Cymbal Superstore is sample grocery store web application, built with React.js and Node.js. This sample was built to showcase Gemini AI Code Assist, including AI-assisted development, operations, and analytics.
Check out the blog post to learn more.
This is a prototype demo, with mocked components and data; it is not a production-grade web application. This is not an official Google product. All demo sources - including source tutorials and image licenses - can be found here.
To deploy this sample to a Google Cloud project, you will need: - A Google Cloud project with billing enabled - Owner permissions in your project - Gemini Code Assist activated in your project. (Learn more) - Security Command Center (Premium) activated in your project.
Then, follow these steps:
To deploy Cymbal Superstore, and then interact with the codebase using Gemini Code Assist, we use Cloud Workstations, a Google Cloud-hosted developer machine.
- Open the Cloud Workstations Console in your project https://console.cloud.google.com/workstations/
- Enable the Workstations API.
- Create a Workstation Configuration using the default base image.
- Create a Workstations cluster using your Configuration. (keep defaults, eg. VPC, subnet). This step takes about 15 minutes to complete.
- Create one Workstation in your cluster.
- Start and Launch your Workstation from the console.
- Inside your Workstation's editor, click Cloud Code - Sign in. Follow the steps to sign in to your GCP account.
- Click Cloud Code - No Project, then select your project.
- Reload the editor. You should see a Gemini AI icon in the left sidebar, as well as a Gemini AI indicator on the bottom-right of your editor.
- From inside your Cloud Workstation, open a terminal.
- Clone this repository:
git clone https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/cymbal-superstore
- Set your Project ID.
PROJECT_ID="your-google-cloud-project-id"
gcloud config set project $PROJECT_ID
- Run the Docker auth credential helper.
gcloud auth configure-docker us-central1-docker.pkg.dev
- Install brew.
sudo apt-get install build-essential procps curl file git
/bin/bash -c "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/HEAD/install.sh)"
(echo; echo 'eval "$(/home/linuxbrew/.linuxbrew/bin/brew shellenv)"') >> /home/user/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
- Use brew to install Terraform.
brew install terraform
- Change into the
cymbal-superstore/terraform/directory. This directory contains Terraform infrastructure as code, which when applied to your project, will deploy Cymbal Superstore.
cd cymbal-superstore/terraform
- In the
terraform/directory, create a file calledterraform.tfvars. Replace PROJECT_ID and PROJECT_NUMBER with your project ID and project number, then save the file.
terraform/terraform.tfvars: ``` project_id="YOUR_PROJECT_ID"
project_number="YOUR_PROJECT_NUMBER"
Note: You can use `gcloud` to obtain your project number: `gcloud projects describe $PROJECT_ID --format="value(projectNumber)"`.
9. Initialize Terraform.
terraform init ```
- See the resources that will be deployed.
terraform plan
- Deploy the Terraform resources to your project.
terraform apply
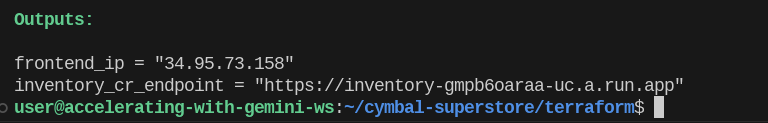
Note: this step takes about 10 minutes to complete. When successful, you will see outputs like this — but with different values for your project.
-
Update your frontend to talk to the backend
inventory_cr_endpointin your output. To do this, copy the value of yourinventory_cr_endpoint, openfrontend/.env.production, and replace the value ofREACT_APP_INVENTORY_URL. -
Re-run
terraform apply. This should only take a minute, as it will redeploy your frontend React app to Cloud Storage using the updated backend URL.
terraform apply
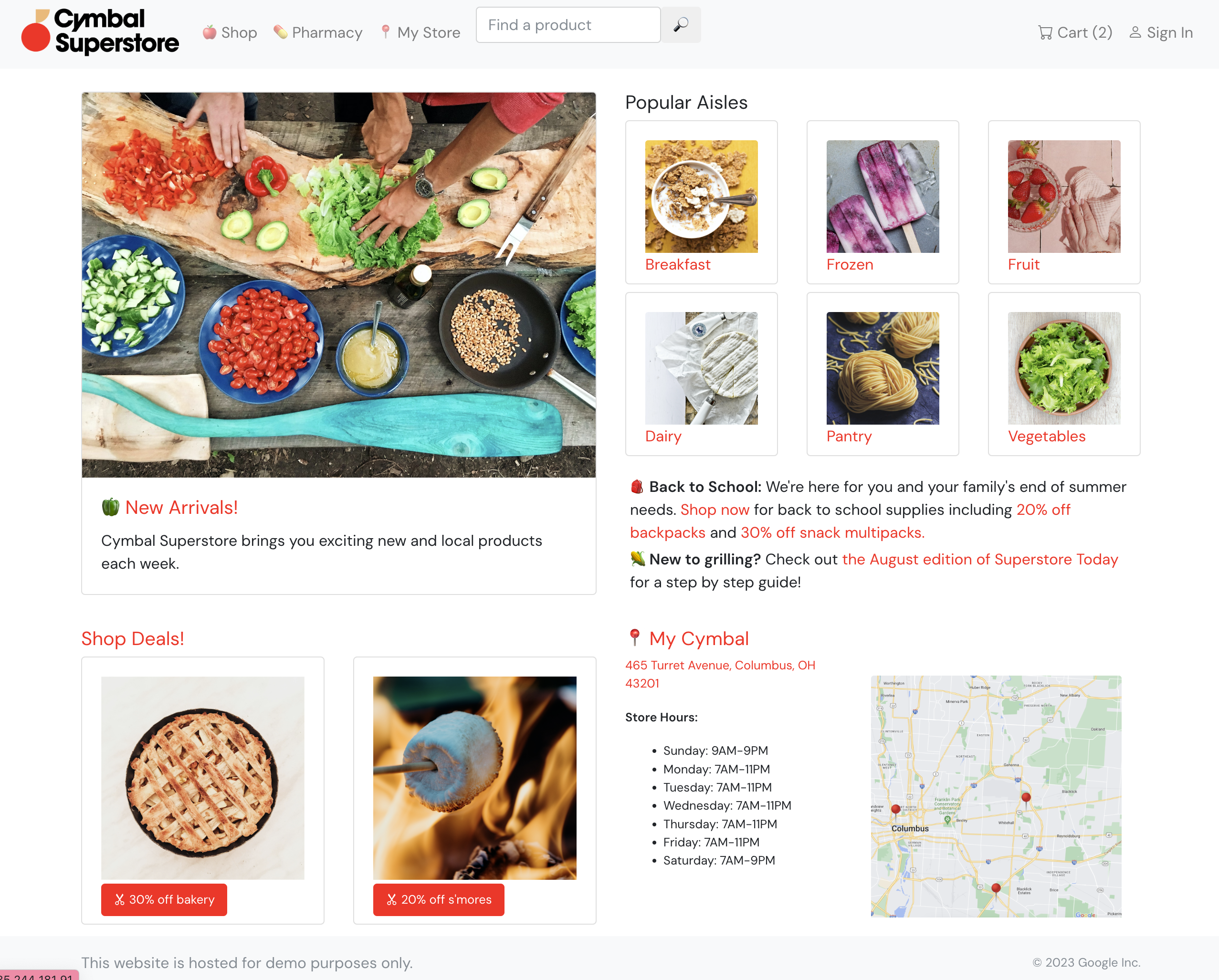
- Open your
frontend_ipin a browser. You should see the Cymbal Superstore frontend.
- Click on New Arrivals. You should see a mocked list of gray product rectangles. This is expected; the Gemini Code Assist demo steps cover the backend implementation of serving this list of new products.
The Spanner component of this demo is mocked - there's no web service writing data to Spanner. Instead, we preload Spanner with mock transaction data so that when we use Gemini in Spanner, we have some data to work with.
- In a terminal, open
scripts/spanner.sh. - Replace
PROJECT_IDwith your project ID. - Run the script to populate the Spanner transactions database:
cd ~/cymbal-superstore/scripts
chmod +x ./spanner.sh
./spanner.shWhen successful, you should see a series of commitTimestamp log messages
indicating that the script is writing data to Spanner.
To test out Gemini Code Assist in Google Cloud features using this sample, try these steps.
Try implementing the GET /newproducts handler in backend/index.ts. Open the
file in your Cloud Workstations editor, then scroll to "DEMO TASK START" (line
94).
Add this prompt as a code comment:
// Get new products from Firestore (added < 7 days ago) and quantity > 0 (in stock)
Observe Gemini's code completion suggestions, and press tab to accept.
Continue pressing tab to accept subsequent code completion suggestions.
Alternatively, get the solution code from scripts/solutioncode-with-bug.ts.
Using the solution code above, try running the backend server. From your Cloud Workstations terminal, run:
cd cymbal-superstore/backend
npm run start
Then, in another terminal tab, curl the server endpoint.
curl localhost:8000/newproducts
You may see an error: curl: (52) Empty reply from server with a log message:
Cannot have inequality filters on multiple properties. This error comes from
the Firestore client library.
To debug, open the Gemini AI Chat icon (chat bubble with a diamond symbol) on the left side of your Workstation editor. Paste in the log message and ask Gemini to help you figure out how to fix.
Gemini's response says that Cloud Firestore does not support multiple inequality
filters in the same query. To resolve, delete the line .where("quantity", ">", 0) so that we only have one filter in our query.
Restart the server, and attempt to curl again. You should successfully get back a list of products.
curl localhost:8000/newproducts
To get the solution function for this step, see
scripts/solutioncode-bug-fixed.ts.
Open backend/index.test.ts. Use Gemini AI chat to generate a test for the
newproducts() function:
Help me write an Express.js test using Jest, in typescript, for the GET /newproducts handler in index.ts. Should check if the response code is 200 and the list of new products is length 8.
Paste the describe().. test into index.test.ts.
After using Gemini Code Assist to build the newproducts() backend feature into
the Inventory API, you can deploy that code to Cloud Run simply by re-running
terraform apply. This step will containerize your updated backend/ code,
push to Container Registry, and redeploy to Cloud Run.
cd ~/cymbal-superstore/terraform
terraform apply
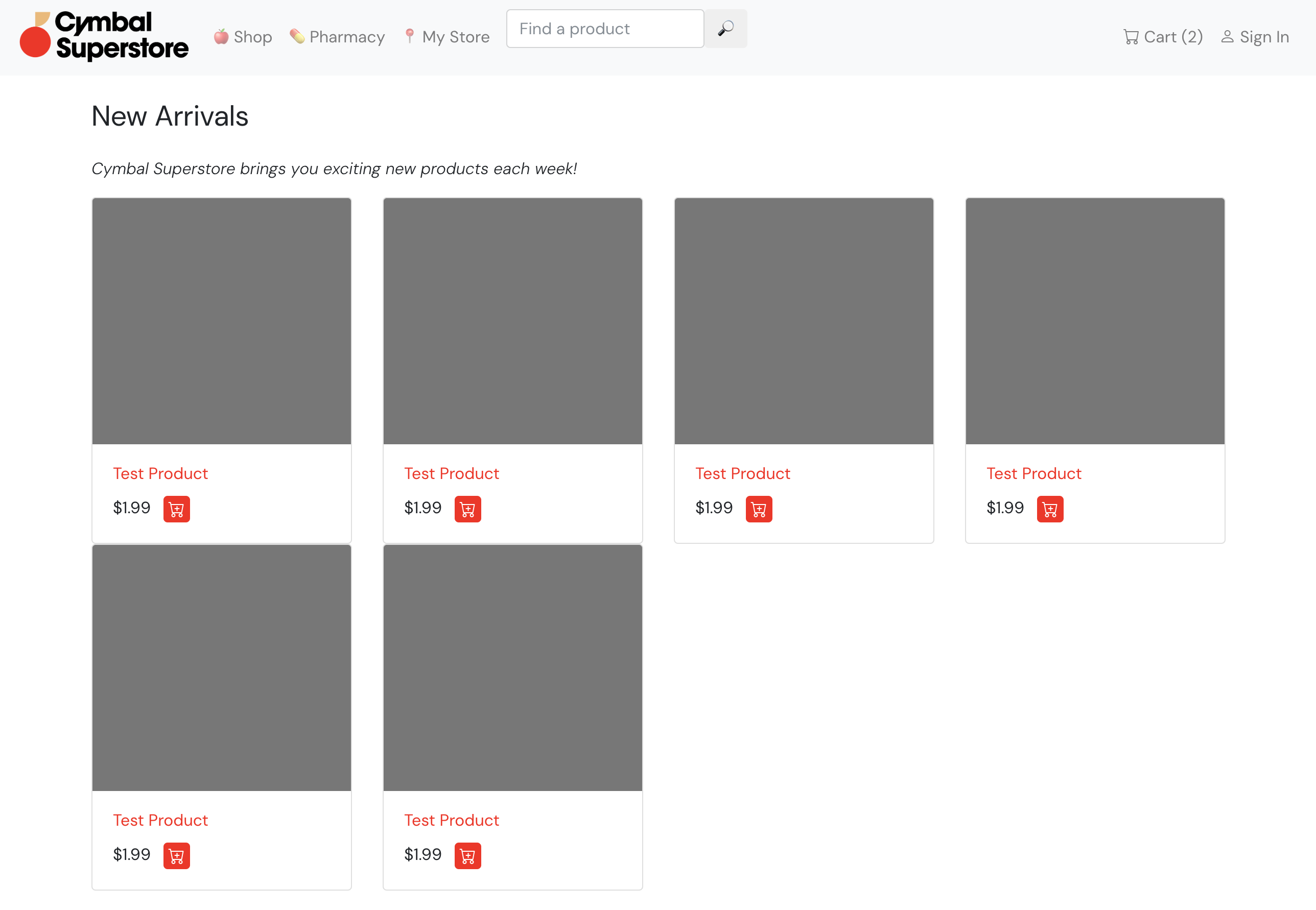
Now, if you hit your frontend_ip and click New Products, you should see a
list of colorful new products, delivered by your new GET /newproducts API
endpoint.
Open the Google Cloud Console. Click the Gemini AI icon on the top right. In the Chat window, ask where to find logs for the Inventory service:
Then, inside Cloud Logging, click on any individual Log message, then click Explain this log entry. A Gemini AI window should appear on the right, explaining the log message.
Inside the Cloud Console, search for "Security Overview." Open Security Command Center, then click Findings on the left side.
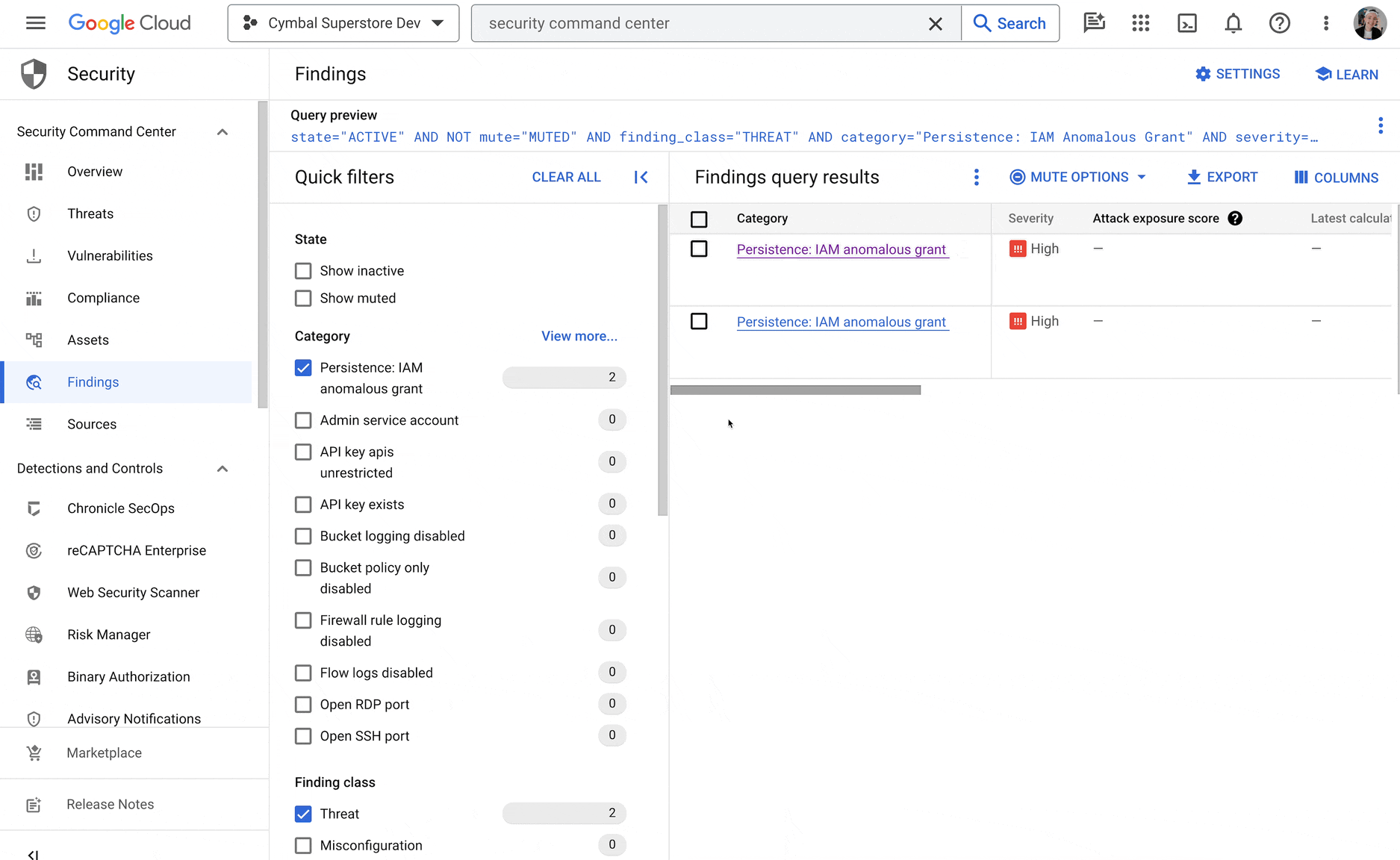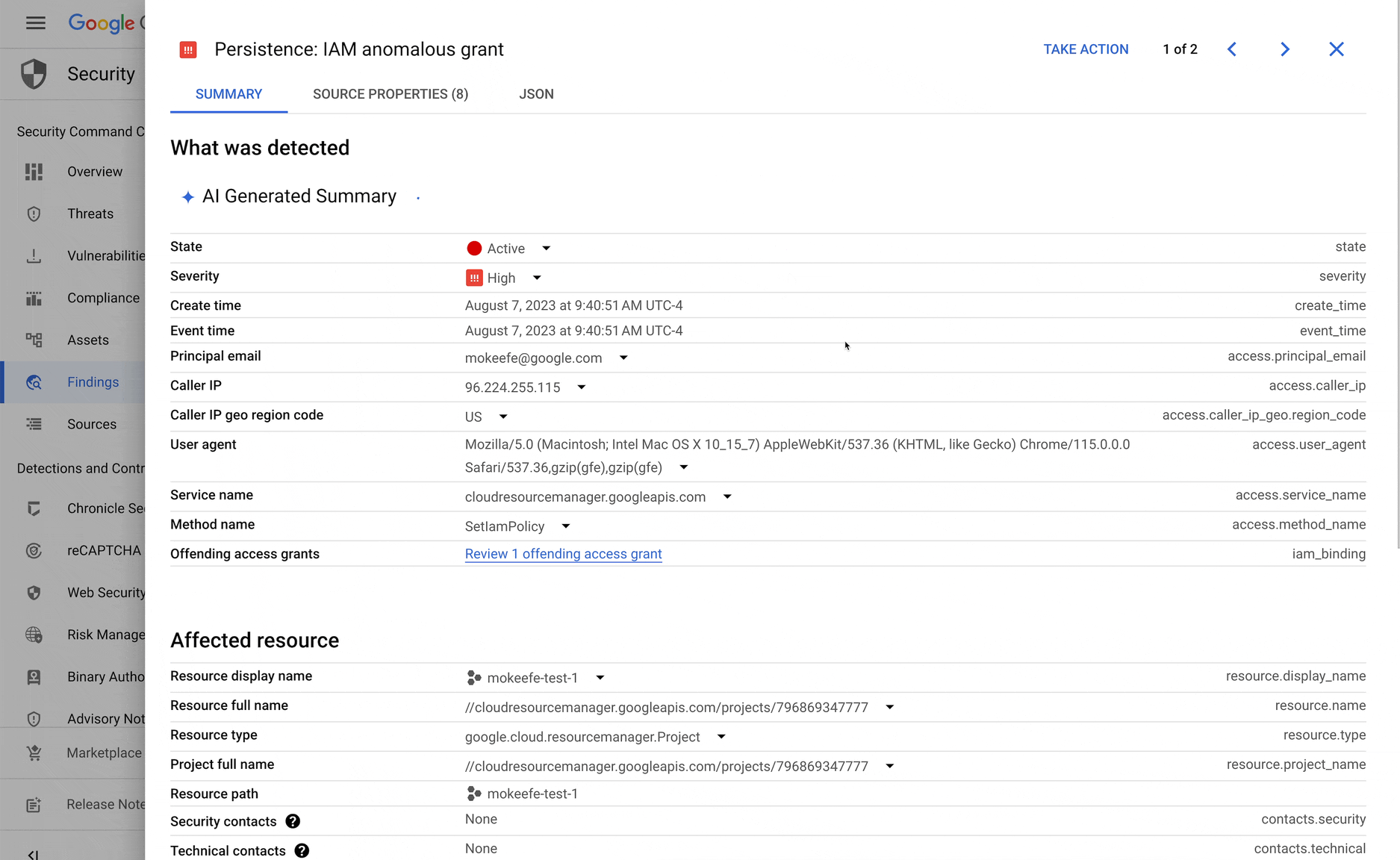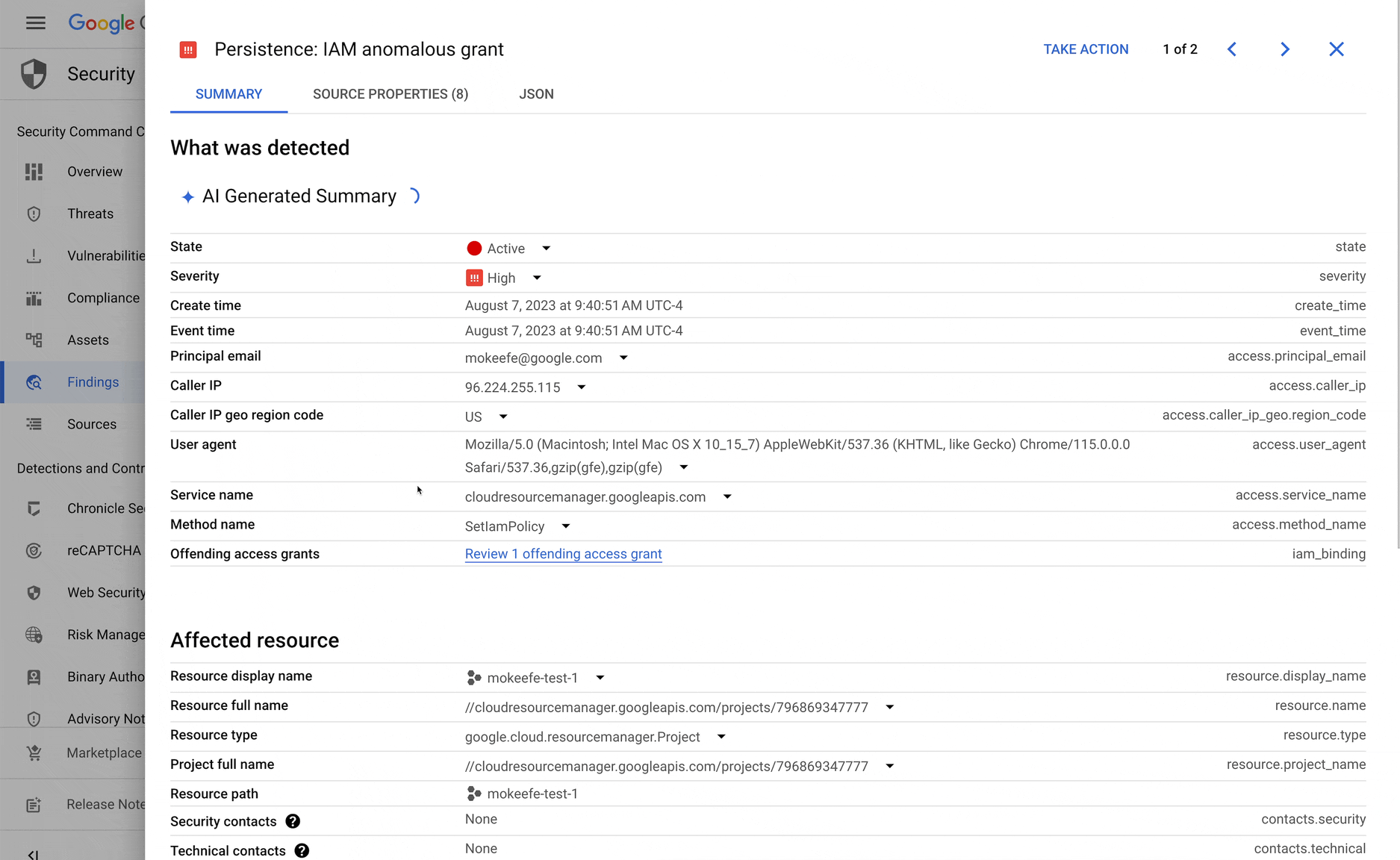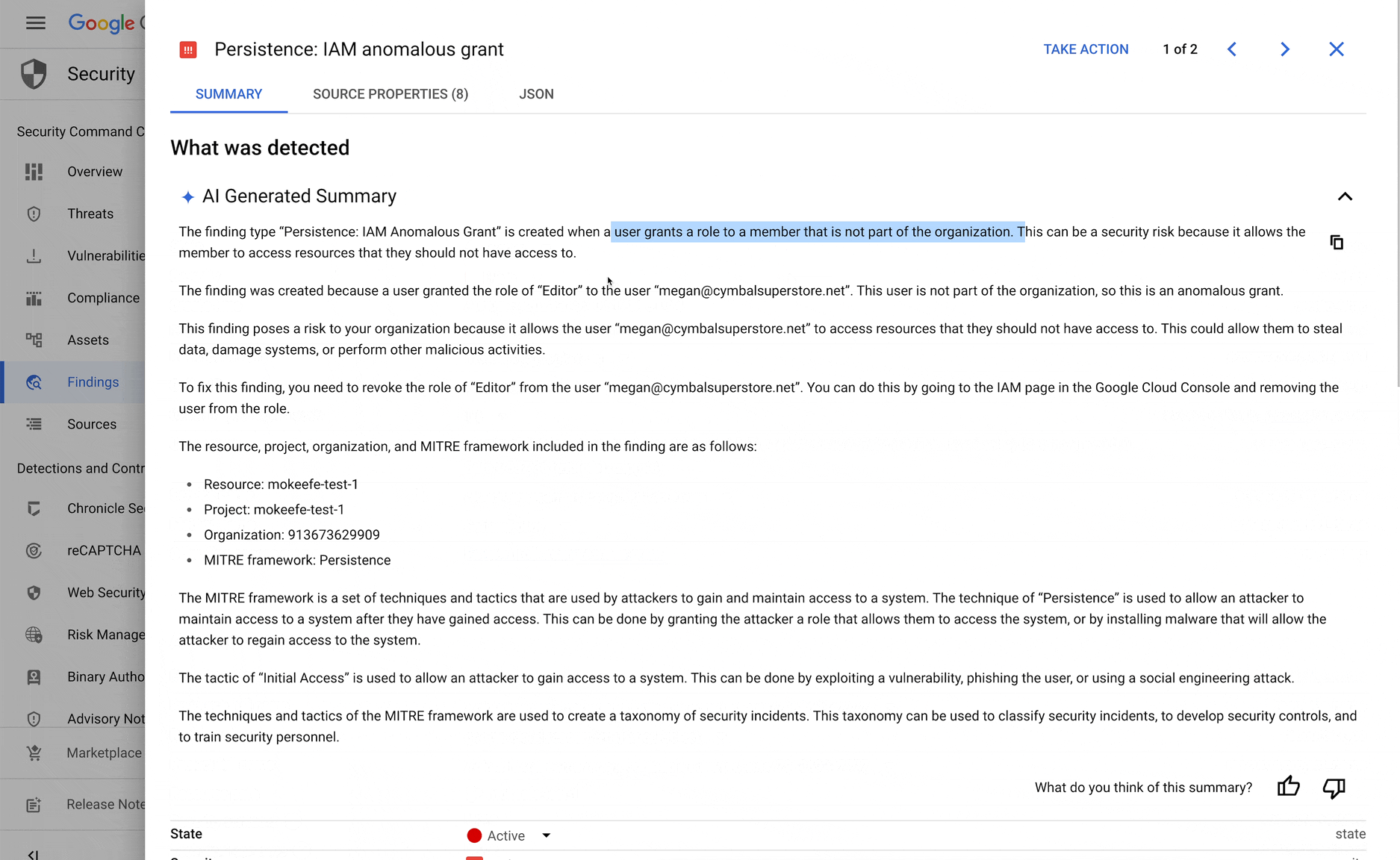
Click on any individual finding, then view an AI-generated summary of the security recommendation.
Note - Security Command Center works best if you wait 1-2 days after activation, so it can gather and surface findings. If you don't have any security findings in your project yet, wait a few hours then try again.
Open BigQuery in the Cloud Console. On the left side, click the cymbalsales
dataset, and below that, the cymbalsalestable. Open a new Query window.
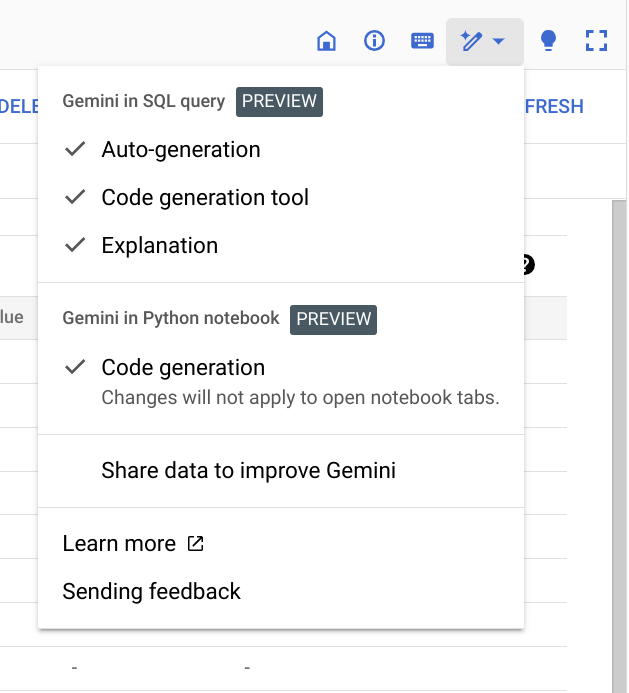
On the top right of the query window, you should see a Gemini AI icon (blue magic wand). Click it to ensure that SQL Code Completion is selected:
Then, try generating some SQL in the BigQuery window, using the following prompt:
SELECT SUM(PRICE_PER_UNIT * QUANTITY_SOLD_AUG_5) AS total_aug_5,
FROM `PROJECT_ID.cymbal_sales.cymbalsalestable`;
# Get sales total_aug_12
Click Run to run your queries and view results.
Open Spanner in the Cloud Console. Then, open the Explorer. Open a new query
window and start typing (eg. SELECT ...) to get SQL suggestions.