Before you publish, ensure that you are logged in to npm with the account that owns the @rabi-siddique scope:
npm loginFollow the prompts to enter your username, password etc.
Once you are logged in and your package.json is correctly set up, try publishing the package with public access:
npm publish --access publicThis command explicitly sets the package to be public, allowing anyone to install it without facing access restrictions.
Attempting to publish the package without updating the version number in package.json will result in the following error:
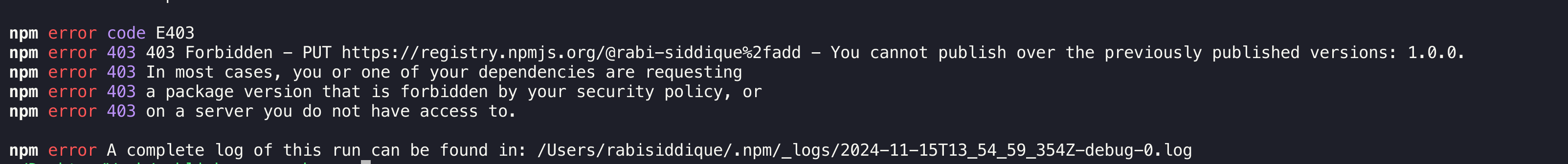
As the error message says: You cannot publish over the previously published version
To successfully publish, increment the version number in package.json to a new value that differs from the previous release. This change ensures that npm recognizes it as a new version, allowing the publication to proceed without errors.
You have the flexibility to choose any version number when publishing your package. For example, if your initial release was version 1.0.1, you could choose to update it to 10.0.5 for a subsequent release:
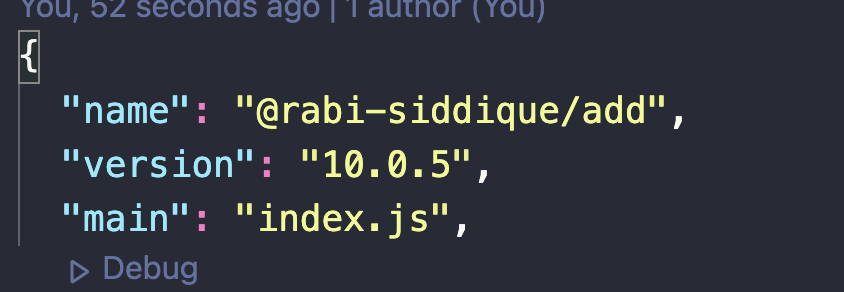
npm allows version downgrades. You can publish a lower version, such as 3.0.5, even after releasing a higher version like 10.0.5, and it will still be processed successfully.
release-it is a tool for automating version management and package publishing workflows. It handles the version bumping, tagging, and publishing of your software projects.
First, you need to add release-it to your project.
npm install --save-dev release-itrelease-it can be configured in various ways, such as through the package.json file, a .release-it.json configuration file, or CLI arguments. Here's an example of basic configuration in your package.json:
"release-it": {
"git": {
"commitMessage": "Release v${version}",
"tagName": "v${version}",
"tagAnnotation": "Release v${version}",
"push": true
},
"npm": {
"publish": true
},
"hooks": {
"after:bump": "npm run build"
}
}This configuration does the following:
-
commitMessage: This defines the commit message format when the version bump is committed. The placeholder${version}dynamically inserts the new version number (e.g., Release v1.2.3). -
tagName: Specifies the format of the Git tag created for the release. For example, a tag namedv1.2.3will be created for version1.2.3. -
tagAnnotation: Provides an annotation or description for the tag. This annotation is useful for documenting the purpose or context of the tag. -
push: true: If true, release-it will automatically push the version bump commit and tag to the remote Git repository. -
npm: The "npm" section specifies how release-it interacts with the npm registry. -
"publish": true: If true, release-it will publish the new version of your package to the npm registry after bumping the version. -
hooks: A section in the configuration file that specifies commands to be run at certain points during the versioning process. -
after:bump: A hook that runs after the version number is bumped in your project. For example, if the version changes from 1.0.0 to 1.1.0, this hook is triggered immediately afterward. -
npm run build: The command executed by theafter:bumphook. In this case, it runs the build script defined in your project's package.json.
I encountered this error in CI while attempting to make a commit:
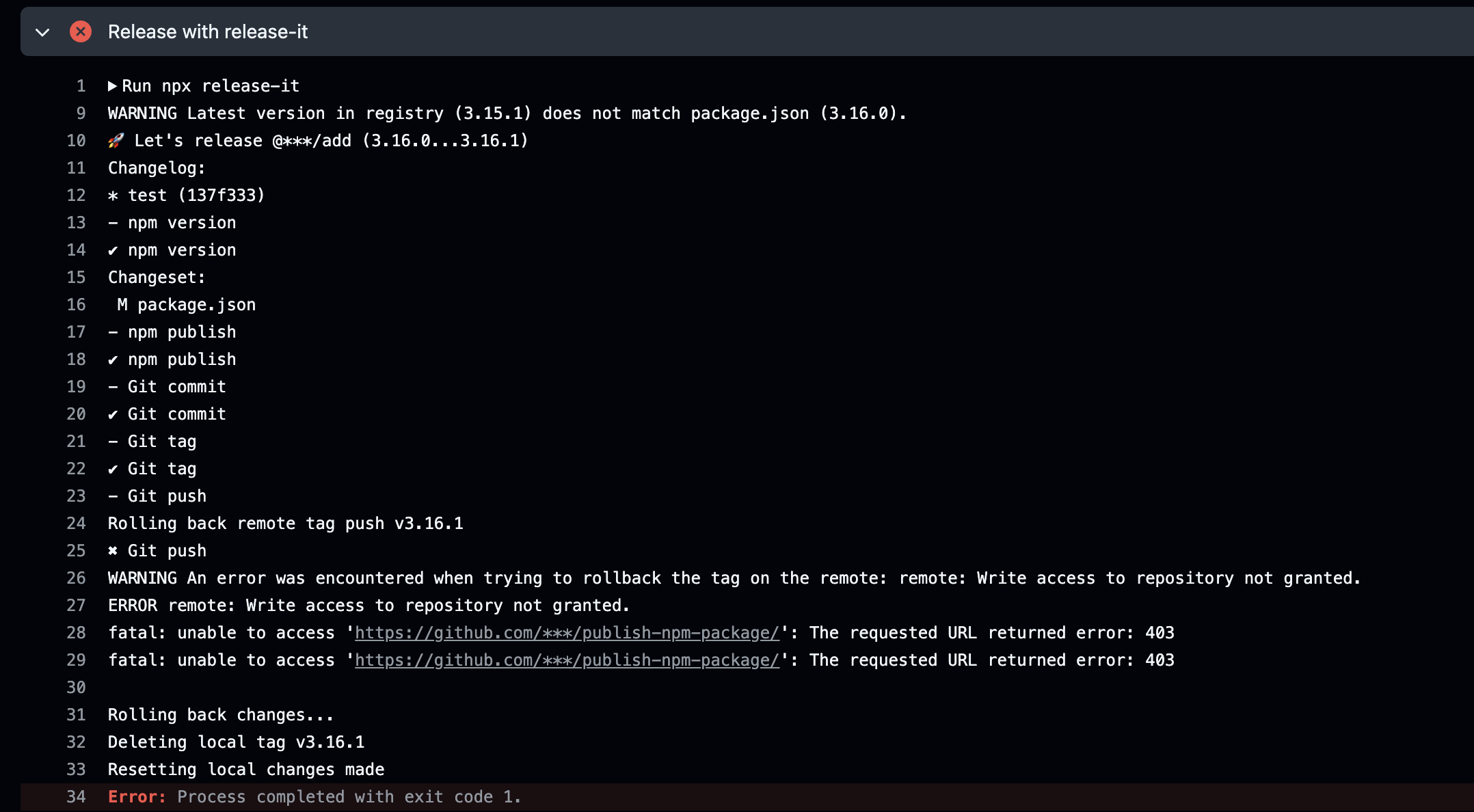
Initially, I suspected that my token lacked push access. This Stack Overflow thread provided a solution.