Official code for the paper On the Inclusion of Spatial Information for Spatio-Temporal Neural Networks
When confronting a spatio-temporal regression, it is sensible to feed the model with any available prior information about the spatial dimension. For example, it is common to define the architecture of neural networks based on spatial closeness, adjacency, or correlation. A common alternative, if spatial information is not available or is too costly to introduce it in the model, is to learn it as an extra step of the model. While the use of prior spatial knowledge, given or learnt, might be beneficial, in this work we question this principle by comparing spatial agnostic neural networks with state of the art models. Our results show that the typical inclusion of prior spatial information is not really needed in most cases. In order to validate this counterintuitive result, we perform thorough experiments over ten different datasets related to sustainable mobility and air quality, substantiating our conclusions on real world problems with direct implications for public health and economy.
- Python >= 3.6
- Pytorch >= 1.3.0
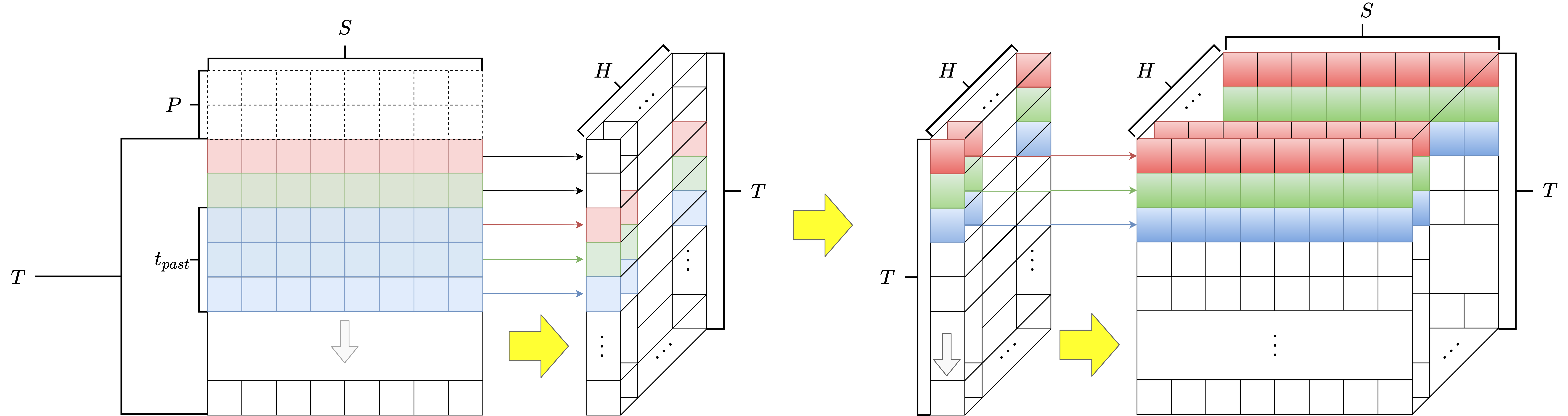
Data consist in a 3D tensor. In the csv file, rows for time dimension and columns for spatial points. During training, channels for number of features-series, height for time lags and width for spatial points.
In general, data presented in the experiments have been widely used in the literature. All datasets are publicly available. To exemplify data format, Acoustic Pollution dataset can be found in data folder.