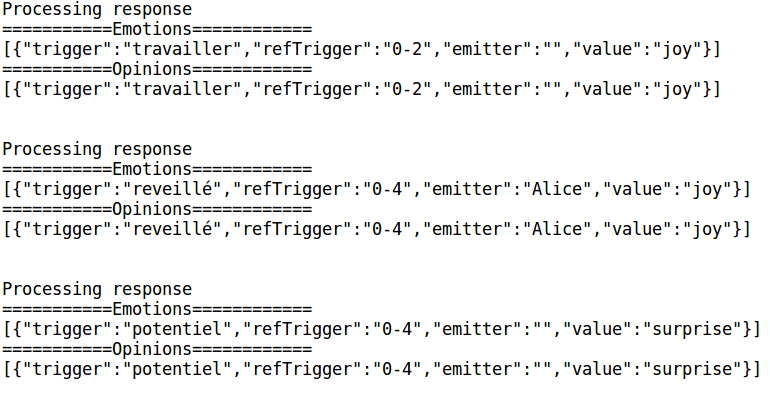
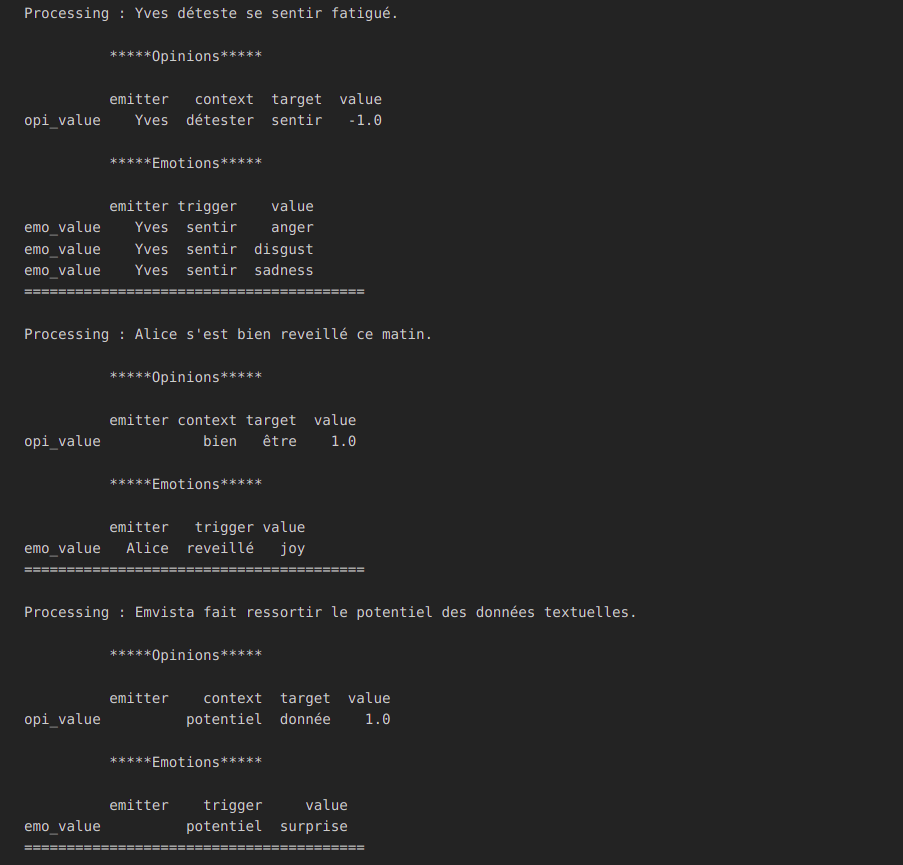
Cet exercice à pour but d'analyser des sentiments en utilisant le service Sentiments de Emvista, accessible à partir de l'API https://pss-api.prevyo.com/pss/api/v1/sentiments
Initialement prévu pour être réalisé en Java, nous avons ajouter un cas d'étude en Python pour illustrer notre test.
Développer un client Java qui se connecte à l’API REST d’Emvista (https://pss.emvista.com/) . En utilisant le service Sentiments envoyer 3 textes différents en parallèle. Pour chacune des réponses, afficher dans la console le résultat sous forme de tableaux : un tableau contenant la liste des opinions avec pour colonne : emitter, context, target, value un tableau contenant la liste des émotions avec pour colonne : emitter, trigger, value.
Prérequis :
- Créer un compte sur https://pss.emvista.com/ pour avoir un token.
- Utiliser la documentation : https://github.com/Emvista/
Rendu :
- Démonstration
- Code source sur un repo Github.
Le code source est disponible dans le dossier Emvista
* Ajouter les librairies externes dans le build Path du projet. Ces librairies sont disponibles dans Emvista/libimport java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.net.URISyntaxException;
import java.net.http.HttpClient;
import java.net.http.HttpRequest;
import java.net.http.HttpResponse;
import java.net.http.HttpResponse.BodyHandlers;
import java.util.HashMap;
import org.json.simple.JSONArray;
import org.json.simple.JSONObject;
import org.json.simple.JSONValue;
import org.json.simple.parser.JSONParser;
import org.json.simple.parser.ParseException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.type.TypeReference;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
public class Requete {
final static String url_string = "https://pss-api.prevyo.com/pss/api/v1/sentiments";
final static String token_string = "eyJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiJ9.eyJzdWIiOiJwc3MiLCJ1c2VyTG9naW4iOiJrYWZhbmRvLnJvZHJpcXVlQGdtYWlsLmNvbSIsInVzZXJJZCI6Mjg5LCJpdGEiOjE2NDEyOTE2NzE2MTgsInJvbGVzIjoiUk9MRV9VU0VSIn0.MmZJdRTWosv2m8R1poiEXWdoedjb7Wh9WkmM9tamDKgn-hYpDWNNQvkHCnv77vqn77QhSKukl8_A86DV1TvS_w";
public static HashMap<String, Object> askSentiments(String sentence) throws URISyntaxException, IOException, InterruptedException {
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(new URI(url_string))
.headers("Content-Type", "application/json")
.headers("accept", "application/json")
.headers("Poa-Token", token_string)
//.POST(HttpRequest.BodyPublishers.ofString(String.format("{ \"text\" : \"%s\",\"parameters\": [{\"name\": \"lang\", \"value\": \"fr\"}] }", sentence)))
.POST(HttpRequest.BodyPublishers.ofString(String.format("{ \"text\" : \"%s\",\"parameters\": [{\"name\": \"lang\", \"value\": \"fr\"}] }", sentence)))
.build();
HttpClient client = HttpClient.newHttpClient();
///System.out.println("Send request");
HttpResponse<String> response = client.send(request, BodyHandlers.ofString());
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
System.out.println("Processing response");
HashMap<String, Object> map = objectMapper.readValue(response.body(), new TypeReference<HashMap<String, Object>>(){});
return map;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static void printMap(HashMap<String, Object> map) throws ParseException {
//System.out.println(map);
//JSONObject jo = new JSONObject(map);
// for(String key : map.keySet()) {
// System.out.println(key + " : " + map.get(key));
// }
System.out.println("===========Emotions============");
//System.out.println(((HashMap<String, Object>)map.get("result")).get("emotions")+ "\n");
Gson gson = new Gson();
String emo = gson.toJson(((HashMap<String, Object>)map.get("result")).get("emotions"));
System.out.println(emo);
//System.out.println("\n");
//JSONParser parser = new JSONParser();
//Object obj = parser.parse(emo);
//JSONArray array = (JSONArray)obj;
//System.out.println(array);
System.out.println("===========Opinions============");
//System.out.println(((HashMap<String, Object>)map.get("result")).get("opinions").getClass().getName());
//System.out.println(((HashMap<String, Object>)map.get("result")).get("opinions"));
String opi = gson.toJson(((HashMap<String, Object>)map.get("result")).get("emotions"));
System.out.println(opi);
System.out.println("\n");
///JSONParser parser = new JSONParser();
//Object obj1 = parser.parse(opi);
//JSONArray array1 = (JSONArray)obj1;
//System.out.println(array1);
//ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<String>((int) ((HashMap<String, Object>)map.get("result")).get("opinions"));
//System.out.println(map.get("result")).get("opinions").getClass().getName());
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
String sentence1 = "J'aime travailler avec du code propre";
HashMap<String, Object> result1 = askSentiments(sentence1);
printMap(result1);
String sentence2 = "Alice s'est bien reveillé ce matin.";
HashMap<String, Object> result2 = askSentiments(sentence2);
printMap(result2);
String sentence3 = "Emvista fait ressortir le potentiel des données textuelles.";
HashMap<String, Object> result3 = askSentiments(sentence3);
printMap(result3);
//System.out.println(result2.getClass().getName());
/*
for (Entry<String, Object> string: result2.entrySet())
{
System.out.println("la clé est :" + string.getKey() + ", la valeur est : " + string.getValue());
}
*/
} catch (URISyntaxException | IOException | InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Le code source est disponible dans le fichier Emvista.ipynb.
* pip install requests
* pip install pandas POur tester, il faut appeler la fonction query_sentiments() qui prend :
- input_texts : le texte à analyser
- api_url : l'url de l'API
- token : le token généré
- language : la langue ('fr' pour le français)
t1 = "Yves déteste se sentir fatigué."
t2 = "Alice s'est bien reveillé ce matin."
t3 = "Emvista fait ressortir le potentiel des données textuelles."
input_texts = [t1,t2,t3]
input_texts = [t1,t2,t3]
api_url = 'https://pss-api.prevyo.com/pss/api/v1/sentiments'
token = "eyJhbGciOiJIUzUxMiJ9.eyJzdWIiOiJwc3MiLCJ1c2VyTG9naW4iOiJrYWZhbmRvLnJvZHJpcXVlQGdtYWlsLmNvbSIsInVzZXJJZCI6Mjg5LCJpdGEiOjE2NDEyOTE2NzE2MTgsInJvbGVzIjoiUk9MRV9VU0VSIn0.MmZJdRTWosv2m8R1poiEXWdoedjb7Wh9WkmM9tamDKgn-hYpDWNNQvkHCnv77vqn77QhSKukl8_A86DV1TvS_w"
language = 'fr'
results = query_sentiments(input_texts,api_url,token,language)