Simple chat application by bluetooth socket in jetpack compose and MVI Architecture, Which is not finished yet since it has some small issues
If you like or are using this project to learn or start your solution, please give it a star. Thanks!
| Main Screen | Chat Screen |
|---|---|
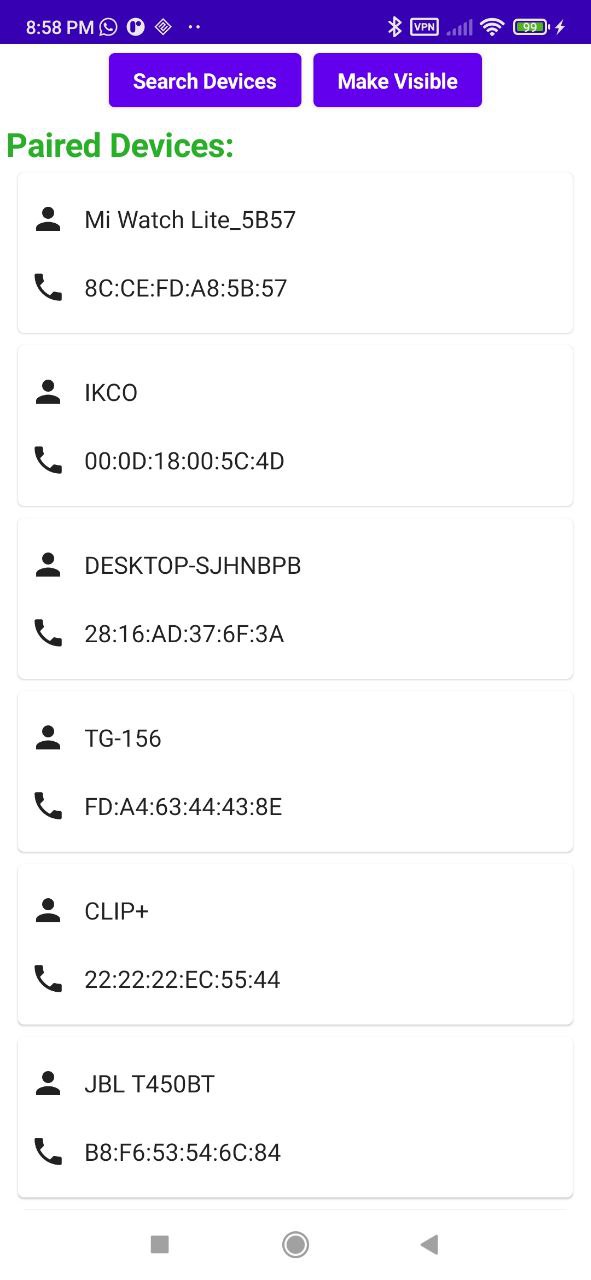 |
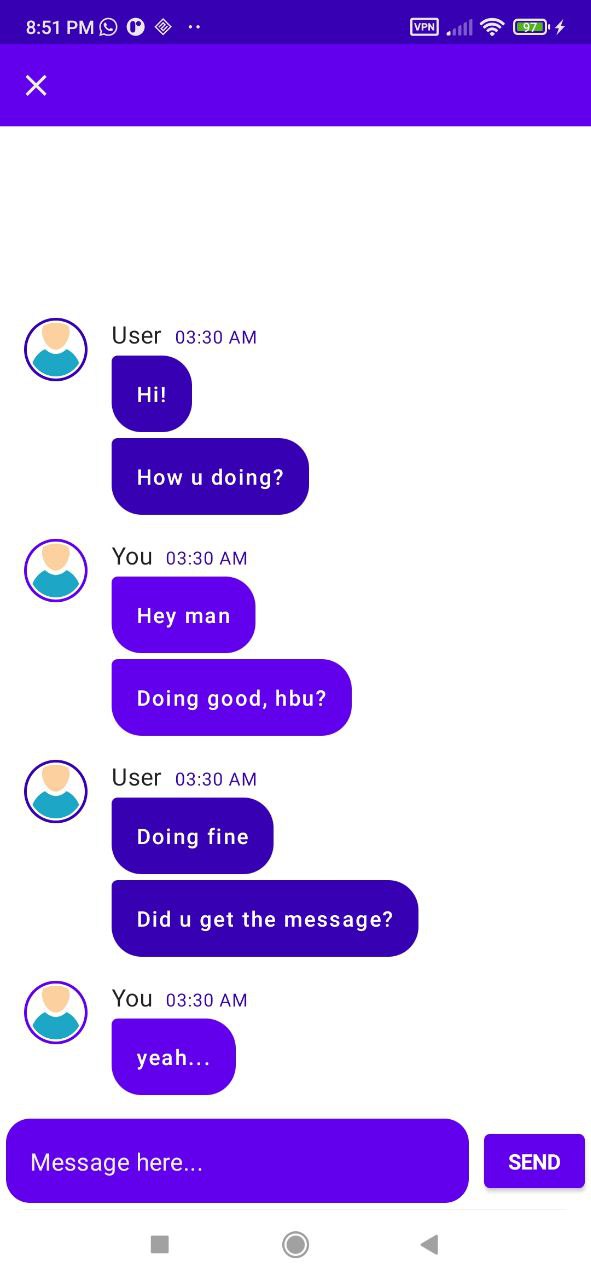 |
Represents the local device Bluetooth adapter.
The BluetoothAdapter lets you perform fundamental Bluetooth tasks, such as initiate device discovery, query a list of bonded (paired) devices, instantiate a BluetoothDevice using a known MAC address, and create a BluetoothServerSocket to listen for connection requests from other devices, and start a scan for Bluetooth LE devices.
- To get a BluetoothAdapter representing the local Bluetooth adapter, call the BluetoothManager#getAdapter function on BluetoothManager.
On JELLY_BEAN_MR1 and below you will need to use the static getDefaultAdapter() method instead.
Fundamentally, this is your starting point for all Bluetooth actions.
- Once you have the local adapter, you can get a set of BluetoothDevice objects representing all paired devices with getBondedDevices(); start device discovery with startDiscovery(); or create a BluetoothServerSocket to listen for incoming RFComm connection requests with listenUsingRfcommWithServiceRecord(java.lang.String, java.util.UUID); listen for incoming L2CAP Connection-oriented Channels (CoC) connection requests with listenUsingL2capChannel(); or start a scan for Bluetooth LE devices with startLeScan(android.bluetooth.BluetoothAdapter.LeScanCallback).
This class is thread safe.
A connected or connecting Bluetooth socket.
-
The interface for Bluetooth Sockets is similar to that of TCP sockets: Socket and ServerSocket.
-
On the server side, use a BluetoothServerSocket to create a listening server socket.
-
When a connection is accepted by the BluetoothServerSocket, it will return a new BluetoothSocket to manage the connection.
-
On the client side, use a single BluetoothSocket to both initiate an outgoing connection and to manage the connection.
-
The most common type of Bluetooth socket is RFCOMM, which is the type supported by the Android APIs.
-
RFCOMM is a connection-oriented, streaming transport over Bluetooth. It is also known as the Serial Port Profile (SPP).
-
To create a BluetoothSocket for connecting to a known device, use BluetoothDevice.createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord().
-
Then call connect() to attempt a connection to the remote device.
-
This call will block until a connection is established or the connection fails.
-
To create a BluetoothSocket as a server (or "host"), see the BluetoothServerSocket documentation.
-
Once the socket is connected, whether initiated as a client or accepted as a server, open the IO streams by calling getInputStream() and getOutputStream() in order to retrieve InputStream and OutputStream objects, respectively, which are automatically connected to the socket.
BluetoothSocket is thread safe.
- In particular, close() will always immediately abort ongoing operations and close the socket.
A listening Bluetooth socket.
-
The interface for Bluetooth Sockets is similar to that of TCP sockets: Socket and ServerSocket.
-
On the server side, use a BluetoothServerSocket to create a listening server socket.
-
When a connection is accepted by the BluetoothServerSocket, it will return a new BluetoothSocket to manage the connection. On the client side, use a single BluetoothSocket to both initiate an outgoing connection and to manage the connection.
-
For Bluetooth BR/EDR, the most common type of socket is RFCOMM, which is the type supported by the Android APIs. RFCOMM is a connection-oriented, streaming transport over Bluetooth BR/EDR.
-
It is also known as the Serial Port Profile (SPP).
-
To create a listening BluetoothServerSocket that's ready for incoming Bluetooth BR/EDR connections, use BluetoothAdapter.listenUsingRfcommWithServiceRecord().
-
For Bluetooth LE, the socket uses LE Connection-oriented Channel (CoC).
-
LE CoC is a connection-oriented, streaming transport over Bluetooth LE and has a credit-based flow control.
-
Correspondingly, use BluetoothAdapter.listenUsingL2capChannel() to create a listening BluetoothServerSocket that's ready for incoming Bluetooth LE CoC connections. For LE CoC, you can use getPsm() to get the protocol/service multiplexer (PSM) value that the peer needs to use to connect to your socket. After the listening BluetoothServerSocket is created, call accept() to listen for incoming connection requests.
-
This call will block until a connection is established, at which point, it will return a BluetoothSocket to manage the connection. Once the BluetoothSocket is acquired, it's a good idea to call close() on the BluetoothServerSocket when it's no longer needed for accepting connections.
-
Closing the BluetoothServerSocket will not close the returned BluetoothSocket.
BluetoothServerSocket is thread safe.
- In particular, close() will always immediately abort ongoing operations and close the server socket.