RedisAnt maintains your client-side cache end-to-end at the speed of light. It connects with your MongoDB database and automatically ingests the requested data in your local cache and keeps the cache fresh as a daisy.
RedisAnt makes it super easy to automate the maintenance of your local cache. You don't have to worry about the logic of adding or updating data. You just have to define the source of your data to your client, and the ants will take care of the rest.
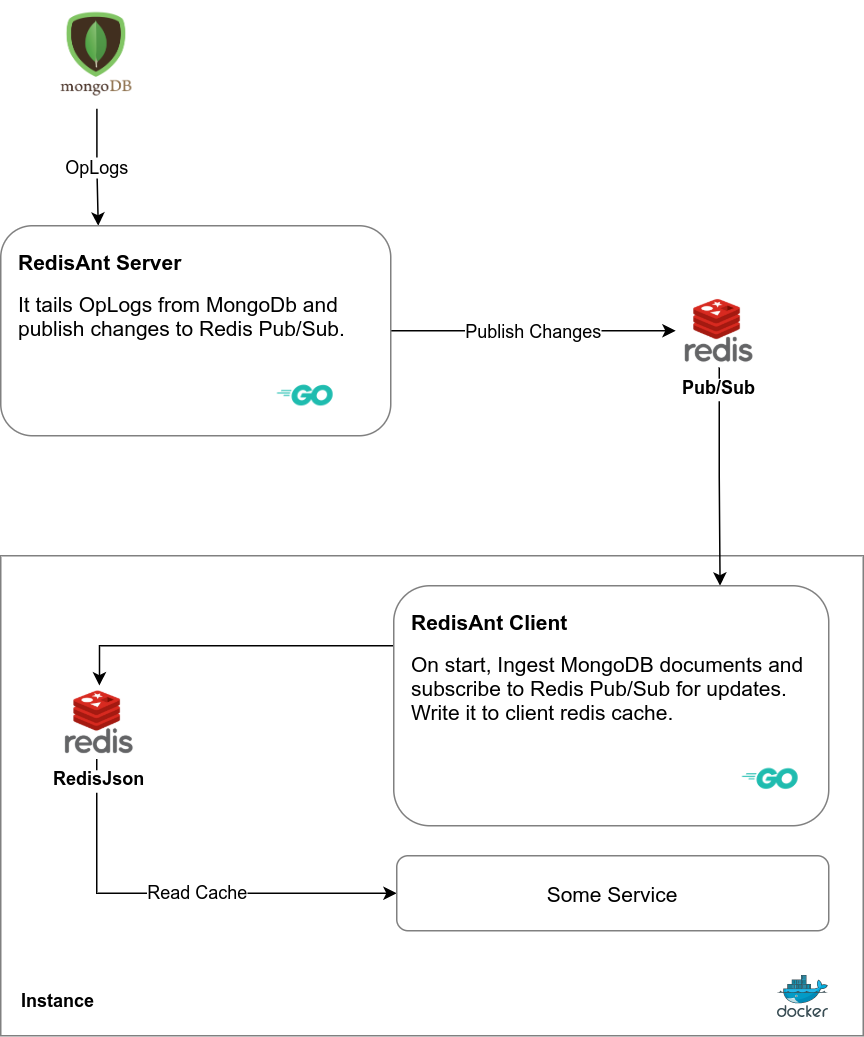
Let's understand how it works.
RedisAnt-Server is responsible for connecting with MongoDB and reading the OpLogs for the collection user wants to sync. When a change is detected, it will immediately publish it to Redis Enterprise Pub/Sub. The source code for this tool can be found at cmd/redis-ant-server.
RedisAnt-Client is responsible for
Getting the initial state when the instance stars, so the service can start using it instantly. Listing to Global Pub/Sub for any changes. In case of any change, it will make them immediately, so the service has the access to the latest data.
Both the services use the ant_source.yml file to work with the source. You need to define the source in this file.
# Database you want to sync
database: "DATABASE"
# Collection you want to sync
collection: "COLLECTION"
# Key field is used to hash and map the cache
key_field: "user_id"
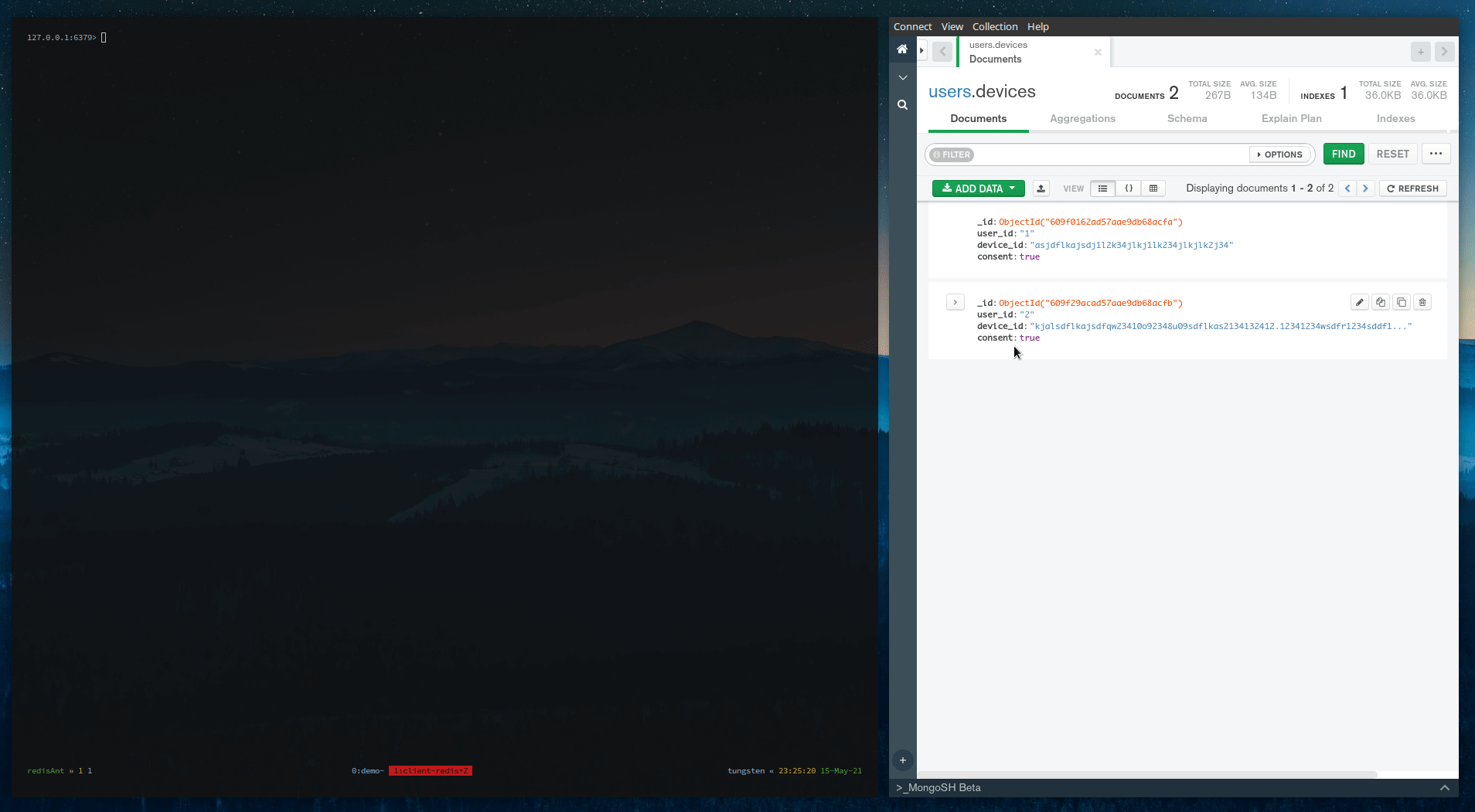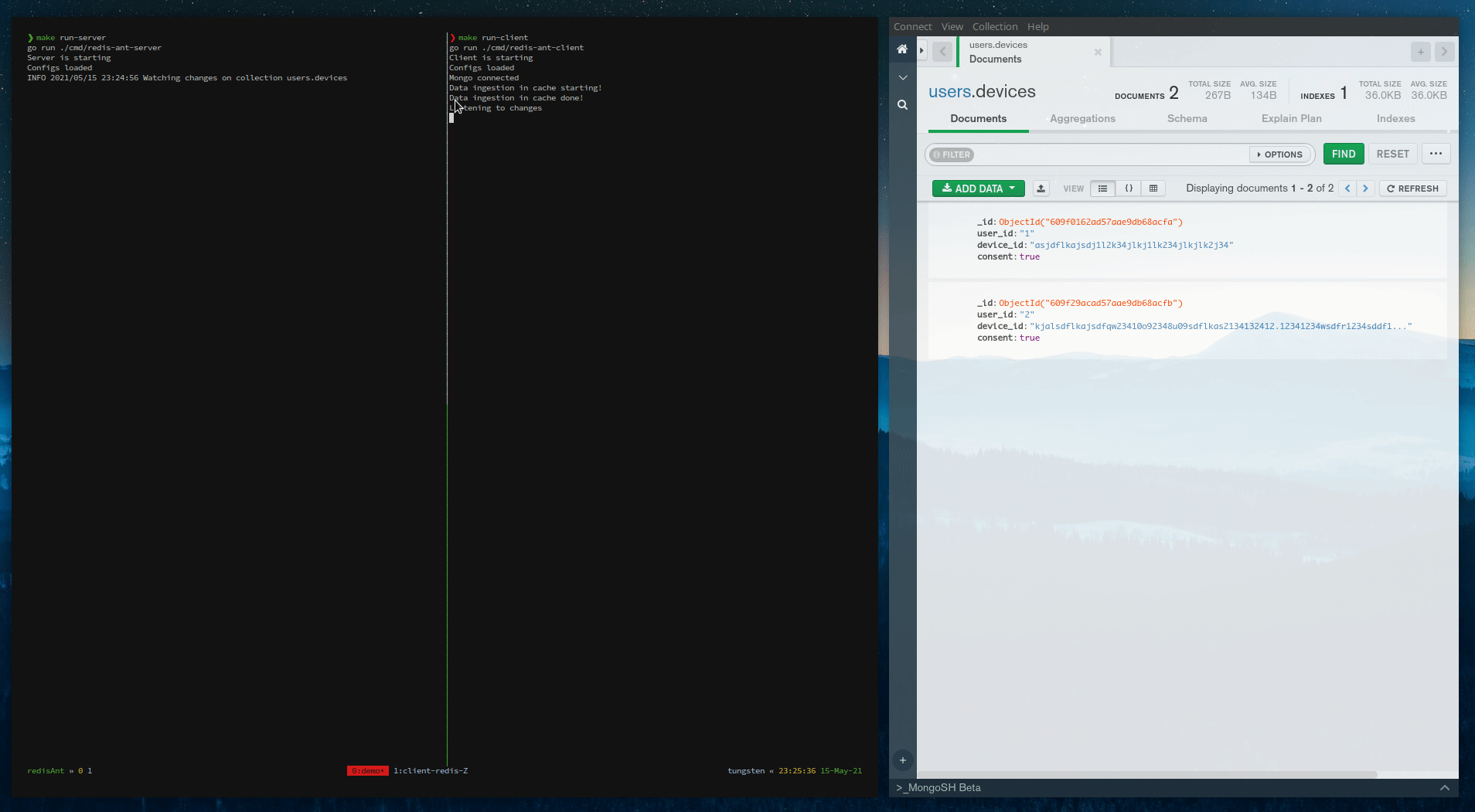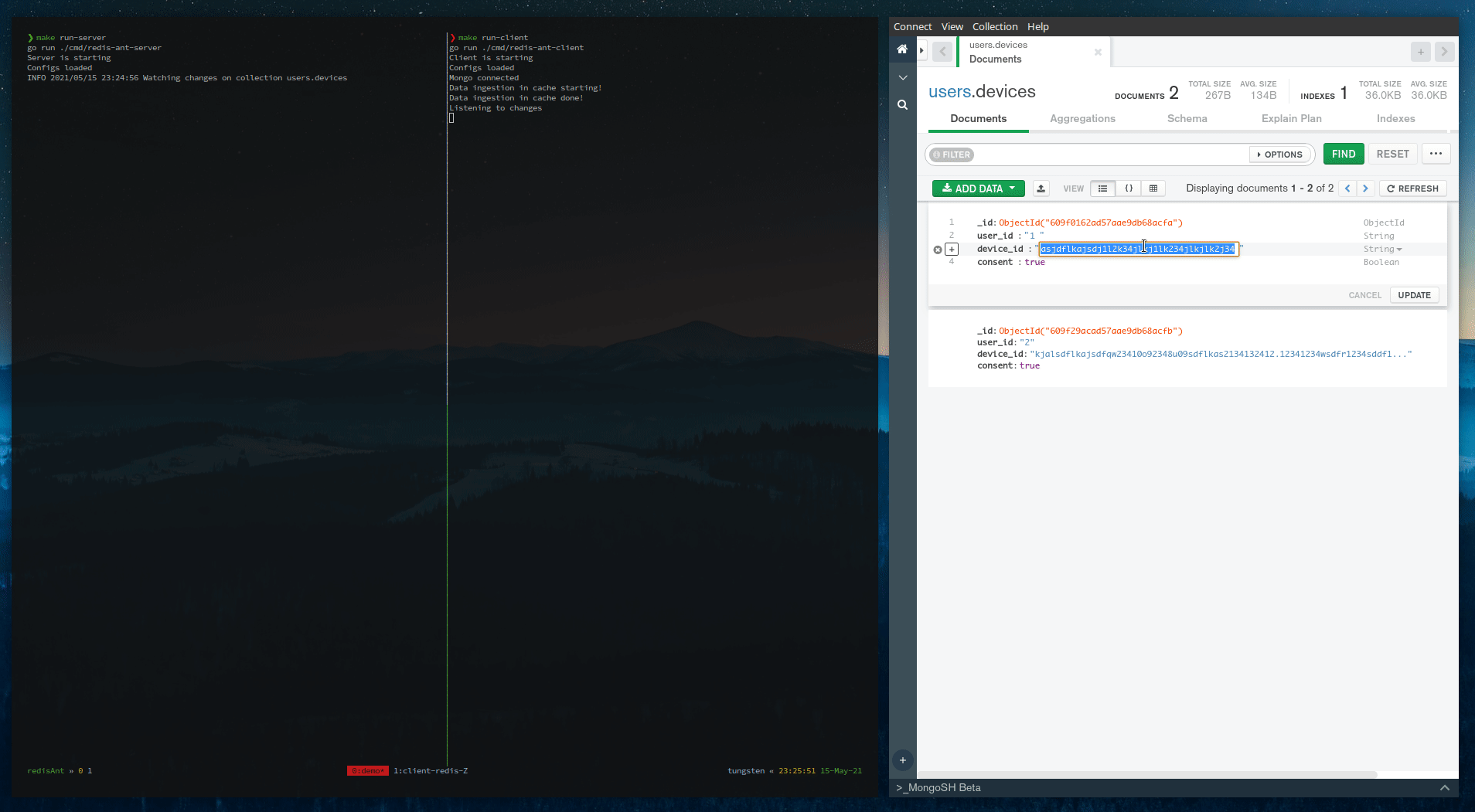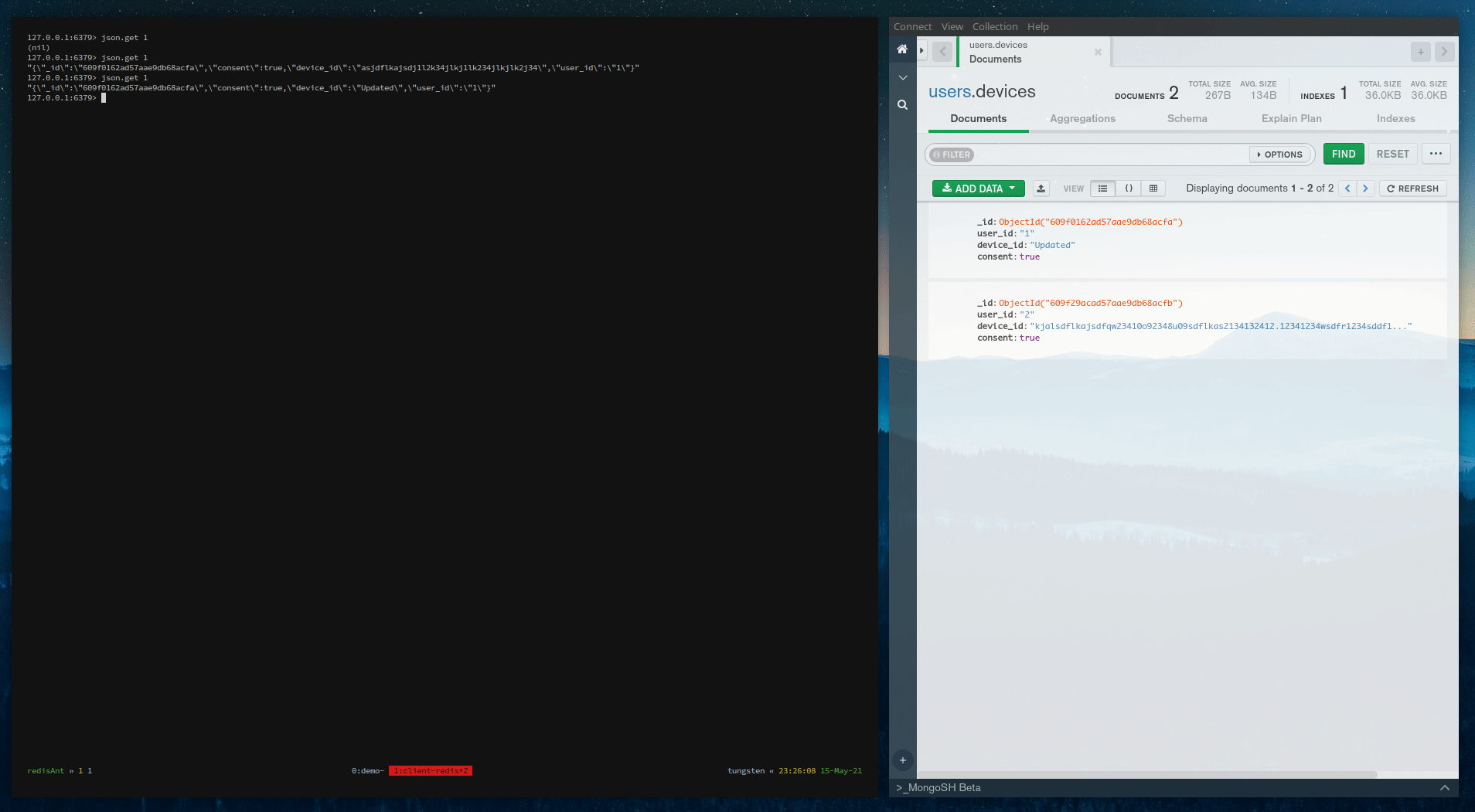
Above is the complete demo. To understand the working, you can see this video
This pre-requisites are not necessarily for running the project, but if you plan to use or contribute to this project or play with the source code, some knowledge of following things is recommended.
To develop or build this project, make sure you have the following environment setup:
- Install, and setup Go environment.
- Install Docker.
- Install Make.
- Clone this project in your go workspace.
Once you have set up the above environment, we will use make to install dependencies. Go to the root of the project and run the following command; it installs all the Go dependencies.
$ make setupIf you are testing it during the hackathon, you can directly jump to the step 4
Step 1: Start Redis Enterprise Cloud and MongoDB
Step 2: Create a env file and add following details to it
export GLOBAL_REDIS_URL=
export GLOBAL_REDIS_PASS=
export GLOBAL_REDIS_PORT=
export MONGO_URI=
export MONGO_USER=
export MONGO_PASS=
export CLIENT_REDIS_URL=localhost:6379
export CLIENT_REDIS_PASS=
export CLIENT_REDIS_PORT=6379
Step 3: Define ant_source.yml file
database: "users"
collection: "devices"
key_field: "user_id"
Make sure the database and collection actually exist.
Step 4: Start the client-side cache
$ make run-client-redis
or if you don't have make
$ docker run --rm -p 6379:6379 --name redis-redisjson redislabs/rejson:latest
Step 5: Start the RedisAnt-Server
$ make deploy-server
or
$ source env
$ ./bin/redis-ant-server
Step 6: Start the RedisAnt-Client
$ make deploy-client
or
$ source env
$ ./bin/redis-ant-client
- For user service to store user details and serve them fast.
- For storing device_id in notification service to send notifications
- Fewer updates comparatively. No transformation/operation required.
- It will automate and reduce the time it takes to set up the syncing.
This project should be considered a pre-alpha and a lot can be improved in it. Here are something I feel can be added or improved:
- We can enable users to select sub-fields they want to sync from Mongo.
- Increase support for multiple collections and databases.
- The same can be applied to the global cache.
Ants are known for working in teams in sync. If one ant finds food, it very quickly transfers the location data to all the other ants. Then all the ants work together to take food from source to destination, bit by bit. I think this tool also works(at least that's what I wanted) in the same way, hence the name RedisAnt.
MongoDB is a no-SQL database and supports JSON document structure. It is a really popular choice for startups(enterprises too) to create their ever-evolving data structure DB.
Redis JSON adds native support for storing and retrieving JSON documents at the speed of Redis.
RedisAnt combines the power of MongoDB and Redis JSON to automate the local caching with zero overhead and high performance.
The client tracking feature of Redis Enterprise helps companies manage client-side cache assisted by the server-side cache. It required some initial configuration and the server needs to be programmed accordingly. Also, it is obnoxious about the database.
RedisAnt is aware of the database, and it communicates with it on your behalf. It manages client-side caching end-to-end without any assistance from the server.
This project was created during Redis Hackathons 2021. I had this idea in my head for quite some time and this hackathon provided the perfect space to play with it.
- Logo is from Flaticon.
- Redis Inc for free access to Redis Enterprise Cloud.