NFStream is a Python framework providing fast, flexible, and expressive data structures designed to make working with online or offline network data both easy and intuitive. It aims to be the fundamental high-level building block for doing practical, real world network data analysis in Python. Additionally, it has the broader goal of becoming a common network data analytics framework for researchers providing data reproducibility across experiments.
| Live Notebook |

|
| Project Website |

|
| Discussion Channel |

|
| Latest Release |

|
| Supported Versions |


|
| Project License |

|
| Build Status |

|
| Code Quality |
)
)
|
| Code Coverage |

|
- Performance: NFStream is designed to be fast: AF_PACKETV3/FANOUT on Linux, parallel processing, native C (using CFFI) for critical computation and PyPy support.
- Encrypted layer-7 visibility: NFStream deep packet inspection is based on nDPI. It allows NFStream to perform reliable encrypted applications identification and metadata fingerprinting (e.g. TLS, SSH, DHCP, HTTP).
- Statistical features extraction: NFStream provides state of the art of flow-based statistical feature extraction. It includes both post-mortem statistical features (e.g. min, mean, stddev and max of packet size and inter arrival time) and early flow features (e.g. sequence of first n packets sizes, inter arrival times and directions).
- Flexibility: NFStream is easily extensible using NFPlugins. It allows to create a new feature within a few lines of Python.
- Machine Learning oriented: NFStream aims to make Machine Learning Approaches for network traffic management reproducible and deployable. By using NFStream as a common framework, researchers ensure that models are trained using the same feature computation logic and thus, a fair comparison is possible. Moreover, trained models can be deployed and evaluated on live network using NFPlugins.
Binary installers for the latest released version are available on Pypi.
pip install nfstreamDealing with a big pcap file and just want to aggregate into labeled network flows? NFStream make this path easier in few lines:
from nfstream import NFStreamer
# We display all streamer parameters with their default values.
# See documentation for detailed information about each parameter.
# https://www.nfstream.org/docs/api#nfstreamer
my_streamer = NFStreamer(source="facebook.pcap", # or network interface
decode_tunnels=True,
bpf_filter=None,
promiscuous_mode=True,
snapshot_length=1536,
idle_timeout=120,
active_timeout=1800,
accounting_mode=0,
udps=None,
n_dissections=20,
statistical_analysis=False,
splt_analysis=0,
n_meters=0,
performance_report=0)
for flow in my_streamer:
print(flow) # print it.# See documentation for each feature detailed description.
# https://www.nfstream.org/docs/api#nflow
NFlow(id=0,
expiration_id=0,
src_ip='192.168.43.18',
src_mac='30:52:cb:6c:9c:1b',
src_oui='30:52:cb',
src_port=52066,
dst_ip='66.220.156.68',
dst_mac='98:0c:82:d3:3c:7c',
dst_oui='98:0c:82',
dst_port=443,
protocol=6,
ip_version=4,
vlan_id=0,
tunnel_id=0,
bidirectional_first_seen_ms=1472393122365,
bidirectional_last_seen_ms=1472393123665,
bidirectional_duration_ms=1300,
bidirectional_packets=19,
bidirectional_bytes=5745,
src2dst_first_seen_ms=1472393122365,
src2dst_last_seen_ms=1472393123408,
src2dst_duration_ms=1043,
src2dst_packets=9,
src2dst_bytes=1345,
dst2src_first_seen_ms=1472393122668,
dst2src_last_seen_ms=1472393123665,
dst2src_duration_ms=997,
dst2src_packets=10,
dst2src_bytes=4400,
application_name='TLS.Facebook',
application_category_name='SocialNetwork',
application_is_guessed=0,
requested_server_name='facebook.com',
client_fingerprint='bfcc1a3891601edb4f137ab7ab25b840',
server_fingerprint='2d1eb5817ece335c24904f516ad5da12',
user_agent='',
content_type='')NFStream performs 48 post mortem flow statistical features extraction which include detailed TCP flags analysis, minimum, mean, maximum and standard deviation of both packet size and interarrival time in each direction.
from nfstream import NFStreamer
my_streamer = NFStreamer(source="facebook.pcap",
# Disable L7 dissection for readability purpose.
n_dissections=0,
statistical_analysis=True)
for flow in my_streamer:
print(flow)# See documentation for each feature detailed description.
# https://www.nfstream.org/docs/api#nflow
NFlow(id=0,
expiration_id=0,
src_ip='192.168.43.18',
src_mac='30:52:cb:6c:9c:1b',
src_oui='30:52:cb',
src_port=52066,
dst_ip='66.220.156.68',
dst_mac='98:0c:82:d3:3c:7c',
dst_oui='98:0c:82',
dst_port=443,
protocol=6,
ip_version=4,
vlan_id=0,
tunnel_id=0,
bidirectional_first_seen_ms=1472393122365,
bidirectional_last_seen_ms=1472393123665,
bidirectional_duration_ms=1300,
bidirectional_packets=19,
bidirectional_bytes=5745,
src2dst_first_seen_ms=1472393122365,
src2dst_last_seen_ms=1472393123408,
src2dst_duration_ms=1043,
src2dst_packets=9,
src2dst_bytes=1345,
dst2src_first_seen_ms=1472393122668,
dst2src_last_seen_ms=1472393123665,
dst2src_duration_ms=997,
dst2src_packets=10,
dst2src_bytes=4400,
bidirectional_min_ps=66,
bidirectional_mean_ps=302.36842105263156,
bidirectional_stddev_ps=425.53315715259754,
bidirectional_max_ps=1454,
src2dst_min_ps=66,
src2dst_mean_ps=149.44444444444446,
src2dst_stddev_ps=132.20354676701294,
src2dst_max_ps=449,
dst2src_min_ps=66,
dst2src_mean_ps=440.0,
dst2src_stddev_ps=549.7164925870628,
dst2src_max_ps=1454,
bidirectional_min_piat_ms=0,
bidirectional_mean_piat_ms=72.22222222222223,
bidirectional_stddev_piat_ms=137.34994188549086,
bidirectional_max_piat_ms=398,
src2dst_min_piat_ms=0,
src2dst_mean_piat_ms=130.375,
src2dst_stddev_piat_ms=179.72036811192467,
src2dst_max_piat_ms=415,
dst2src_min_piat_ms=0,
dst2src_mean_piat_ms=110.77777777777777,
dst2src_stddev_piat_ms=169.51458475436397,
dst2src_max_piat_ms=409,
bidirectional_syn_packets=2,
bidirectional_cwr_packets=0,
bidirectional_ece_packets=0,
bidirectional_urg_packets=0,
bidirectional_ack_packets=18,
bidirectional_psh_packets=9,
bidirectional_rst_packets=0,
bidirectional_fin_packets=0,
src2dst_syn_packets=1,
src2dst_cwr_packets=0,
src2dst_ece_packets=0,
src2dst_urg_packets=0,
src2dst_ack_packets=8,
src2dst_psh_packets=4,
src2dst_rst_packets=0,
src2dst_fin_packets=0,
dst2src_syn_packets=1,
dst2src_cwr_packets=0,
dst2src_ece_packets=0,
dst2src_urg_packets=0,
dst2src_ack_packets=10,
dst2src_psh_packets=5,
dst2src_rst_packets=0,
dst2src_fin_packets=0)NFStream performs early (up to 255 packets) flow statistical features extraction (also referred as SPLT analysis in the literature). It is summarized as a sequence a these packets directions, sizes and interarrival times.
from nfstream import NFStreamer
my_streamer = NFStreamer(source="facebook.pcap",
# We disable both l7 dissection and statistical analysis
# for readability purpose.
n_dissections=0,
statistical_analysis=False,
splt_analysis=10)
for flow in my_streamer:
print(flow)# See documentation for each feature detailed description.
# https://www.nfstream.org/docs/api#nflow
NFlow(id=0,
expiration_id=0,
src_ip='192.168.43.18',
src_mac='30:52:cb:6c:9c:1b',
src_oui='30:52:cb',
src_port=52066,
dst_ip='66.220.156.68',
dst_mac='98:0c:82:d3:3c:7c',
dst_oui='98:0c:82',
dst_port=443,
protocol=6,
ip_version=4,
vlan_id=0,
tunnel_id=0,
bidirectional_first_seen_ms=1472393122365,
bidirectional_last_seen_ms=1472393123665,
bidirectional_duration_ms=1300,
bidirectional_packets=19,
bidirectional_bytes=5745,
src2dst_first_seen_ms=1472393122365,
src2dst_last_seen_ms=1472393123408,
src2dst_duration_ms=1043,
src2dst_packets=9,
src2dst_bytes=1345,
dst2src_first_seen_ms=1472393122668,
dst2src_last_seen_ms=1472393123665,
dst2src_duration_ms=997,
dst2src_packets=10,
dst2src_bytes=4400,
# The sequence of 10 first packet direction, size and inter arrival time.
splt_direction=[0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1],
splt_ps=[74, 74, 66, 262, 66, 1454, 66, 1454, 66, 463],
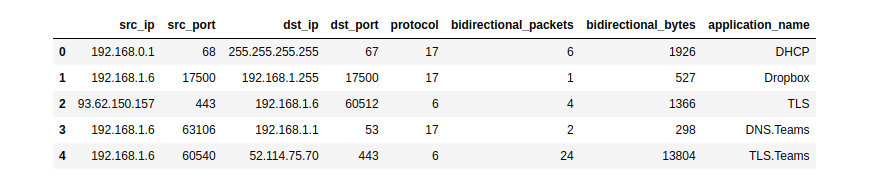
splt_piat_ms=[0, 303, 0, 0, 313, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1])NFStream natively supports Pandas as export interface.
# See documentation for more details.
# https://www.nfstream.org/docs/api#pandas-dataframe-conversion
from nfstream import NFStreamer
my_dataframe = NFStreamer(source='teams.pcap').to_pandas()[["src_ip",
"src_port",
"dst_ip",
"dst_port",
"protocol",
"bidirectional_packets",
"bidirectional_bytes",
"application_name"]]
my_dataframe.head(5)NFStream natively supports CSV file format as export interface.
# See documentation for more details.
# https://www.nfstream.org/docs/api#csv-file-conversion
flows_count = NFStreamer(source='facebook.pcap').to_csv(path=None,
flows_per_file=0,
columns_to_anonymize=[])Didn't find a specific flow feature? add a plugin to NFStream in few lines:
from nfstream import NFPlugin
class MyCustomFeature(NFPlugin):
def on_init(self, packet, flow):
# flow creation with the first packet
if packet.raw_size == self.custom_size:
flow.udps.packet_with_custom_size = 1
else:
flow.udps.packet_with_custom_size = 0
def on_update(self, packet, flow):
# flow update with each packet belonging to the flow
if packet.raw_size == self.custom_size:
flow.udps.packet_with_custom_size += 1
extended_streamer = NFStreamer(source='facebook.pcap',
udps=MyCustomFeature(custom_size=555))
for flow in extended_streamer:
# see your dynamically created metric in generated flows
print(flow.udps.packet_with_custom_size) In the following example, we demonstrate a simplistic machine learning approach training and deployment. We suppose that we want to run a classification of Social Network category flows based on bidirectional_packets and bidirectional_bytes as features. For the sake of brevity, we decide to predict only at flow expiration stage.
from nfstream import NFPlugin, NFStreamer
import numpy
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
df = NFStreamer(source="training_traffic.pcap").to_pandas()
X = df[["bidirectional_packets", "bidirectional_bytes"]]
y = df["application_category_name"].apply(lambda x: 1 if 'SocialNetwork' in x else 0)
model = RandomForestClassifier()
model.fit(X, y)class ModelPrediction(NFPlugin):
def on_init(self, packet, flow):
flow.udps.model_prediction = 0
def on_expire(self, flow):
# You can do the same in on_update entrypoint and force expiration with custom id.
to_predict = numpy.array([flow.bidirectional_packets,
flow.bidirectional_bytes]).reshape((1,-1))
flow.udps.model_prediction = self.my_model.predict(to_predict)
ml_streamer = NFStreamer(source="eth0", udps=ModelPrediction(my_model=model))
for flow in ml_streamer:
print(flow.udps.model_prediction)More NFPlugin examples and details are provided on the official documentation. You can also test NFStream without installation using our live demo notebook.
If you want to build NFStream from sources. Please read the installation guide.
Please read Contributing for details on our code of conduct, and the process for submitting pull requests to us.
NFStream is intended for network data research and forensics. Researchers and network data scientists can use these framework to build reliable datasets, train and evaluate network applied machine learning models. As with any packet monitoring tool, NFStream could potentially be misused. Do not run it on any network of which you are not the owner or the administrator.
The following people contributed to NFStream:
- Zied Aouini: Creator and main developer.
- Adrian Pekar: Testing, datasets generation and storage.
- Romain Picard: Several Plugins implementation.
- Radion Bikmukhamedov: Initial work on SPLT analysis NFPlugin.
The following organizations are supporting NFStream:
- SoftAtHome: Main supporter of NFStream development.
- Technical University of Košice: Hardware and infrastructure for datasets generation and storage.
- ntop: Technical support of nDPI integration.
This project is licensed under the LGPLv3 License - see the License file for details