B)
'(:state :C)
'(:state :D
:terminal t))
('(:from :A :to :B
:event :A->B)
'(:from :A :to :C
:event :A->C)
'(:from :C :to :D
:event :C->D))))
(current-state a-state-machine) ; => :A
(possible-events a-state-machine) ; => (LIST :A->B :A->C)
(possible-events a-state-machine :B) ; => NIL
(possible-events a-state-machine :C) ; => (LIST :C->D);;; You can `jump!' to any state, without any restriction/constraint!
(jump! a-state-machine :FIN);;; Where,
(defvar a-state-machine (state-machine-of '(:current-state :A)
('(:state :A)
'(:state :B)
'(:state :C)
'(:state :D
:terminal t))
('(:from :A :to :B
:event :A->B)
'(:from :A :to :C
:event :A->C)
'(:from :C :to :D
:event :C->D))))
(current-state a-state-machine) ; => :A
(trigger! a-state-machine :A->C)
;; OR
(trigger! a-state-machine :A->C
:additional-arg-1 'additional-arg-2-for-hook-functions)
;;
;; => `(values NEW-STATE-SYMBOL REJECTED-BY REJECTION-REASON)'
;;
;; * on Success:
;; - `NEW-STATE-SYMBOL' is a symbol of corresponding state definition
;; of the new state.
;; - and `REJECTED-BY', `REJECTION-REASON' both is `nil'.
;;
;; * if `a-state-machine' has terminated or the specified `event'
;; cannot be triggered from current state:
;; - `NEW-STATE-SYMBOL' is nil.
;; - `REJECTED-BY' is `:CANNOT-BE-TRIGGERED'
;; and `REJECTION-REASON' is the specified `event' parameter.
;;
;; * any before hook function could reject the transition by invoking
;; `reject-transition!'. In this case, any subsequent hook function
;; evaluation will be stopped and the function's evaluated values are:
;;
;; - `NEW-STATE-SYMBOL' is `nil',
;; - `REJECTED-BY' is could be one of
;; `:STATE-MACHINE-BEFORE-HOOK-REJECTED' or
;; `:STATE-DEFINITION-BEFORE-HOOK-REJECTED' or
;; `:TRANSITION-DEFINITION-BEFORE-HOOK-REJECTED'.
;; - `REJECTION-REASON' is a cons cell of `(DATUM . REJECTED-HOOK-FUNCTION-VALUE)'
;; where `DATUM' is the value the hook function passed as `:datum' key parameter to
;; `reject-transition!'.
;;
(current-state a-state-machine) ; => :C
- Function
find-state-definition-by-state - Function
find-transition-definition-by-state-and-event
Function schedule-next-trigger! (a-state-machine event &rest
args) schedules triggering event after next trigger!
invocation.
Without invoking trigger!, just scheduling does not affect.
schedule-next-trigger! check possibility of requesting :event
by current state of a-state-machine, using
compute-last-state.
But checks by compute-last-state is only with states of current
and scheduled events, cannot predict the rejection by a hook
function.
Schedule without any checking, could be done with
schedule-next-trigger-without-check!.
Empties any scheduled triggering events.
Every last triggered events, its params and results are recorded
in *trigger-history*.
Each time invoke trigger! clears *trigger-history* and append
new history items.
*trigger!-clear-history* variable is true by default, dynamic
bind this as false, make trigger! function skip the clearing of
*trigger-history*.
;;; Evaluate the body within dynamic binding of `*trigger-schedules'
;;; and `*trigger-history':
(with-own-trigger-schedules-and-history
(:schedules '()
:history '())
;; the body, evaluated as `prog'
(trigger! a-state-machine :A->B)
;; ...
) ; => (LIST SCHEDULES HISTORY)
;; Returns last state of `SCHEDULES' and `HISTORY' as a list.Every object and function in this system does not prevent multi threading issues. Thus please do not share any instance value between multiple threads, state transition and all other mutating operations should be invoked and executed within same thread.
- Keybase: https://keybase.io/ageldama
- Licensed under MIT License. (Read
LICENSEfile)