This package will serve as a base to develop circuit based applications or logical games on top of it. This package does not depend on any external library other than pure Python.
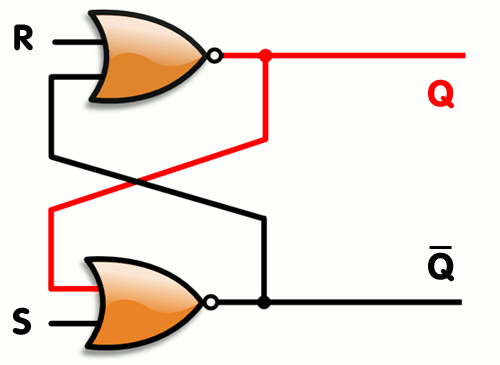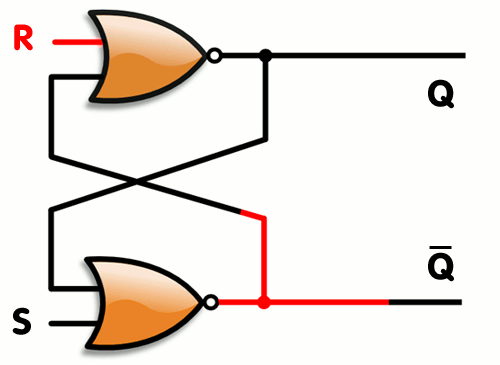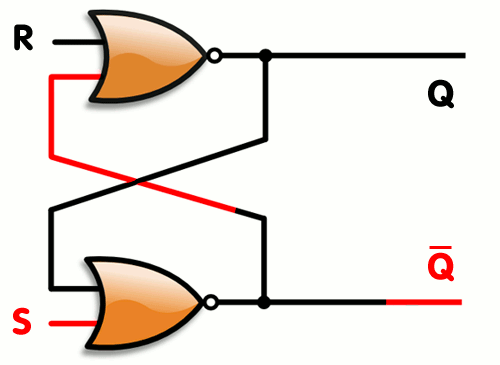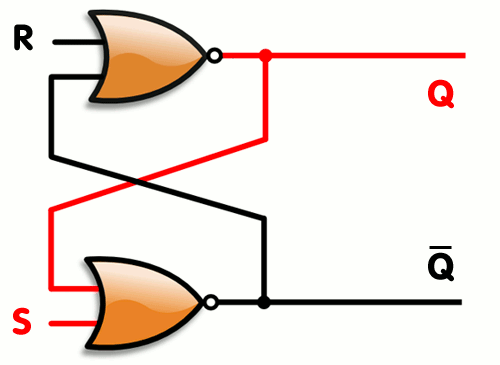
Here's an example of SR latch constructed from a pair of cross-coupled NOR gates
from BinPy import *
NOR1 = Nor('NOR1') #First NOR gate
NOR2 = Nor('NOR2') #Second NOR gate
NOR2.C.connect(NOR1.B) #Connecting output of second NOR with input of first NOR
NOR1.C.connect(NOR2.A) #Connecting output of first NOR with input of second NOR
NOR1.A.set(1);NOR2.B.set(0) #Set state
print 'Q: ',NOR2.C.getState(), '\t','Q\': ',NOR1.C.getState()
NOR1.A.set(0);NOR2.B.set(1) #Reset state
print 'Q: ',NOR2.C.getState(), '\t','Q\': ',NOR1.C.getState()
NOR1.A.set(0);NOR2.B.set(0) #Hold state
print 'Q: ',NOR2.C.getState(), '\t','Q\': ',NOR1.C.getState()
NOR1.A.set(1);NOR2.B.set(1) #Invalid state
print 'Q: ',NOR2.C.getState(), '\t','Q\': ',NOR1.C.getState()Output
Q: True Q': False
Q: False Q': True
Q: False Q': True
Q: False Q': FalseOperations, Combinatonal Logic and Algorithms
from BinPy import *
#Operations
operator = Operation()
print operator.add([1,0,1,1],[1,1])
print operator.subtract([1,0,1,1],[1,1])
#Combinational Logic
myMUX = MUX()
print "MUX Out: ", myMUX.run([1,0,0,0,1,1,1,1],[0,0,1])
#Algorithms
#Includes the Quine-McCluskey algorithm for solving K-Maps
FinalEquation = QM(['A','B'])
print "Minimized Boolean Equation : " , FinalEquation.get_function(qm.solve([0,1,2],[])[1])
#IC
myIC = IC_7400()
p = {1:1,2:0,4:0,5:0,7:0,10:1,9:1,13:0,12:0,14:1}
myIC.setIC(p)
print "IC_7400 Out: ", myIC.run()
myIC1 = IC_7401()
p = {2:0,3:1,5:0,6:0,7:0,8:1,9:1,11:0,12:0,14:1}
myIC1.setIC(p)
print "IC_7401 Out: ", myIC1.run()Output
{'carry': 0, 'sum': [1, 1, 1, 0]}
{'carry': 1, 'difference': [1, 0, 0, 0]}
MUX Out: 0
IC_7400 Out: {8: 0, 11: 1, 3: 1, 6: 1}
IC_7401 Out: {1: 1, 10: 0, 4: 1, 13: 1}
Minimized Boolean Equation : ((NOT B) OR (NOT A))-
All basic logic gates (NOT, OR, NOR, AND, NAND, XOR, XNOR)
-
Combinational logics
- Adder
- Subtractor
- Multiplier
- MUX (2:1, 4:1, 8:1, 16:1)
- DEMUX (1:2, 1:4, 1:8, 1:16)
- Encoder
-
IC
- 7400
- 741G00
- 7401
- 7402
- 741G02
- 7403
- 741G03
- 7404
- 741G04
- 7405
- 741G05
- 7408
- 741G08
- 7410
- 7411
- 7442
- 7443
- 7444
- 7451
- 7454
- 7455
- 7458
-
Algorithms
- Quine-McCluskey Algorithm (To find minimized Boolean Equation)
- Moore Machine Optimizer
- Introduction of all ICs
- Introduction of problem solving algorithms
- Addition of Microprocessors and Analog Devices
- Graphical representation of the circuit
- ...