Facts are all you need (tm) ... and maybe an LLM, a text embedder, mongo and some python!
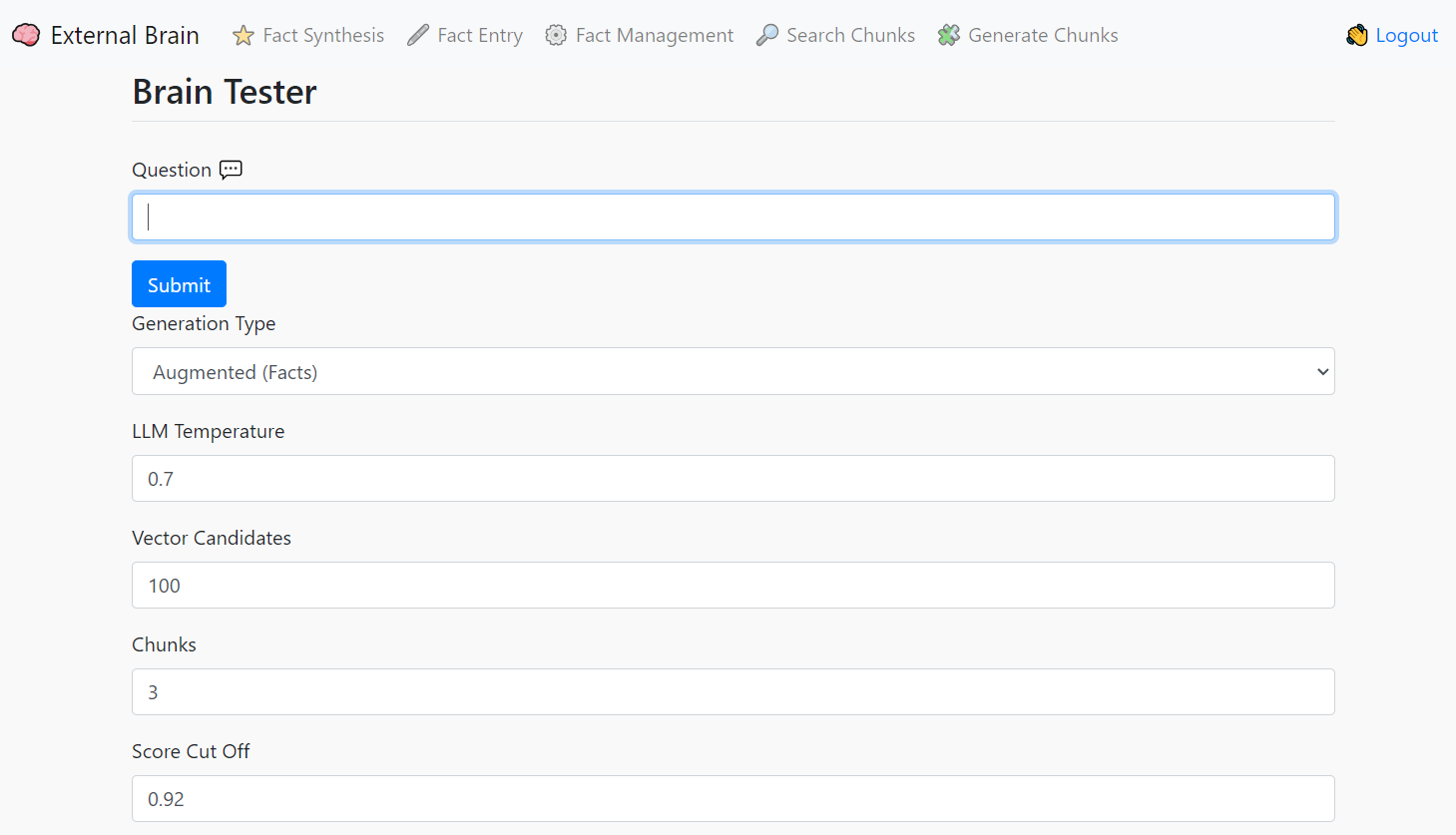
External Brain is a tool for asserting facts or writing down your thoughts, storing them in a durable data store and giving you the ability to ask an LLM questions about them later.
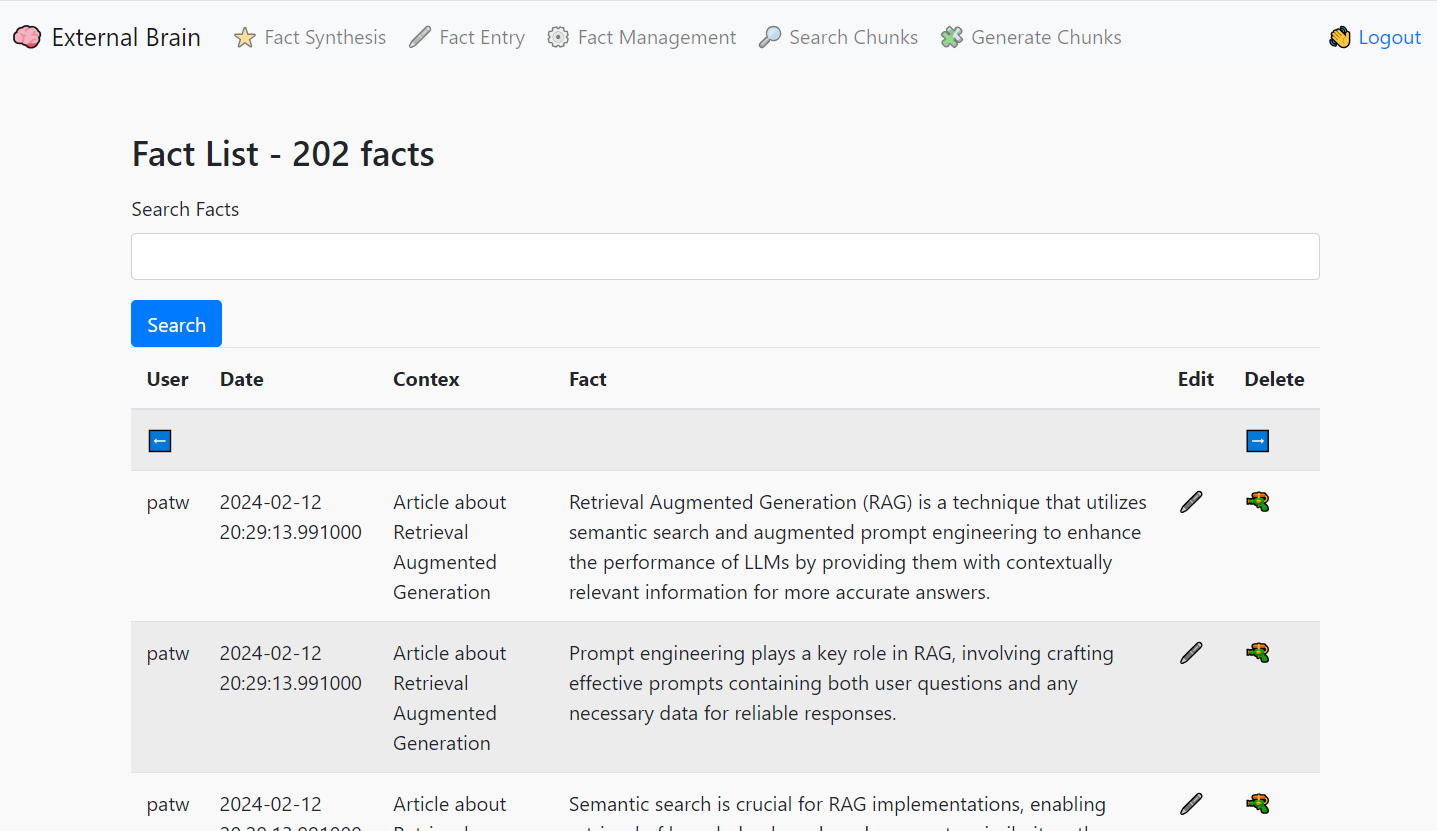
- Use the input tool to summarize whatever text you send it. It will use the LLM to produce bullet point facts for all your data
- Facts get grouped into fact chunks and vectorized by a text embedder
- Questions to the External Brain will retrieve facts before answering, grouding the response with your own facts!
- Never Forget a Detail: Keep important ideas and notes at your fingertips.
- Unlock Hidden Connections: Discover patterns and insights you might have overlooked.
- Supercharge Your Research: Find relevant supporting information quickly.
Let's look at how you can set up this system to start reaping these benefits.
External Brain's fact and chunk storage operates on MongoDB Atlas. You can test it on a free tier (m0) account here.
-
Data Storage (Documents and Chunks):
- Documents: Represent the original source documents you want to store facts from.
- Chunks: Smaller, manageable segments of the documents created during preprocessing. Each chunk is treated as an individual MongoDB document.
- Chunk Embeddings: Use a text embedder (like BreadVec) to generate vector representations of each chunk. Store these embeddings directly in the chunk documents.
-
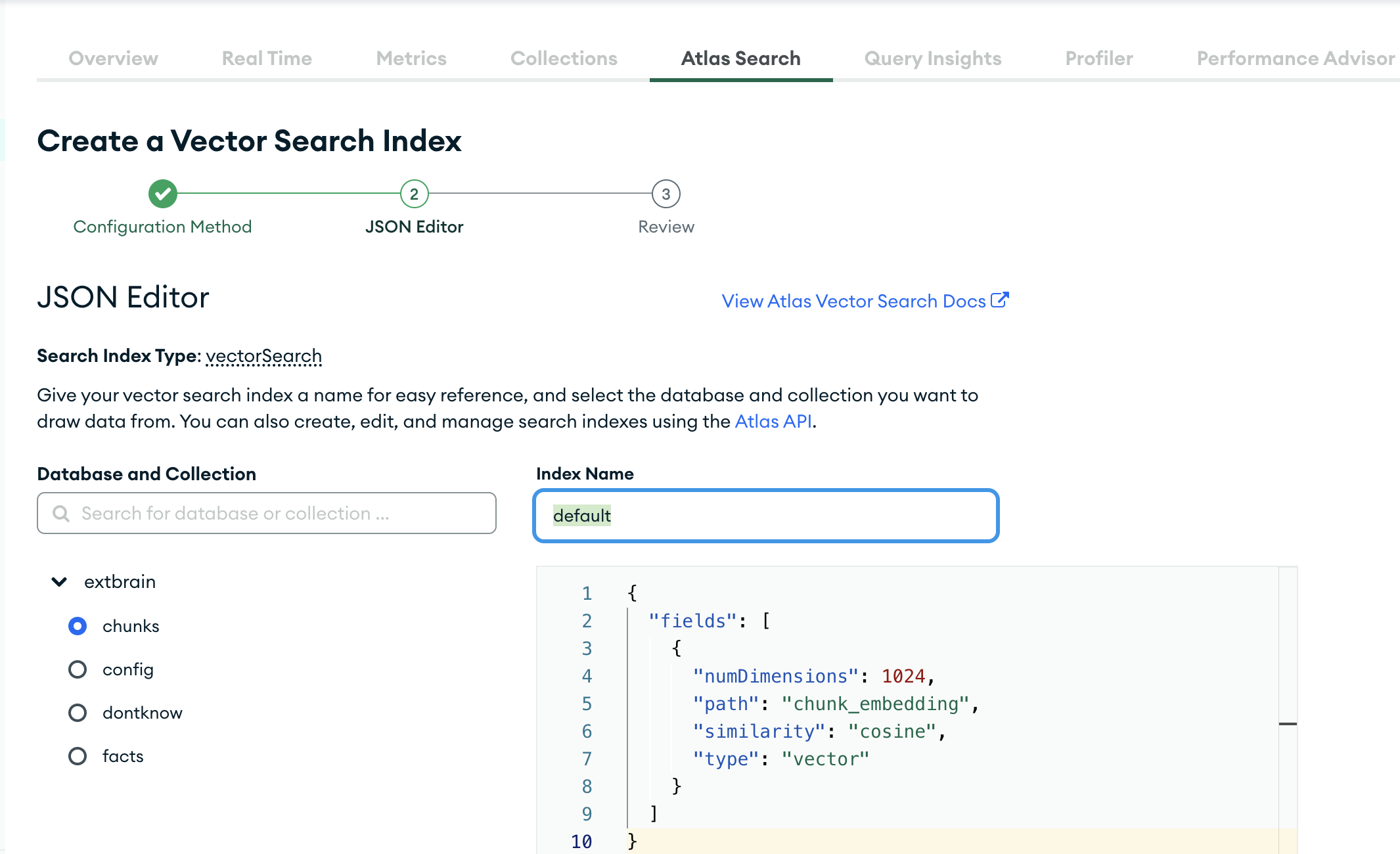
Vector Search Index:
- Create a MongoDB Atlas Search index specifically on the chunk embedding field. This will enable fast semantic similarity search during retrieval.
-
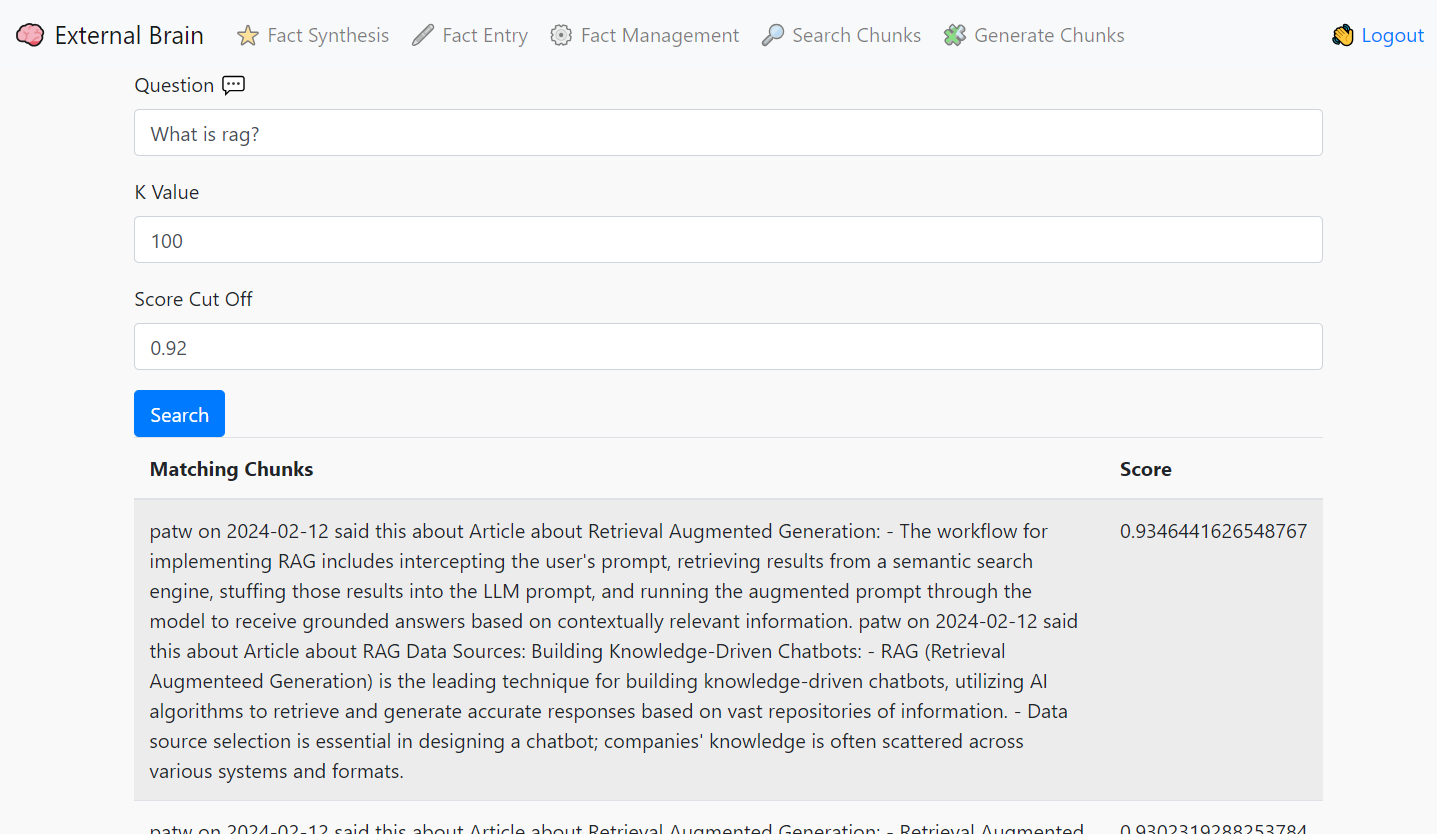
Retrieval (When a user asks a question):
- Question Embedding: Generate a vector embedding of the user's question using the same text embedder.
- Semantic Search: Use MongoDB Atlas's vector search capabilities to retrieve the most semantically relevant chunks from your database based on the question embedding.
- Relevance Filtering: You may apply additional filtering or ranking to the retrieved chunks based on metadata or calculated relevance scores to ensure the best chunks are used for answer generation.
-
Generation (LLM Usage):
- LLM Input: Feed the retrieved chunks (along with the original question) into your LLM (e.g., OpenAI, Mistral.ai, or a locally run llama.cpp instance).
- Answer Generation: The LLM will process the information to generate a comprehensive answer, grounded in the facts stored within your MongoDB Atlas database.
Create a dedicated cluster on MongDB Atlas (7.x or higher), Under Database Access add a database user in Password mode, with the built in role of "read/write any database". Click on Network Access and add your personal IP or 0.0.0.0 if you're comfortable with any IP connecting to this cluster.
If you don't plan on running in local mode (see instructions below), obtain an API key from OpenAI (https://platform.openai.com/signup) or MistralAI (https://console.mistral.ai/).
Run the following in the ExternalBrain directory:
pip install -r requirements.txt
git pull https://github.com/patw/ExternalBrain.git
cd ExternalBrain
- Follow the instructions below on configuring the .env, model and embedder configs
docker build -t extbrain .
docker run -d -p 7861:5000 extbrain
External Brain was designed around using llama.cpp in server mode for the LLM, however it can now be run with OpenAI or Mistral.ai keys! Check out the sample.env file for configuration options.
Copy the sample.env file to .env and edit this file. This contains all the important configuration variables for the application to run.
- MONGO_CON - This will be your srv style connection into Atlas Mongo, you can get this from the Atlas UI by selecting Connection and using python for the language
- MONGO_DB - The database you want to connect to. "extbrain" is default.
- SECRET_KEY - This is the session key for Flask, it can be anything you want
- USERS - This is a json doc of user/password keys, set this to something you remember so you can log into system
- API_KEY - This is the key that the discord_bot, slack_Bot and web_bot need to connect to extBrain, set it to something strong and complex and use the same key in those tools
- SERVICE - This can be "local" for llama.cpp in server mode + BreadVec, "mistral" for Mistral.ai or "openai" for OpenAI
- MODEL_NAME - This is the model name to use with each service. Local doesn't use this but Mistral and OpenAI need this configured.
- OPENAI_API_KEY - This is your OpenAI Key. You only need this configured if you are using OpenAI.
- MISTRAL_API_KEY - This is your Mistral.ai Key. You only need this configured if you are using Mistral.ai.
After the application has been configured (.env is correct), you can start it with the script files and load the UI by going to:
./extbrain.sh
extbrain.bat
If you want to run extBrain entirely locally, without using any cloud provider you can! Follow the instructions below to install a vectorizer service and an LLM. I highly recommend an M1/M2/M3 mac for this task or a PC with an nVidia graphics card and at least 8 gigs of VRAM. It will run on CPU, but the experience is really poor compared to these accelerated plaforms.
Rename the model.json.sample to model.json. This file is used to set the prompt format and ban tokens, the default is ChatML format so it should work with most recent models. Set the llama_endpoint to point to your llama.cpp running in server mode.
Rename embedder.json.sample to embedder.json and point to the endpoint of your BreadVec service.
Install and configure https://github.com/patw/BreadVec
Detailed instructions are in that repo.
We highly recommend OpenHermes 2.5 Mistral-7b fine tune for this task, as it's currently the best (Feb 2024) that I've tested. You can find different quantized versions of the model here:
https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/OpenHermes-2.5-Mistral-7B-GGUF/tree/main
I'd suggest the Q6 quant for GPU and Q4_K_M for CPU
Go to the llama.cpp releases and download either the win-avx2 package for CPU or the cublas for nvidia cards:
https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/releases
Extract the files out and run the following for nvidia GPUs:
server.exe -m <model>.gguf -t 4 -c 2048 -ngl 99 --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8086
For CPU only:
server.exe -m <model>.gguf -c 2048 --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8086
Replace with whatever model you downloaded and put into the llama.cpp directory
Follow the install instructions for llama.cpp at https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp
Git clone, compile and run the following for GPU:
./server -m models/<model>.gguf -t 4 -c 2048 -ngl 99 --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8086
For CPU only:
./server -m models/<model>.gguf -c 2048 --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8086
Replace with whatever model you downloaded and put into the llama.cpp/models directory