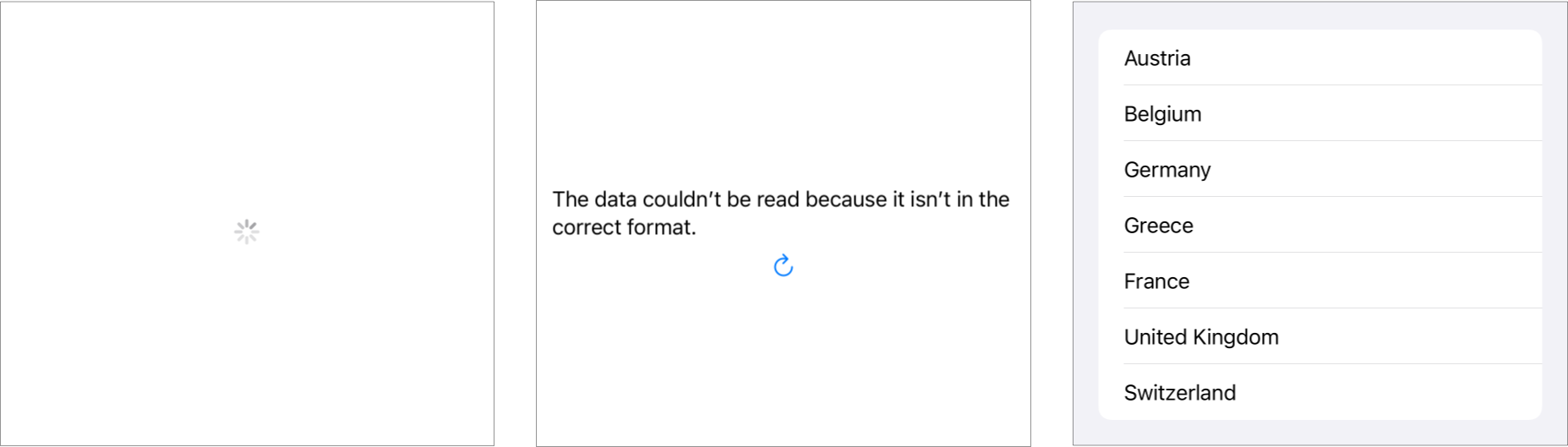
AsyncView is a SwiftUI View for handling in-progress and error states when loading data asynchronously using async/await. It's like AsyncImage but for data.
I recommend to define a type for every API and implement a method for every endpoint/remote call. For example, to load a JSON list of countries:
struct Country: Identifiable, Codable {
var id: String
var name: String
}
class CountriesEndpoints {
let urlSession = URLSession.shared
let jsonDecoder = JSONDecoder()
static let shared = CountriesEndpoints()
func countries() async throws -> [Country] {
let url = URL(string: "https://www.ralfebert.de/examples/v3/countries.json")!
let (data, _) = try await urlSession.data(from: url)
return try self.jsonDecoder.decode([Country].self, from: data)
}
}Have a look at MetMuseumEndpoints for a more realistic API.
For presenting data loaded from a URL endpoint directly in a SwiftUI View, you can use AsyncView:
import SwiftUI
import AsyncView
struct CountriesView: View {
var body: some View {
AsyncView(
operation: { try await CountriesEndpoints.shared.countries() },
content: { countries in
List(countries) { country in
Text(country.name)
}
}
)
}
}It is also possible to extract the loading operation as a model instance using AsyncModel and use AsyncModelView:
import SwiftUI
import AsyncView
struct CountriesView: View {
@StateObject var countriesModel = AsyncModel { try await CountriesEndpoints.shared.countries() }
var body: some View {
AsyncModelView(model: countriesModel) { countries in
List(countries) { country in
Text(country.name)
}
}
}
}For more complex models, you can also define the model as a separate class:
class CountriesModel: AsyncModel<[Country]> {
override func asyncOperation() async throws -> [Country] {
try await CountriesEndpoints.shared.countries()
}
}
struct CountriesView: View {
@StateObject var countriesModel = CountriesModel()
var body: some View {
AsyncModelView(model: countriesModel) { countries in
List(countries) { country in
Text(country.name)
}
}
}
}Countries - Branch swiftui3-factbook-asyncview shows a list of countries.
MuseumGuide loads a random artwork from the Met Museum API:
See my blog post "Structuring asynchronous loading operations in SwiftUI" for a walk-through tutorial on how to build this package which serves as an in-depth explanation of this package.