This is the official implementation provided with our paper beeFormer: Bridging the Gap Between Semantic and Interaction Similarity in Recommender Systems.
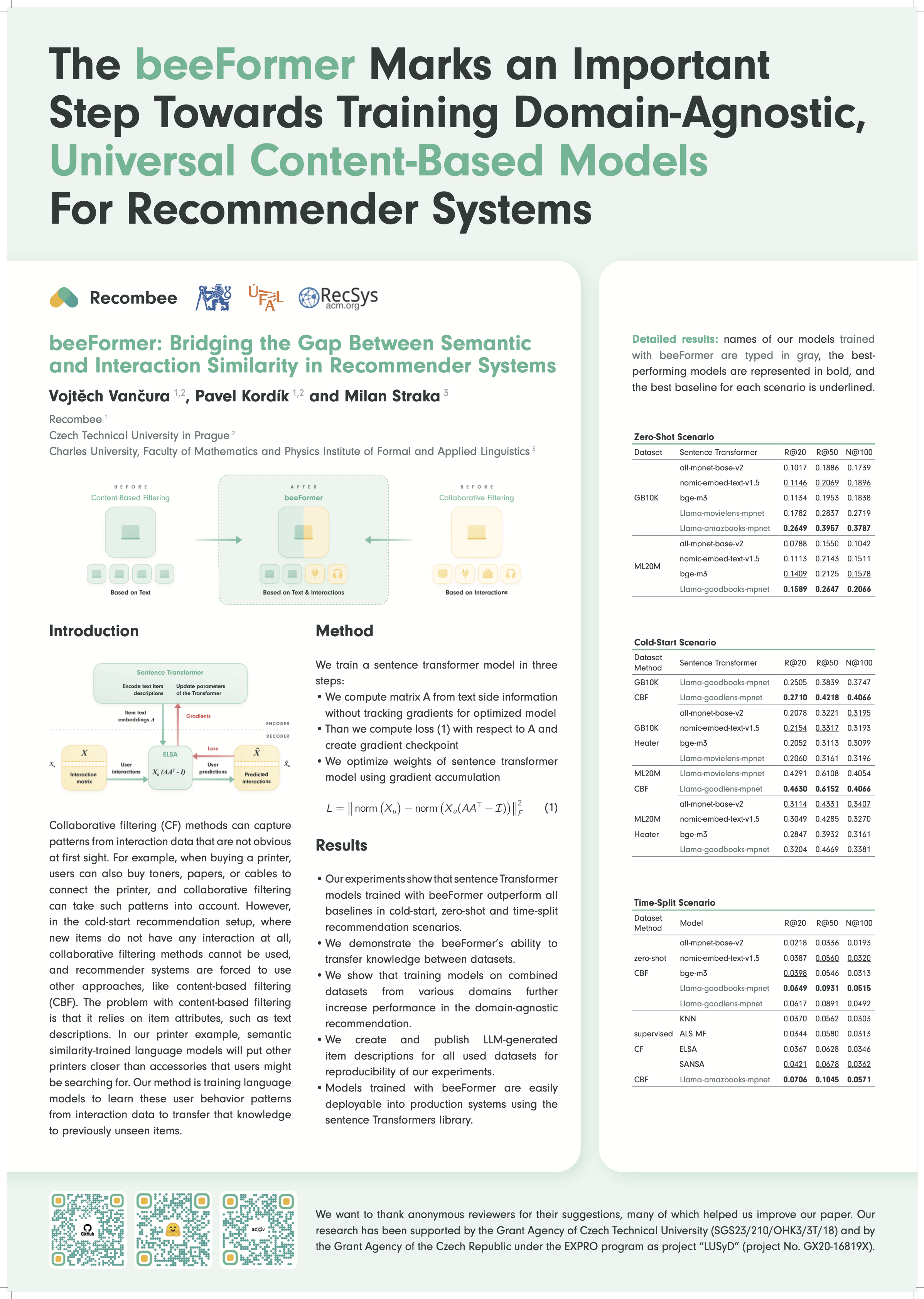
Collaborative filtering (CF) methods can capture patterns from interaction data that are not obvious at first sight. For example, when buying a printer, users can also buy toners, papers, or cables to connect the printer, and collaborative filtering can take such patterns into account. However, in the cold-start recommendation setup, where new items do not have any interaction at all, collaborative filtering methods cannot be used, and recommender systems are forced to use other approaches, like content-based filtering (CBF). The problem with content-based filtering is that it relies on item attributes, such as text descriptions. In our printer example, semantic similarity-trained language models will put other printers closer than accessories that users might be searching for. Our method is training language models to learn these user behavior patterns from interaction data to transfer that knowledge to previously unseen items. Our experiments show that performance benefits from this approach are enormous.
- create virtual environment
python3.10 -m venv beefand activate itsource beef/bin/activate - clone this repository and navigate to it
cd beeformer - install packages
pip install -r requirements.txt - download the data for movielens: navigate to the
_dataset/ml20mfolder and runsource download_data - download the data for goodbooks: navigate to the
_dataset/goodbooksfolder and runsource download_data - download the data for amazonbooks: navigate to the
_dataset/amazonbooksfolder and runsource download_data && python preprocess.py - in the root folder of the project run the
train.py, for example like this:
python train.py --seed 42 --scheduler None --lr 1e-5 --epochs 5 --dataset goodbooks --sbert "sentence-transformers/all-mpnet-base-v2" --max_seq_length 384 --batch_size 1024 --max_output 10000 --sbert_batch_size 200 --use_cold_start true --save_every_epoch true --model_name my_model- Evaluate the results. To reproduce numbers from the paper using our hugginface repository, run for example:
python evaluate_itemsplit.py --seed 42 --dataset goodbooks --sbert beeformer/Llama-goodbooks-mpnetor
python evaluate_timesplit.py --seed 42 --dataset amazon-books --sbert beeformer/Llama-amazbooks-mpnetWe consider ratings of 4.0 and higher as an interaction. We only keep the users with at least 5 interactions.
Since there are no text descriptions in the original data, we manually connect several datasets with the original data and train our models on it. However, this approach has several limitations: texts from different sources have different styles and different lengths, and this might influence the results. Therefore, we use the Llama-3.1-8b-instruct model to generate item descriptions for us. We use the following conversation template:
import pandas as pd
from tqdm import tqdm
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
items = pd.read_feather("items_with_gathered_side_info.feather")
llm = LLM(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct",dtype="float16")
tokenizer = llm.get_tokenizer()
conversation = [ tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
[
{'role': 'system','content':"You are ecomerce shop designer. Given a item description create one paragraph long summarization of the product."},
{'role': 'user', 'content': "Item description: "+x},
{'role': 'assistant', 'content': "Sure, here is your one paragraph summary of your product:"},
],
tokenize=False,
) for x in tqdm(items.gathered_features.to_list())]
output = llm.generate(
conversation,
SamplingParams(
temperature=0.1,
top_p=0.9,
max_tokens=512,
stop_token_ids=[tokenizer.eos_token_id, tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids("<|eot_id|>")],
)
)
items_descriptions = [o.outputs[0].text for o in output]However, LLM refused to generate descriptions for some items (For example, because it refuses to generate explicit content). We removed such items from the dataset. We also removed items for which we were not able to connect meaningful descriptions from other datasets, which led to LLM completely hallucinating item descriptions.
We share the resulting LLM-generated item descriptions in datasets/ml20m, dataset/goodbooks and datasets/amazonbooks folders.
| GoodBooks-10k | MovieLens-20M | Amazon Books | |
|---|---|---|---|
| # of items in X | 9975 | 16902 | 63305 |
| # of users in X | 53365 | 136589 | 634964 |
| # of interactions in X | 4119623 | 9694668 | 8290500 |
| density of X [%] | 0.7739 | 0.4199 | 0.0206 |
| density of X^TX [%] | 41.22 | 26.93 | 7.59 |
We share pretrained models at https://huggingface.co/beeformer.
We used hyperparameters for training our models as follows.
| hyperparameter | description | beeformer/Llama-goodbooks-mpnet | beeformer/Llama-movielens-mpnet | beeformer/Llama-goodlens-mpnet | beeformer/Llama-amazbooks-mpnet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| seed | random seed used during training | 42 | 42 | 42 | 42 |
| scheduler | learning rate scheduling strategy | constant learning rate | constant learning rate | constant learning rate | constant learning rate |
| lr | learning rate | 1e-5 | 1e-5 | 1e-5 | 1e-5 |
| epochs | number of trained epochs | 5 | 5 | 10 | 5 |
| devices | training script allow to train on multiple gpus in parallel - we used 4xV100 | [0,1,2,3] | [0,1,2,3] | [0,1,2,3] | [0,1,2,3] |
| dataset | dataset used for training | goodbooks | ml20m | goodlens | amazon-books |
| sbert | original sentence transformer model used as an initial model for training | sentence-transformers/all-mpnet-base-v2 | sentence-transformers/all-mpnet-base-v2 | sentence-transformers/all-mpnet-base-v2 | sentence-transformers/all-mpnet-base-v2 |
| max_seq_length | limitation of sequence length; shorter sequences trains faster original mpnet model uses max 512 tokens in. sequence | 384 | 384 | 384 | 384 |
| batch_size | number of users sampled in random batch from interaction matrix | 1024 | 1024 | 1024 | 1024 |
| max_output | negative sampling hyperparameter (m in the paper). Negatives are sampled uniformly at random. | 10000 | 10000 | 10000 | 12500 |
| sbert_batch_size | number of items processed together during training step (gradient accumulation step size) | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| use_cold_start | split the dataset item-wise (some items are hidden to test the genralization towards new items) | true | true | true | false |
| use_time_split | sort interactions by timestamp and use last 20% of interactions as a test set (generalization from the past to the future) | false | false | false | true |
If you find this repository helpful, feel free to cite our paper:
@inproceedings{10.1145/3640457.3691707,
author = {Van\v{c}ura, Vojt\v{e}ch and Kord\'{\i}k, Pavel and Straka, Milan},
title = {beeFormer: Bridging the Gap Between Semantic and Interaction Similarity in Recommender Systems},
year = {2024},
isbn = {9798400705052},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3640457.3691707},
doi = {10.1145/3640457.3691707},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 18th ACM Conference on Recommender Systems},
pages = {1102–1107},
numpages = {6},
keywords = {Cold-start recommendation, Recommender systems, Sentence embeddings, Text mining, Zero-shot recommendation},
location = {Bari, Italy},
series = {RecSys '24}
}