1. 如何替换启动页
yarn add react-native-bootsplash
yarn react-native generate-bootsplash path-to-logo-image
可选参数:
-
--background-color=[color] 启动页背景色。hex 格式
-
--logo-width=[width] 1 倍图 logo 大小(正方形)。默认为 100
-
--assets-path=[path] logo 存放在项目目录下的位置
-
--flavor=[flavor] 安卓下有效。表示不是
main目录的安卓资源文件夹
生成文件示例:
android/app/src/main/res/drawable/bootsplash.xml
android/app/src/main/res/values/colors.xml (creation and edition)
android/app/src/main/res/mipmap-hdpi/bootsplash_logo.png
android/app/src/main/res/mipmap-mdpi/bootsplash_logo.png
android/app/src/main/res/mipmap-xhdpi/bootsplash_logo.png
android/app/src/main/res/mipmap-xxhdpi/bootsplash_logo.png
android/app/src/main/res/mipmap-xxxhdpi/bootsplash_logo.png
ios/YourProjectName/BootSplash.storyboard
ios/YourProjectName/Images.xcassets/BootSplashLogo.imageset/bootsplash_logo.png
ios/YourProjectName/Images.xcassets/BootSplashLogo.imageset/bootsplash_logo@2x.png
ios/YourProjectName/Images.xcassets/BootSplashLogo.imageset/bootsplash_logo@3x.png
# Only if --assets-path was specified
assets/bootsplash_logo.png
assets/bootsplash_logo@1,5x.png
assets/bootsplash_logo@2x.png
assets/bootsplash_logo@3x.png
assets/bootsplash_logo@4x.png
2. 如何替换应用图标
yarn add -D @bam.tech/react-native-make
npx react-native set-icon --path path-to-image
要求:
path-to-image指向图片的路径必填- 图片必须是正方形的
- 图片不能有透明图层,两个平台都不支持
- 图片最大尺寸是 1024 * 1024
- 支持安卓自适应图标
- 图片格式支持.png 和 .jpeg
- 安卓平台下,上面的命令会在 android/app/src/main/res 目录下生成一堆图标文件
3. 如何生成 svg 图标
- 保证你的项目里安装了
react-native-svg和@td-design/svgicon-cli - 把图表对应的 svg 文件放在根目录下的 icon-svg 文件夹下
- 执行命令
npx svgicon-init生成配置文件:
{
"save_dir": "", // 生成图标文件的保存位置,推荐 ./src/components/Icon
"trim_icon_prefix": "icon", // 图标文件的统一前缀
"default_icon_size": 20, // 图标文件的默认大小
"icon_svg": "./icon-svg", // 图标文件的存放位置
"for_library": false // 是否为组件库生成图标,默认是false,表示是为项目生成图标
}- 执行命令
npx svgicon-create在对应的save_dir下生成图标组件
4. 如何应用字体文件
在@td-design/react-native 组件库中,我们内置了对PingFang SC Regular 和 Roboto 字体的默认支持,但是需要在项目中加载这两个字体文件。做法如下:
- 在
react-native.config.js文件中增加以下配置:
module.exports = {
// 其他配置
assets: ['./assets/fonts/'], // stays the same
};
- 在
assets/fonts/目录下,将这两个字体文件复制进来 - 执行
npx react-native link命令,会自动将字体文件映射到 Android 和 IOS 原生配置中
通过以上步骤增加字体之后,不需要其他额外的配置就可以在项目中看到效果了。你也可以通过在theme.ts文件中定义自己的 textVariants。
5. 组件库默认主题
const basePalette = {
// 基础色
white: '#FFFFFF',
black: '#000000',
transparent: 'transparent',
// 功能色
func50: '#FBF5F5',
func100: '#FFF7E3',
func200: '#FFD21D',
func300: '#52C41A',
func400: '#1890FF',
func500: '#F86E21',
func600: '#F4333C',
func700: 'transparent',
func800: 'transparent',
func900: 'transparent',
};
/** 默认调色板 */
const palette = {
...basePalette,
// 主色
primary50: '#E5F1FF',
primary100: '#3AA3FF',
primary200: '#005DFF',
primary300: 'rgba(0, 93, 255, 0.7)',
primary400: 'rgba(0, 93, 255, 0.4)',
primary500: 'transparent',
primary600: 'transparent',
primary700: 'transparent',
primary800: 'transparent',
primary900: 'transparent',
// 中性色
gray50: '#F5F5F5',
gray100: '#E5E5E5',
gray200: '#CCCCCC',
gray300: '#999999',
gray400: '#666666',
gray500: '#333333',
gray600: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.4)',
gray700: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.04)',
gray800: 'transparent',
gray900: 'transparent',
};
const lightTheme = createTheme({
spacing: {
x1: px(4),
x2: px(8),
x3: px(12),
x4: px(16),
x5: px(20),
x6: px(24),
x7: px(28),
x8: px(32),
x9: px(36),
x10: px(40),
},
borderRadii: {
x1: px(4),
x2: px(8),
x3: px(12),
x4: px(16),
x5: px(20),
x6: px(24),
x7: px(28),
x8: px(32),
x9: px(36),
x10: px(40),
},
zIndices: {
1: 1,
9: 9,
19: 9,
29: 9,
39: 9,
49: 9,
59: 9,
69: 9,
79: 9,
89: 9,
99: 99,
199: 199,
299: 299,
399: 399,
499: 499,
599: 599,
699: 699,
799: 799,
899: 899,
999: 999,
},
breakpoints: {
phone: 0,
tablet: 768,
largeTablet: 1024,
},
colors: {
...palette,
background: palette.gray50,
mask: palette.gray600,
border: palette.gray200,
icon: palette.gray300,
disabled: palette.gray200,
text: palette.gray500,
text_active: palette.white,
},
textVariants: {
h0: {
fontWeight: 'bold',
fontSize: px(28),
lineHeight: px(39),
fontFamily: 'PingFang SC',
},
h1: {
fontWeight: '500',
fontSize: px(18),
lineHeight: px(25),
fontFamily: 'PingFang SC',
},
h2: {
fontWeight: '500',
fontSize: px(16),
lineHeight: px(22),
fontFamily: 'PingFang SC',
},
h3: {
fontWeight: '500',
fontSize: px(14),
lineHeight: px(19),
fontFamily: 'PingFang SC',
},
h4: {},
h5: {},
h6: {},
h7: {},
h8: {},
h9: {},
p0: {
fontSize: px(16),
lineHeight: px(22),
fontFamily: 'PingFang SC',
},
p1: {
fontSize: px(14),
lineHeight: px(19),
fontFamily: 'PingFang SC',
},
p2: {
fontSize: px(12),
lineHeight: px(16),
fontFamily: 'PingFang SC',
},
p3: {
fontSize: px(10),
lineHeight: px(14),
fontFamily: 'PingFang SC',
},
p4: {},
p5: {},
p6: {},
p7: {},
p8: {},
p9: {},
d0: {
fontSize: px(24),
lineHeight: px(28),
fontFamily: 'Roboto',
},
d1: {
fontSize: px(18),
lineHeight: px(21),
fontFamily: 'Roboto',
},
d2: {
fontSize: px(14),
lineHeight: px(19),
fontFamily: 'Roboto',
},
d3: {
fontSize: px(12),
lineHeight: px(14),
fontFamily: 'Roboto',
},
d4: {},
d5: {},
d6: {},
d7: {},
d8: {},
d9: {},
},
});
/** 深色调色板 */
const darkPalette = {
...basePalette,
// 主色
primary50: 'rgba(0, 93, 255, 0.3)',
primary100: '#3AA3FF',
primary200: '#005DFF',
primary300: 'rgba(0, 93, 255, 0.7)',
primary400: 'rgba(0, 93, 255, 0.4)',
primary500: 'transparent',
primary600: 'transparent',
primary700: 'transparent',
primary800: 'transparent',
primary900: 'transparent',
// 中性色
gray50: '#131C22',
gray100: 'rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.15)',
gray200: 'rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.25)',
gray300: 'rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.4)',
gray400: 'rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.6)',
gray500: 'rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.8)',
gray600: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.4)',
gray700: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.04)',
gray800: 'transparent',
gray900: 'transparent',
};
const darkTheme: Theme = {
...lightTheme,
colors: {
...darkPalette,
background: darkPalette.gray50,
mask: darkPalette.gray600,
border: darkPalette.gray400,
icon: darkPalette.gray300,
disabled: darkPalette.gray200,
text: darkPalette.gray500,
text_active: darkPalette.white,
},
};6. 创建 keystore
创建开发环境 keystore
$ keytool -genkey -v -keystore ./android/app/debug.keystore -storepass android -alias androiddebugkey -keypass android -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -validity 10000
创建生产环境 keystore
$ keytool -genkeypair -v -storetype PKCS12 -keystore ./android/app/my-release-key.keystore -alias my-key-alias -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -validity 10000
7. 配置外链打开 app 内指定页面以及传参
本模板已经内置了通过外链唤起 app 的功能。那么如何通过外链打开 app 的同时能够打开指定的页面以及传参呢? 我们可以借助 react-navigation 提供的能力轻松做到这一点。原文链接
export const linking: LinkingOptions<AppParamList> = {
enabled: true,
// 外链唤起的前缀,通常会配两个,其中一个是网站的域名。
prefixes: [],
// 配置外链路由跟app内的screen的映射关系。而screen在react-navigation中实际上对应的是navigation state.
config: {},
};点击外链,打开 app 的某个页面,实际上是把外链地址映射成 react navigation 的[navigation state](https://reactnavigation.org/docs/navigation-state)。比如, /rooms/chat 映射之后的结构是:
const state = {
routes: [
{
name: 'rooms',
state: {
routes: [
{
name: 'chat',
},
],
},
},
],
};外链的另一种形式是 RESTFul 风格的。比如feed/latest,那这种结构在配置 config 的时候就需要特殊处理一下:
const config = {
screens: {
Chat: 'feed/:sort',
Profile: 'user',
// other screens
},
};
export const linking: LinkingOptions<AppParamList> = {
enabled: true,
// 外链唤起的前缀,通常会配两个,其中一个是网站的域名。
prefixes: [],
// 配置外链路由跟app内的screen的映射关系。而screen在react-navigation中实际上对应的是navigation state.
config,
};在上面的配置中,Chat页面对应的外链就是/feed/**, Profile页面对应的外链就是/user。对应的StackNavigation配置如下:
<Stack.Navigator>
<Stack.Screen name="Chat" component={ChatScreen} />
<Stack.Screen name="Profile" component={ProfileScreen} />
</Stack.Navigator>如果我们的页面存在于一个嵌套的 navigator 里面,这时候config也要体现出嵌套的结构。比如:
function App() {
return (
<Stack.Navigator>
<Stack.Screen name="Home" component={HomeScreen} />
<Stack.Screen name="Profile" component={ProfileScreen} />
</Stack.Navigator>
);
}
function HomeScreen() {
return (
<Tab.Navigator>
<Tab.Screen name="Chat" component={ChatScreen} />
</Tab.Navigator>
);
}Chat页面是嵌在Home页面里的,它对应的config如下:
const config = {
screens: {
Home: {
// 体现嵌套
screens: {
Chat: 'feed/:sort',
},
},
Profile: 'user',
},
};传参
传参在外链上有 2 中体现.
/user?id=jane/user/jane针对这两种不同的传参方式,config 的配置也不一样。第一种传参方式:
const config = {
screens: {
Profile: 'user', // 参数会自动传递到params里面
},
};第二种传参方式:
const config = {
screens: {
Profile: {
path: 'user/:id',
// 默认情况下参数都会被当成字符串处理
// 如果想要对参数做处理,可以添加`parse`和`stringify`两个属性
// 处理之后传入params的就变成了{id: 'user-jane'}
parse: {
id: id => `user-${id}`,
},
stringify: {
id: id => id.replace(/^user-/, ''),
},
},
},
};可选参数
我们可以使用?来标记某个参数是可选的。这种情况主要针对上面的第二种传参形式。比如我们有这样一个外链:user/jane/settings,它对应的config如下:
const config = {
screens: {
Profile: 'user/:id/:section',
parse: {
id: id => `user-${id}`,
},
stringify: {
id: id => id.replace(/^user-/, ''),
},
},
};加入section是一个可选参数,也就是说会存在这样的外链user/jane,我们可以在:section后加一个?,变成:
const config = {
screens: {
Profile: 'user/:id/:section?',
parse: {
id: id => `user-${id}`,
},
stringify: {
id: id => id.replace(/^user-/, ''),
},
},
};这样,user/jane外链传递到 Screen 里的参数就是: {id: 'jane'}, user/jane/settings外链传递到 Screen 里的参数就是: {id: 'jane', section: 'settings'},
处理 404
如果打开的是一个无效的外链,也就意味着它实际上并不会映射到我们的 app 里的任何一个 Screen,这个时候我们可以通过配置*来解决映射问题。配置如下:
const config = {
screens: {
Home: {
screens: {
Profile: 'users/:id',
Settings: 'settings',
},
},
NotFound: '*',
},
};如果一个外链既不是user/:id,也不是settings,那它就会显示NotFound页面。
function NotFoundScreen({ route }) {
if (route.path) {
return <WebView source={{ uri: `https://mywebsite.com/${route.path}` }} />;
}
return <Text>This screen doesn't exist!</Text>;
}我们还可以配置得更加具体。比如:
const config = {
screens: {
Home: {
screens: {
Profile: 'users/:id',
Settings: {
path: 'settings',
screens: {
InvalidSettings: '*',
},
},
},
},
NotFound: '*',
},
};这时候有一个外链:settings/notification,它就会被映射到InvalidSettings页面。
配置默认路由
通过initialRouteName属性来配置默认路由。
const config = {
screens: {
Home: {
initialRouteName: 'Feed',
screens: {
Profile: 'users/:id',
Settings: 'settings',
},
},
},
};默认路由不能传递参数!!所以在配置默认路由的时候一定要确认它是无参的。
严格匹配路径
在嵌套的配置下,路由映射会优先尝试把所有嵌套路由的路径都匹配上。比如一下的配置:
const config = {
screens: {
Home: {
path: 'feed',
screens: {
Profile: 'users/:id',
},
},
},
};Profile 的映射路由实际上变成了feed/users/:id,这个时候外链users/:id就映射不到Profile页面了。为了解决这个问题,我们可以给 Profile 的配置增加一个exact: true的配置项。
const config = {
screens: {
Home: {
path: 'feed',
screens: {
Profile: {
path: 'users/:id',
exact: true,
},
},
},
},
};省略路由
const config = {
screens: {
Home: {
path: 'home',
screens: {
Profile: 'users/:id',
},
},
},
};在上面的配置中,我们可以通过外链/home映射到Home页面,但是实际上我们可能想要不是/home而是直接/。我们就可以通过把 path 改成path: ''来实现。
const config = {
screens: {
Home: {
path: '',
screens: {
Profile: 'users/:id',
},
},
},
};格式化参数
在上面的例子里我们已经提到了可以通过parse和stringify两个属性来格式化参数,这里就不在赘述。
高级用法
有时候写死映射可能并不适用于所有场景,这时候我们可以通过getStateFromPath这个属性来自定义自己想要的外链解析:
export const linking: LinkingOptions<AppParamList> = {
enabled: true,
// 外链唤起的前缀,通常会配两个,其中一个是网站的域名。
prefixes: [],
// 配置外链路由跟app内的screen的映射关系。而screen在react-navigation中实际上对应的是navigation state.
config,
getStateFromPath(path, options) {
// 返回的是一个navigation state的结构
},
};8. 修改 cocopods 源:
cd ~/.cocoapods/repos
pod repo remove master
git clone https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/git/CocoaPods/Specs.git master
9. 集成 fastlane
10. 集成 code-push 并配置私有化服务器
-
按照code-push-server 这篇文章的介绍安装好私有化服务器
-
安装 code-push-cli
npm install -g @shm-open/code-push-cli
- 登录私有化服务器
code-push login [your server url]
默认用户名和密码是:admin/123456
- 创建应用
code-push app add <appName> <os> <platform>
例如:
code-push app add MyApp-Android android cordova
code-push app add MyApp-iOS ios react-native
- 重命名应用/删除应用
// rename
code-push app rename <appName> <newAppName>
// delete
code-push app rm <appName>
- 查看所有应用
code-push app ls
- 生成部署密钥
code-push deployment add <appName> <deploymentName>
例如:
和创建应用一样,这里也有对应的 rename/delete/list 命令:
code-push deployment rm <appName> <deploymentName>
code-push deployment rename <appName> <deploymentName> <newDeploymentName>
code-push deployment ls <appName> [--displayKeys|-k]
- 发布更新
code-push release-react <appName> <platform>
[--bundleName <bundleName>]
[--deploymentName <deploymentName>]
[--description <description>]
[--development <development>]
[--disabled <disabled>]
[--entryFile <entryFile>]
[--gradleFile <gradleFile>]
[--mandatory]
[--noDuplicateReleaseError]
[--outputDir <outputDir>]
[--plistFile <plistFile>]
[--plistFilePrefix <plistFilePrefix>]
[--sourcemapOutput <sourcemapOutput>]
[--sourcemapOutputDir <sourcemapOutputDir>]
[--targetBinaryVersion <targetBinaryVersion>]
[--rollout <rolloutPercentage>]
[--privateKeyPath <pathToPrivateKey>]
[--config <config>]
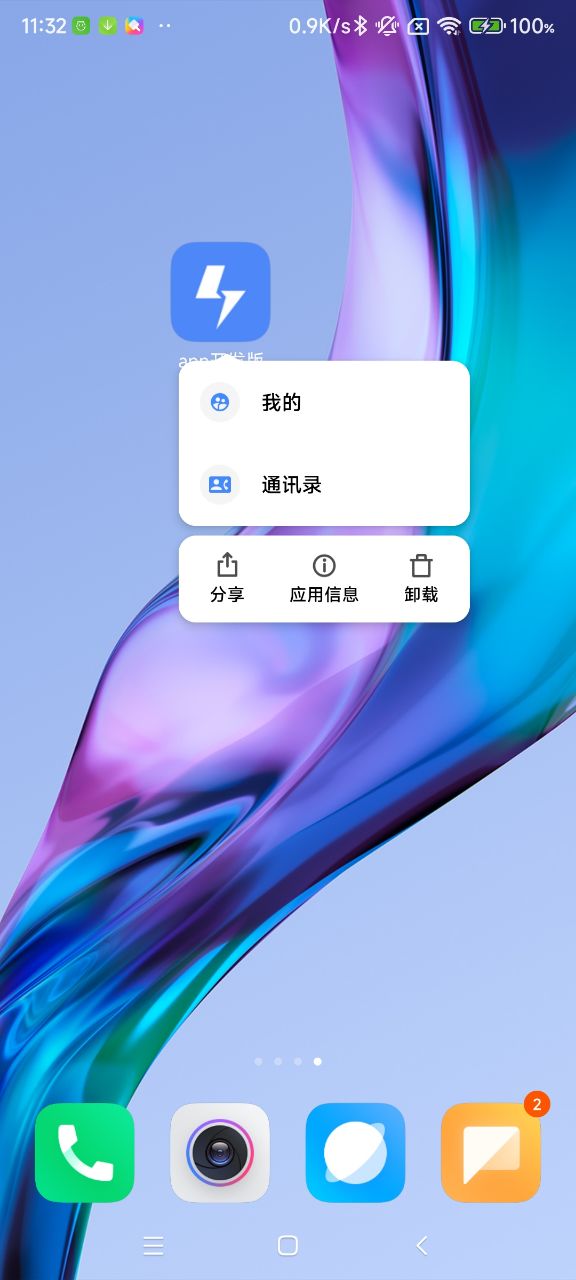
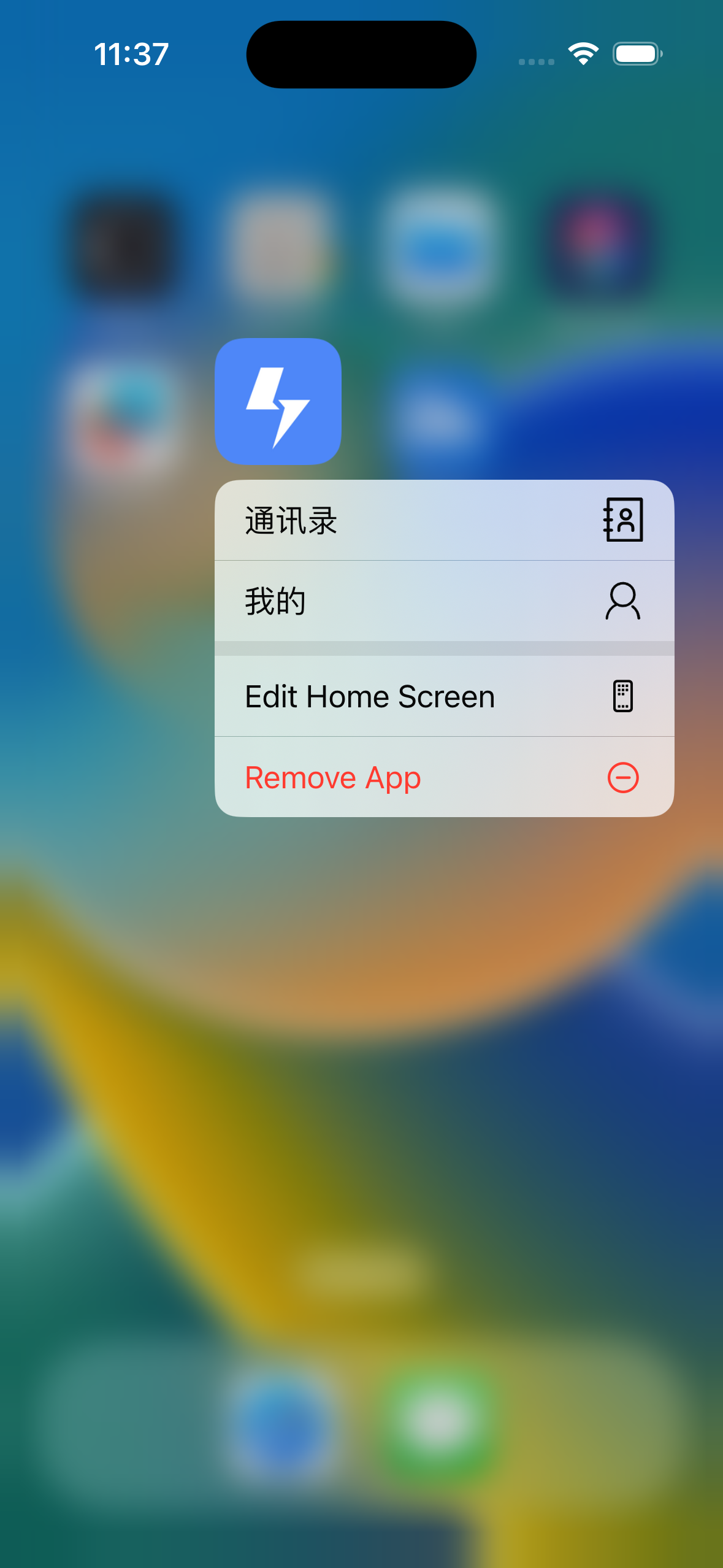
11. 支持 Shortcut(Android) / QuickAction(IOS)功能
1. 什么是 Shortcut / QuickAction
Android Shortcut 和 Apple Quick Action 都是针对移动设备操作系统的快捷方式功能。
-
Android Shortcut 是 Android 操作系统提供的一种快捷方式功能,它可以让用户通过在主屏幕上长按应用图标来打开特定的应用程序功能或操作,例如直接进入应用程序中的某个部分或执行某个操作。Android Shortcut 可以自定义,开发者可以为自己的应用程序添加自定义的快捷方式。
-
Apple Quick Action 则是 iOS 操作系统提供的快捷方式功能,它可以让用户通过在主屏幕上按住应用图标,快速地访问应用程序中的常用功能或操作。例如,你可以在主屏幕上直接查看最近的通知或发送一条新的消息。与 Android Shortcut 不同的是,Apple Quick Action 的功能是由操作系统自动为应用程序生成的,开发者无法自定义。
2. 如何使用
2.1 Android
在app/src/main/res目录下,新建drawable目录, 然后把图片放到这个目录下。图片的名字可以自己定义,但是要和useShortcut.ts里的icon对应上。
你可以借助icons-app-shortcut这个工具来生成不同分辨率的图片。
2.2 IOS
在ios/rnTemplate/Images.xcassets目录下新建 icon 名称对应的.imageset目录,然后把图片放到这个目录下(具体可以查看代码里的例子)。图片的尺寸要求一倍图是35*35,二倍图是70*70,三倍图是105*105。图片的名字可以自己定义,但是要和useShortcut.ts里的icon对应上。
2.3 JS
在useShortcut.ts文件里有shortcuts的定义,实际使用时可以替换成自己的。
// 定义shortcuts,你可以替换成你自己的
const shortcuts = [
{ type: 'contact', title: '通讯录', icon: 'shortcut_contact' },
{ type: 'mine', title: '我的', icon: 'shortcut_mine' },
];这里的icon对应的是上面 Android 和 IOS 里存放的图片的名字。