OAuthSwift
Swift based OAuth library for iOS and macOS.
Support OAuth1.0, OAuth2.0
Twitter, Flickr, Github, Instagram, Foursquare. Fitbit, Withings, Linkedin, Dropbox, Dribbble, Salesforce, BitBucket, GoogleDrive, Smugmug, Intuit, Zaim, Tumblr, Slack, Uber, Gitter, Facebook, Spotify, Typetalk, SoundCloud, etc
Installation
OAuthSwift is packaged as a Swift framework. Currently this is the simplest way to add it to your app:
- Drag OAuthSwift.xcodeproj to your project in the Project Navigator.
- Select your project and then your app target. Open the Build Phases panel.
- Expand the Target Dependencies group, and add OAuthSwift framework.
- import OAuthSwift whenever you want to use OAuthSwift.
Support Carthage
- Install Carthage (https://github.com/Carthage/Carthage)
- Create Cartfile file
github "OAuthSwift/OAuthSwift" ~> 1.1.0
- Run
carthage update. - On your application targets’ “General” settings tab, in the “Embedded Binaries” section, drag and drop OAuthSwift.framework from the Carthage/Build/iOS folder on disk.
Support CocoaPods
- Podfile
platform :ios, '8.0'
use_frameworks!
pod 'OAuthSwift', '~> 1.1.0'
How to
Setting URL Schemes
In info tab of your target
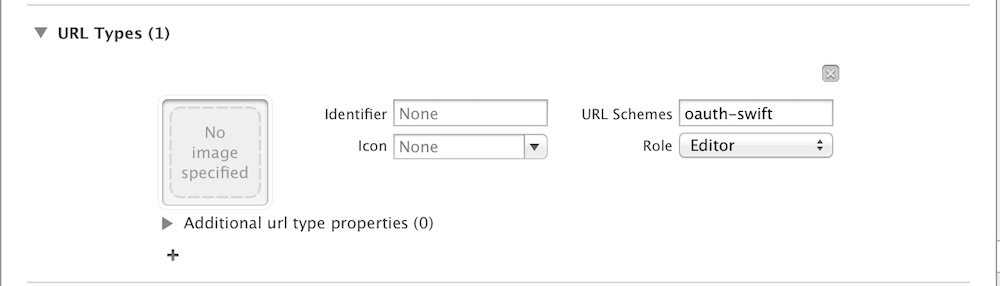 Replace oauth-swift by your application name
Replace oauth-swift by your application name
Handle URL in AppDelegate
- On iOS9 implement
UIApplicationDelegatemethod
func application(_ app: UIApplication, open url: URL, options: [UIApplicationOpenURLOptionsKey : Any] = [:]) -> Bool {
if (url.host == "oauth-callback") {
OAuthSwift.handle(url: url)
}
return true
}if (options[.sourceApplication] as? String == "com.apple.SafariViewService") {
- On previous iOS version
func application(_ application: UIApplication, open url: URL, sourceApplication: String?, annotation: Any) -> Bool {- On macOS you must register an handler on
NSAppleEventManagerfor event typekAEGetURL(see demo code)
func applicationDidFinishLaunching(_ aNotification: NSNotification) {
NSAppleEventManager.shared().setEventHandler(self, andSelector:#selector(AppDelegate.handleGetURL(event:withReplyEvent:)), forEventClass: AEEventClass(kInternetEventClass), andEventID: AEEventID(kAEGetURL))
}
func handleGetURL(event: NSAppleEventDescriptor!, withReplyEvent: NSAppleEventDescriptor!) {
if let urlString = event.paramDescriptor(forKeyword: AEKeyword(keyDirectObject))?.stringValue, let url = URL(string: urlString) {
OAuthSwift.handle(url: url)
}
}Authorize with OAuth1.0
// create an instance and retain it
oauthswift = OAuth1Swift(
consumerKey: "********",
consumerSecret: "********",
requestTokenUrl: "https://api.twitter.com/oauth/request_token",
authorizeUrl: "https://api.twitter.com/oauth/authorize",
accessTokenUrl: "https://api.twitter.com/oauth/access_token"
)
// authorize
let handle = oauthswift.authorize(
withCallbackURL: URL(string: "oauth-swift://oauth-callback/twitter")!,
success: { credential, response, parameters in
print(credential.oauthToken)
print(credential.oauthTokenSecret)
print(parameters["user_id"])
// Do your request
},
failure: { error in
print(error.localizedDescription)
}
)OAuth1 without authorization
No urls to specify here
// create an instance and retain it
oauthswift = OAuth1Swift(
consumerKey: "********",
consumerSecret: "********"
)
// do your HTTP request without authorize
oauthswift.client.get("https://api.example.com/foo/bar",
success: { response in
//....
},
failure: { error in
//...
}
)Authorize with OAuth2.0
oauthswift = OAuth2Swift(
consumerKey: "********",
consumerSecret: "********",
authorizeUrl: "https://api.instagram.com/oauth/authorize",
responseType: "token"
)
let handle = oauthswift.authorize(
withCallbackURL: URL(string: "oauth-swift://oauth-callback/instagram")!,
scope: "likes+comments", state:"INSTAGRAM",
success: { credential, response, parameters in
print(credential.oauthToken)
// Do your request
},
failure: { error in
print(error.localizedDescription)
}
)
See demo for more examples
Handle authorize URL
The authorize URL allows the user to connect to a provider and give access to your application.
By default this URL is opened into the external web browser (ie. safari), but apple does not allow it for app-store iOS applications.
To change this behavior you must set an OAuthSwiftURLHandlerType, simple protocol to handle an URL
oauthswift.authorizeURLHandler = ..For instance you can embed a web view into your application by providing a controller that displays a web view (UIWebView, WKWebView).
Then this controller must implement OAuthSwiftURLHandlerType to load the URL into the web view
func handle(_ url: NSURL) {
let req = URLRequest(URL: targetURL)
self.webView.loadRequest(req)
...and present the view (present(viewController, performSegue(withIdentifier: , ...)
You can extend OAuthWebViewController for a default implementation of view presentation and dismiss
Use the SFSafariViewController (iOS9)
A default implementation of OAuthSwiftURLHandlerType is provided using the SFSafariViewController, with automatic view dismiss.
oauthswift.authorizeURLHandler = SafariURLHandler(viewController: self, oauthSwift: oauthswift)Of course you can create your own class or customize the controller by setting the variable SafariURLHandler#factory.
Make signed request
Just call HTTP functions of oauthswift.client
oauthswift.client.get("https://api.linkedin.com/v1/people/~",
success: { response in
let dataString = response.string
print(dataString)
},
failure: { error in
print(error)
}
)
// same with request method
oauthswift.client.request("https://api.linkedin.com/v1/people/~", .GET,
parameters: [:], headers: [:],
success: { ...See more examples in the demo application: ViewController.swift
OAuth provider pages
- Flickr
- Github
- Foursquare
- Fitbit
- Withings
- Dropbox
- Dribbble
- Salesforce
- BitBucket
- GoogleDrive
- Smugmug
- Intuit
- Zaim
- Tumblr
- Slack
- Uber
- Gitter
- Spotify
- Trello
- Buffer
- Goodreads
- Typetalk
- SoundCloud
- Digu
- NounProject
Images
Contributing
See CONTRIBUTING.md
Integration
OAuthSwift could be used with others frameworks
You can sign Alamofire request with OAuthSwiftAlamofire
To achieve great asynchronous code you can use one of these integration frameworks
License
OAuthSwift is available under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for more info.