In this project, I use docker-compose to create services within same network and the services can communicate with each others internally.
I use monorepo in this project as all services are the module in a single repository for easier management and easier code tracing in IDE.
I use Makefile to handle the tasks of building project and dockerization.
1. make build
2. make dockerize
3. make run-docker
What you will be expected after running the commands above:
3 services will be up including pizza-api, order-service and MySQL database.
if you want to stop docker services, you can run make stop-docker.
For testing the API, I recommend to use Postman to send the POST call to this endpoint http://localhost/pizza
pizza-api acts as a gateway for user to call the api in frontend, after the traffic coming to our app, pizza-api will then forward it to order-service. After that, order-service creates pizza order and save it to MySQL.
HTTPS: To secure our endpoint and traffic, HTTPS must be applied to encrypt user traffic and data. In this project, for demo purpose, I just use HTTP, but in production environment, we must use HTTPS.
Encryption: In real use case, when ordering pizza, the payment process will be involved in our system, we need to deal with the payment data carefully, if the data is sensitive, we must do Encryption on such data or Don't store it if we don't need such data.
In this project, only pizza-api is exposed to the public, other services are not exposed due to security reason. The services can only communicate internally or through pizz-api. That means, we can control our public traffic in pizza-api or before pizza-api such as load balancer.
In this project, I hardcoded the credentials in YAML file, but we should use more secure approach to manage the credentials in production environment such as Git-Secret or Vault to encrypt the credentials.
Since the api doesn't have much business logic, so I haven't implemented Unit Test or Integration Test in this project. To ensure the correctness and reliability of the system, we need to implement test cases in actual environment. Especially, unit test is quite important in a project as it can ensure the correctness of business logic, and we can implement integration test to ensure the correctness of data flow and behaviour that all components composed together. After that, we can do Regression Test to re-run/re-test the functions to ensure that the software is still working after changes.
After the functional test, we can do Load Test to test the maximum working load limit of our system because we need to aware that where is the bottleneck of the system and how much traffic the system can serve.
In this simple example project, we don't have much data to log, but we must do logging in real system. Before implement logging, we need to study what kind of information that can help us to debug or we need to know. In general, we can classify the log to different level such
as Info, Debug, Warn, and Error. Also, for the type of log, we can have Action Log to log all the api actions such as request time, endpoint, user info, user device and, etc.. Other than that, we can have our Business Log, this kind of log is used to log the error or warning of the business
logic maybe user input a wrong format of data. Furthermore, we also need to monitor Infrastructure Log, if we implement K8S in the future we can monitor the K8S status by grabbing the log from K8S and also monitor the system resources and performance.
This design can be further improved by scaling the instances horizontally when there is high traffic coming to our system. As the image presented, we can scale our microservices to serve user traffic.
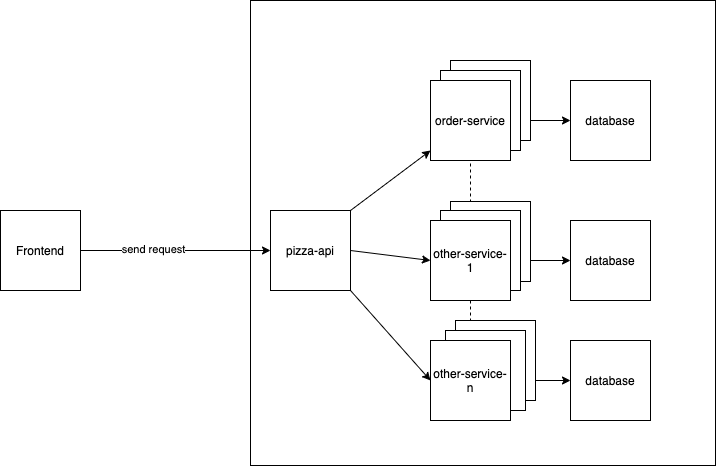
To achieve this, we can utilize Kubernetes to help us manage our containers and resources.
Kubernetes can provide our system scalability and monitor our resources.
If the bottleneck is database, we can do master-salve replication on database to increase the database performance. After we applied master-slave strategy, we can separate the read/write traffics and let the traffic distribute to different database instances. The date will be written to master and sync to slaves and read request will go to slaves. It provides more availability characteristic to the system but we trade off the data consistency because when data synchronize to slaves, there is possible to have latency.
If there is lot of data in the database and the query become slow, we can do sharding on database like separating the order by month:
pizza-order-2021-09
pizza-order-2021-10
pizza-order-2021-11
...
etc.
after that, we can distribute our data horizontally and the query speed will be improved as we don't store numerous data inside one table.
But definitely, the architecture complexity will be increased if we do sharding on database, because we need to write our own hashing function to route the traffic to different table or different database.
We can adopt Kafka as message stream middleware to process the data asynchronously and use Server-sent Events technique to stream the data to client side for real time order tracking. For example, when the order is created,it may go through few statuses when the pizza joint process the order (
e.g CREATED, PROCESSING, DELIVERING, DELIVERED etc.). We can utilize the said techniques to monitor the status and push the latest status to users for order tracking.
On Pizza Joint side, we also can utilize this technique to let the pizza joint staffs know the latest orders in real-time. When the order is created in backend, it pushes to staff portal to notify the staffs immediately.
