Make change directory easy and save your time.
Table of Content
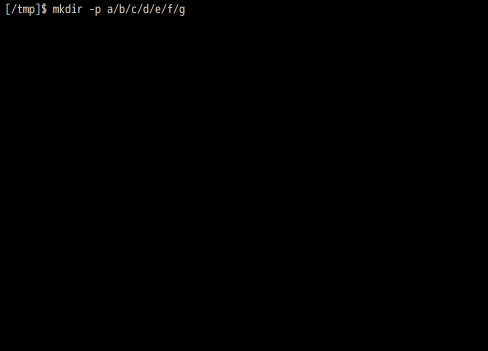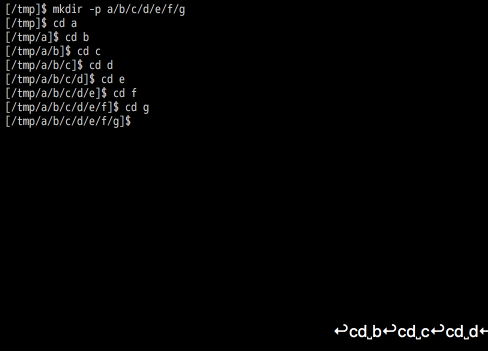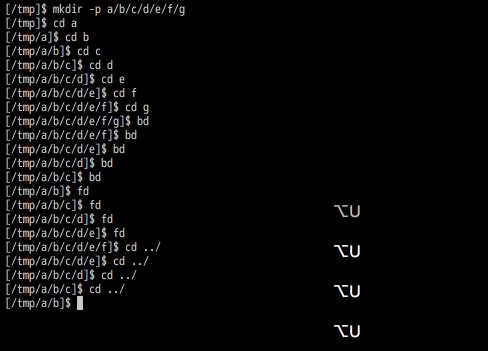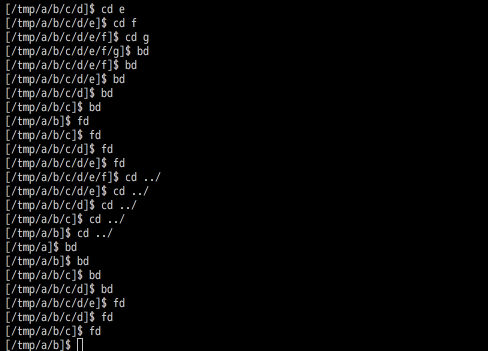
bd/fd commands
Use keybindings at Bash
Note: Gif shows keys of Opt in Mac, but it is same as Cmd/Alt (iTerm's setting).
Use keybindings at Zsh
Note: Gif shows keys of Opt in Mac, but it is same as Cmd/Alt (iTerm's setting).
You can get sd_cl by following methods.
You can use an install script on the web like:
$ curl -fsSL https://raw.github.com/rcmdnk/sd_cl/install/install.sh| sh
This will install scripts to /usr/etc
and you may be asked root password.
If you want to install other directory, do like:
$ curl -fsSL https://raw.github.com/rcmdnk/sd_cl/install/install.sh| prefix=~/usr/local/ sh
On Mac, you can install scripts by Homebrew:
$ brew install rcmdnk/rcmdnkpac/sd_cl
If you have brew file, add following lines to Brewfile:
tap 'rcmdnk/rcmdnkpac'
brew 'sd_cl'
then, do:
$ brew file install
Or if you write like:
tapall 'rcmdnk/rcmdnkpac'
and do brew file install, you will have all useful scripts in
rcmdnkpac.
This installs sd_cl to ${HOMEBREW_PREFIX}/etc (default: /usr/local/etc/).
Or, simply download scripts and set where you like.
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rcmdnk/sd_cl/master/etc/sd_cl
or you can get it from GitHub directly.
Get sd_cl and set to where you like,
then, source it in your .bashrc or .zshrc like
source /path/to/sd_clCommands to manage stored directories.
sd w/o arguments saves current directory to the last directory (default) list.
Usage: sd [-ecpwrCLh] [directory]
If neither '-e' nor '-C' is specified, 'directory' (or current directory if 'directory' is not given)
is stored in the list.
Arguments:
-e Edit directory list file
-C Clear directories
-H Use the directory history file (~/.config/sd_cl/history)
-c Use the last directory file (~/.config/sd_cl/lastdir)
-p Use the pre-defiend dirctory file (~/.config/sd_cl/predef)
-L Print license and quit
-h Print this HELP and quit
Commands to change the directory to the stored one.
cl w/o arguments change the directory to the last saved directory.
Usage: cl [-lecCpwrbvLh] [-n <number> ] [<number>] [<directory>]
If there are no arguments, you will move to the last saved directory by sd command.
If you give any directory name, it searches for it in saved directories
and cd to there if only one is found.
If more than one directories are found, go to the selection mode.
Arguments:
-l Show saved directories
-e Edit directory list file
-c Show saved directories and choose a directory
-C Clear directories
<number> Move to <number>-th last directory
-n <number> Move to <number>-th last directory
-H Move to the directory in history (~/.config/sd_cl/history)
-p Move to pre-defiend dirctory in ~/.config/sd_cl/predef
-w Move to other window's (screen/tmux) dirctory in ~/.config/sd_cl/window
-r Move to ranking directory in ~/.config/sd_cl/ranking
-b Move back in moving histories
-f Move forward in moving histories
-v Move from current directory, like Vim
-s <tool> Set selection tool (multi tools can be set by comma separated array, default=sentaku,peco,percol,fzf,fzy,selecta,gof,picka)
-L Print license and quit
-h Print this HELP and quit
-l, -c, -C and -n (<number>) are used exclusively.
-p (pre-defined directory list), -w (window directory list),
-r (ranking directory), -b (back in moving history), -f (forward in moving history), or -v (vim mode)
change the list file.
e.x.) cl -p 3 moves to the 3rd directory stored in pre-defined directory list.
sd_cl will load new functions:
sd(Save Directory)cl(Change to the Last directory)
sd saves current directory to the directory history list.
If you give a directory name, it saves the given directory.
cl is used to change the directory to saved directories.
If it is called w/o arguments, you will move to the last saved directory by sd.
By the default, 20 directories are kept as a history.
You can choose from the history by using
$ cl -c
This command invokes a selection tool defined by SD_CL_TOOL,
one of installed selection tools or shell interactive selection.
(See below for more details.)
If you give -p, -w, -r, -b, -f or -v instead of -c,
then each list is used for the selection instead of the last directory list.
(see Directory lists.)
If you give a part of the directory name like:
$ cl foo
then it starts a selection mode with directories including foo.
If it is only 1, it directly changes a directory to there.
Tab completion is available for both Bash and Zsh.
$ cl [Tab] # Completion with saved directory list.
$ cl foo [Tab] # Completion with directory names including 'foo'.
If you give a part of directory name to cl,
you will just move to the directory like normal cd.
After tab completion, if there are still some candidates,
cl starts the selection mode.
If you give a number, N, to cl,
you will jump into N-th direcoty on the list.
$ cl 3
This is default list.
The list is stored in SD_CL_LASTDIR_FILE.
sd w/o any arguments stores current directory to this list.
cl calls this list by default.
The number of directories stored in the list is defined by SD_CL_N.
If you use -H for sd or cl, it uses directory history,
stored in SD_CL_HISTORY_FILE.
It is updated every cd.
Set SD_CL_HISTORY=0 to disable to update the history.
Set SD_CL_HISTORY_EXCLUDE=/a/b/c,/d/e/f to exclude directories from hte list.
The default value is $HOME.
Set SD_CL_HISTORY_MAX to set max number of directories in the history.
The default is 1000.
If you use -p for sd or cl, it uses pre-defined directory list,
stored in SD_CL_PREDEF_FILE.
This list is similar to the last directory list
but you can store some dedicated directories which should not be modified by sd.
You can edit the pre-defined list by sd -e -p.
If you are working in GNU screen or tmux, each window's directory is saved automatically.
The list is stored in SD_CL_WINDOW_FILE.
You can call this list by cl -w.
By using cl -w -l, you can see the list with
window_number and pane_number (always 0 for GNU screen).
If you want to see these numbers even in the selection mode,
set SD_CL_SHOW_MORE_INFO=1
sd_cl makes a directory ranking by your usage of directories.
The list is stored in SD_CL_RANKING_FILE.
The list can be called by cl -r.
cl -r -l shows the ranking point, too.
As same as window directory list,
if SD_CL_SHOW_MORE_INFO=1, then the ranking point is shown in the selection mode, too.
The default ranking method (SD_CL_RANKING_METHOD=2) depends on how much you execute command in the directory.
After any commands, the ranking point is added to the current directory.
If you set SD_CL_RANKING_METHOD=1,
the point is added only when cd is executed.
If you don't want to make the ranking list, set SD_CL_RANKING_METHOD=0.
To exclude directories from the ranking,
set SD_CL_RANKING_EXCLUDE.
It can be comma separated list if you want to more than one directories, like:
SD_CL_RANKING_EXCLUDE=/tmp,~/tmp,/home/user/Desktop
The default value is SD_CL_RANKING_EXCLUDE=$HOME.
The ranking behavior can be changed by
SD_CL_RANKING_N_CD (default: 100) or SD_CL_RANKING_N_CMD (default: 1000)
for SD_CL_RANKING_METHOD=1 case or SD_CL_RANKING_METHOD=2 case, respectively.
The smaller the value is set, the more the ranking is changable.
With cl -b/cl -f, you can go back/foward the directories in your cd history.
Option -v will give you the continuous selection mode to change the directory,
like vim file explorer.
For the selection mode, you can use your favorite selection tool.
The selection tool must accept pipe line input list, be able to select a line, and return the line.
Following tools are searched for and one of which is used if exists.
- rcmdnk/sentaku: Utility to make sentaku (selection, 選択(sentaku)) window with shell command. (use
sentaku -s lineoption) - peco/peco: Simplistic interactive filtering tool
- mooz/percol: adds flavor of interactive filtering to the traditional pipe concept of UNIX shell
- junegunn/fzf: A command-line fuzzy finder
- jhawthorn/fzy: A better fuzzy finder
- garybernhardt/selecta: A fuzzy text selector for files and anything else you need to select. Use it from vim, from the command line, or anywhere you can run a shell command.
- mattn/gof
- mptre/pick: A fuzzy search tool for the command-line
You can decide a selection tool as you like by setting SD_CL_TOOL, like
SD_CL_TOOL=sentaku,peco,percol,fzf,fzy,selecta,gof,picka
in your .bashrc or .zshrc.
One or more tools can be set by comma separated array.
If any of tools is not available, simple shell selection tool is launched.
If you want to use simple shell selection as top priority, set SD_CL_TOOL=NONE or SD_CL_TOOL=shell (or SD_CL_TOOL="").
- bd (back Directory): Wrap function for
cl -b. - fd (Forward Directory): Wrap function for
cl -f. - up : Move up one directory.
- cdpwd : works as
cd -P .orcd $(pwd -P), i.e. resolves symbolic links of the current path. - cdlink : works as
cd -P <path>, i.e. resolves symbolic links in . - cd :
cdis wrapped to manage history, ranking, etc...
If you don't want to wrap cd, set SD_CL_ISCDWRAP=0.
For Bash/Zsh, Meta(Alt)-o and Meta(Alt)-i
are bounden to bd and fd, respectively.
In addition, Meta(Alt)-u is bounden to up (move up one directory).
set SD_CL_BIND=0 to disable these binds.
If you want to assign different keys, set SD_CL_BIND=0.
Then, for Zsh, add bindings in .zshrc something like:
SD_CL_ZSH_BIND=0
source /path/to/sd_cl
bindkey '^[a' bd
bindkey '^[b' fd
bindkey '^[c' up
For Bash, add bindings in .bashrc something like:
SD_CL_ZSH_BIND=0
source /path/to/sd_cl
bind '"\ea": "\C-ubd\C-m"'
bind '"\eb": "\C-ufd\C-m"'
bind '"\ec": "\C-uup\C-m"'
Following options can be set before sourcing sd_cl in .bashrc or .zshrc.
# Selection tool
SD_CL_TOOL=${SD_CL_TOOL:-sentaku,peco,percol,fzf,fzy,selecta,gof,picka}
# Number of kept last directories
SD_CL_N=${SD_CL_N:-20}
# Show window/pane or ranking information at selection
SD_CL_SHOW_MORE_INFO=${SD_CL_SHOW_MORE_INFO:-0}
# Directory store file
SD_CL_CONFIG_DIR=${SD_CL_CONFIG_DIR:-$HOME/.config/sd_cl}
SD_CL_LASTDIR_FILE=${SD_CL_LASTDIR_FILE:-${SD_CL_CONFIG_DIR}/lastdir}
SD_CL_PREDEF_FILE=${SD_CL_PREDEF_FILE:-${SD_CL_CONFIG_DIR}/predef}
SD_CL_WINDOW_FILE=${SD_CL_WINDOW_FILE:-${SD_CL_CONFIG_DIR}/window}
SD_CL_RANKING_FILE=${SD_CL_RANKING_FILE:-${SD_CL_CONFIG_DIR}/ranking}
# Ranking method
SD_CL_RANKING_METHOD=${SD_CL_RANKING_METHOD:-2}
SD_CL_RANKING_TRIAL_FILE=${SD_CL_RANKING_TRIAL_FILE:-${SD_CL_CONFIG_DIR}/ranking_trial}
SD_CL_RANKING_N_CD=${SD_CL_RANKING_N_CD:-100}
SD_CL_RANKING_N_CMD=${SD_CL_RANKING_N_CMD:-1000}
SD_CL_RANKING_EXCLUDE=${SD_CL_RANKING_EXCLUDE:-"$HOME"}
# post cd (overwrite cd (Bash) or chpwd (Zsh))
SD_CL_ISPOSTCD=${SD_CL_ISPOSTCD:-1}
# COMPLETION
SD_CL_NOCOMPLETION=${SD_CL_NOCOMPLETION:-0}
SD_CL_NOCOMPINIT=${SD_CL_NOCOMPINIT:-0}
# keybind
SD_CL_KEYBIND=1
# cd wrap to pushd/popd
SD_CL_ISCDWRAP=${SD_CL_ISCDWRAP:-1}
You can decide a selection tool as you like by setting SD_CL_TOOL, like
SD_CL_TOOL=sentaku,peco,percol,fzf,fzy,selecta,gof,picka
One or more tools can be set by comma separated array.
If any of tools is not available, simple shell selection tool is launched.
If you want to use simple shell selection as top priority, set SD_CL_TOOL=NONE or SD_CL_TOOL=shell (or SD_CL_TOOL="").
SD_CL_N defines how many directories are kept in the last directory file.
At selection mode, only directory names are shown by default.
If SD_CL_SHOW_MORE_INFO=1, additional information of window/pane (for window list)
or ranking information are shown.
Such information are always shown in the list command (-l).
SD_CL_CONFIG_DIR is the directory for the configuration files.
Next four file names are file names for the last directories (default),
predefined directories, window directories, and ranking directories, respectively.
SD_CL_RANKING_METHOD sets the method to make a ranking list.
- 0: Do not make a ranking list.
- 1: Add a directory when cd is executed.
- 2: Add a directory at any commands.
SD_CL_RANKING_N_CD and SD_CL_RANKING_N_CMD are parameters of the ranking
for SD_CL_RANKING_METHOD is 1 and 2 cases, respectively.
If you set the parameter smaller, the ranking becomes more changeable.
If you want to exclude some directories from the ranking,
set SD_CL_RANKING_EXCLUDE.
Default value is $HOME. If you want to exclude several directories,
give comma separated directories like:
SD_CL_RANKING_EXCLUDE=/tmp,~/tmp,/home/user/Desktop
If you set SD_CL_ISPOSTCD to 0, it doesn't save window's directory
in GNU screen or tmux.
If you set SD_CL_NOCOMPLETION to 1, completion will be disabled.
For Zsh user, if you already initialized completions with compinit,
please set SD_CL_NOCOMPINIT=1.
Otherwise sd_cl execute:
autoload -Uz compinit
compinit
If you don't want to bind keys to bd/fd/up,
set SD_CL_KEYBIND=0.
If you don't want to wrap cd with pushd, set SD_CL_ISCDWRAP to 0.
If you already have wrapper function for cd or the setting for chpwd at Zsh,
you should be better to set:
SD_CL_ISPOSTCD=0 # Don't do automatic save
SD_CL_ISCDWRAP=0 # Don't wrap cd
Otherwise sd_cl overwrites these functions.
If you want to have automatic save in GNU screen/tmux with your cd/chpwd,
first, set above SD_CL_ISPOSTCD and SD_CL_ISCDWRAP as 0 to disable to wrap in sd_cl,
then call _sd_cl_post_cd in your cd function for Bash like:
builtin cd "$@"
local ret=$?
if [ $ret -eq 0 ];then
_sd_cl_post_cd
fi
return $ret
or simply call post_cd in chpwd for Zsh case.
If you want to enable pushd wrap in your cd function,
replace your builtin(command) cd command with
_wrap_cd "$@"
i.e., if you want to enable both in Bash, you should replace above builtin cd "$@"
with _wrap_cd "$@".
pushd/popd/dirs
Builtin commands of the shell.
pushd <dir> stores current directory and then move to given one.
popd takes out the directory from the list and move to there.
dirs shows the list.
Their functions are very useful and they are always available.
But they are not used so much because (I think) p u s h d are too many to put
as frequent commands like cd.
A lot of attempts to make wrapper functions for these commands can be found.
The simplest one is something like:
alias cd="pushd"
alias bd="popd"chdhist.sh wraps cd to store a directory history.
It loads following commands, too:
$ - # Move back
$ + # Move forward
$ = # Show the list
Command selection tool, autojump, written in Python.
To use it, users load a function j by sourcing /usr/local/etc/autojump.sh,
and j calls autojump to select a directory.
/usr/local/etc/autojump.sh also add autojump_add_to_database to
PROMPT_COMMAND.
autojump_add_to_database updates the directory history list after every command.
Each directory has key weight, which is defined by how much user spends in a directory.
Users can go the directory contains a word foo by
$ j foo
if it is in the list.
If there are more than one corresponding directories, the highest weight directory is chosen.
$ jc foo
searches for directories only under the current directory.
It also loads command jo which opens the directory by an explorer.
z is similar tool to autojump, but written in Shell Script.
So it is almost no dependency on external commands (though it uses such awk, grep).
Sourcing z.sh loads z command.
In addition, it adds _z --add... to PROMPT_COMMAND.
_z --add... updates the directory list with current directory,
and adds frecency(=frequency+recency), which is defined by how frequently and recently user works in there.
$ z foo
This select the directory contains foo.
If there are more than one corresponding directories, the highest frecency directory is chosen.
z has also some selection mode like z -r foo (most highest frequency) or z -t -foo (most highest recency).
cd wrap tool written in Shell Script.
By sourcing init.sh, cd will work as history register and directory searcher.
After every cd, it adds the current directly,
all directoies in the path to the current directory,
and child directories of the current directory.
enhancd doesn't add a weight.
$ source ./init.sh
Then,
$ cd foo
searches for a directory including foo from the list.
If there are more than one directories, it launches a selection mode. You need one of selection tools like fzy, fjf, peco, sentaku, etc...
enhanced wraps such cd .. and cd -, too,
to launches a selection mode for upper directories or past directories, respectively.