panda_sync is a Dart library designed to facilitate the development of offline-first applications
using Flutter. It provides seamless data synchronization between local storage and a remote server,
ensuring your app remains functional even without internet connectivity. The
- Offline-First Functionality: Automatically handles data synchronization when the device is online.
- Local Storage with Isar: Utilizes Isar, a high-performance NoSQL database, for local data storage.
- Network Request Management: Uses Dio for making network requests and managing connectivity states.
- Type Registration: Enforces type registration for data serialization and deserialization.
- Automatic Retry: Automatically retries failed network requests when the device regains connectivity.
- Customizable: Allows customization of request handling and data processing.
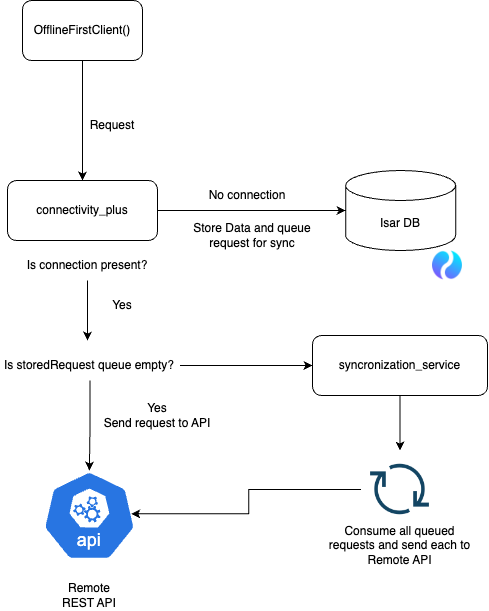
This repository implements an offline-first client for Flutter applications.
The OfflineFirstClient class leverages Dio for HTTP requests, Isar for local storage, and a custom
synchronization service to handle queued requests when the device is offline. Below is a diagram and
a step-by-step explanation of how it works:
-
Request Initialization: The process starts when the
OfflineFirstClientinitiates a request. -
Connectivity Check: The
connectivity_pluspackage checks whether an internet connection is available. -
No Connection:
- If there is no connection, the data is stored locally in the Isar database.
- The request is queued for synchronization once the connection is restored.
-
Connection Present:
- If a connection is present, the client checks if there are any stored requests in the queue.
-
Empty Queue:
- If the queue is empty, the request is sent directly to the remote REST API.
-
Non-empty Queue:
- If the queue is not empty, the
synchronization_serviceprocesses all queued requests. - Each queued request is sent to the remote REST API.
- If the queue is not empty, the
-
Remote REST API:
- The request reaches the remote REST API and gets processed.
- The response is handled by the
OfflineFirstClient, updating local storage as necessary.
- Dio: Used for making HTTP requests.
- Isar: A local database used for storing data when the device is offline.
- connectivity_plus: A package that provides network connectivity status.
- Synchronization Service: Handles queued requests and synchronizes them with the server once the connection is available.
By following this flow, the OfflineFirstClient ensures that your application remains functional
even when the network is unavailable, synchronizing data seamlessly once the connection is restored.
Add the following dependency to your pubspec.yaml file:
dependencies:
panda_sync: ^1.0.0 # Add the latest versionBefore using the library, initialize Isar core:
import 'package:panda_sync/panda_sync.dart';
void main() async {
await OfflineFirstLocalStorageInit.initialize();
runApp(MyApp());
}import 'package:panda_sync/panda_sync.dart';
import 'package:json_annotation/json_annotation.dart';
part 'task_model.g.dart';
//This example uses json_serializable but this is not mandatory
@JsonSerializable()
class Task extends Identifiable {
@override
int id;
...
factory Task.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) => _$TaskFromJson(json);
static Map<String, dynamic> taskToJson(Task task) => _$TaskToJson(task);
}
import 'package:panda_sync/panda_sync.dart';
import 'model/task_model.dart'; // Import your model
void main() async {
await OfflineFirstLocalStorageInit.initialize();
TypeRegistry.register<Task>('TaskBox', Task.taskToJson, Task.fromJson);
runApp(MyApp());
}
Use the registerTokenHandlers method to provide functions for obtaining and refreshing the token.
configureClient() {
final client = OfflineFirstClient();
client.registerTokenHandlers(
getTokenHandler: () async {
// Retrieve the token from secure storage or any other source
return 'your-access-token';
},
refreshTokenHandler: () async {
// Implement the logic to refresh the token
},
);
}If a request returns any 401 Unauthorized error, the library will call the provided refresh token handler, update the token, and retry the request.
Create an instance of OfflineFirstClient:
final OfflineFirstClient offlineFirstClient = OfflineFirstClient();Here's how to use the library in a service class:
getTasks() {
try {
Response<List<Task>> response = await offlineFirstClient.getList<Task>(
'http://10.0.2.2:8080/api/tasks');
return response.data!;
} catch (e) {
throw Exception('Failed to load tasks: $e');
}
}Please refer to the code documentation for extensive info on the methods
We welcome contributions! Please follow these steps to contribute:
1. Fork the repository.
2. Create a new branch (`git checkout -b my-feature-branch`).
3. Make your changes.
4. Commit your changes (`git commit -am 'Add new feature'`).
5. Push to the branch (git push origin my-feature-branch).
6. Create a Pull Request.
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
For any questions or suggestions, feel free to open an issue or contact any maintainer.