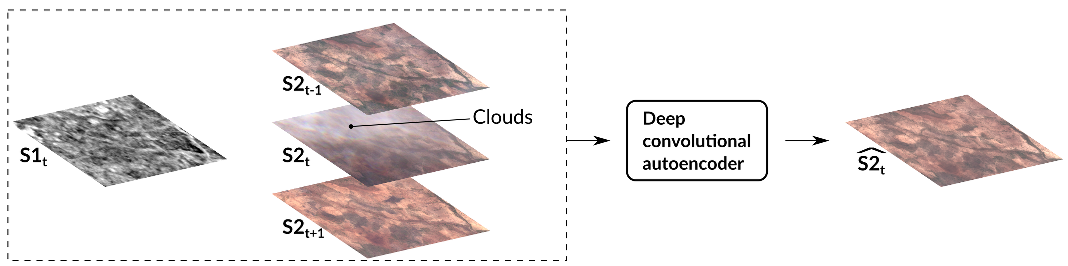
This repository is archived check decloud which implements more recent advances, with higher TRL.
Official implementation of Optical image gap filling using deep convolutional autoencoder from optical and radar images presented at IGARSS 2019.
R. Cressona , D. Iencoa , R. Gaetanob , K. Osea , D. Ho Tong Minha
a: IRSTEA, UMR TETIS, University of Montpellier, France
b: CIRAD, UMR TETIS, University of Montpellier, France
- The Orfeo ToolBox (OTB)
- TensorFlow
- OTBTF remote module of OTB (can be built without TensorFlow support, but you would be able only to train the model, not to generate images with TensorflowModelServe or fine-tune an existing SavedModel with TensorflowModelTrain.)
The easiest way is to use the dockerfile of OTBTF since compiling OTB+TensorFlow takes some time.
Build the docker image, then just enter the docker and clone this repository.
Let's explain a bit how you can use Deep-Gapfill
Use the OTB application ComputeImagesStatistics, or gdalinfo -stats (or whatever your favorite stats application is) to compute some stats of your input images. These statistics will be used to rescale your input images between 0 and 1. Keep the values somewhere, because later you will need them to denormalize the output images. The BandMathX OTB application is nice to perform the rescaling. Note that the input images must be resampled at the same resolution.
You can use QGIS for that. The goal is to use the images clouds masks to select where you want to use training patches and validation patches. In the end you should have two vector data files (one for training patches_train.shp, and one for validation patches_valid.shp) containing points centered on the patches you want to use. The grid, centroids and Random selection tools from QGIS are your friends here. Be careful with no-data values! Patches should not contain any no-data pixel.
Use the OTBTF PatchesExtraction application to extract patches in the images. First, tell OTBTF that you need 4 sources (one for SAR: s1t, and three for optical images: s2t-1,s2t,s2t+1).
export OTB_TF_NSOURCES=3
Then run PatchesExtraction with $s1t, $s2t, $s2tA and $s2tB corresponding to your normalized images. The following shows the command line for the training dataset.
otbcli_PatchesExtraction \
-source1.il $s1t -source1.patchsizex 64 -source1.patchsizey 64 -source1.out /data/patches/training/s1.tif \
-source2.il $s2t -source2.patchsizex 64 -source2.patchsizey 64 -source2.out /data/patches/training/im1.tif \
-source3.il $s2tA -source3.patchsizex 64 -source3.patchsizey 64 -source3.out /data/patches/training/im2.tif \
-source4.il $s2tB -source4.patchsizex 64 -source4.patchsizey 64 -source4.out /data/patches/training/im3.tif \
-vec /data/vector/patches_train.shp -field "fid" # Or whatever existing field there is... you need to put one existing field. I'll correct this issue soon.
Do the same for validation dataset.
otbcli_PatchesExtraction \
-source1.il $s1t -source1.patchsizex 64 -source1.patchsizey 64 -source1.out /data/patches/validation/s1.tif \
-source2.il $s2t -source2.patchsizex 64 -source2.patchsizey 64 -source2.out /data/patches/validation/im1.tif \
-source3.il $s2tA -source3.patchsizex 64 -source3.patchsizey 64 -source3.out /data/patches/validation/im2.tif \
-source4.il $s2tB -source4.patchsizex 64 -source4.patchsizey 64 -source4.out /data/patches/validation/im3.tif \
-vec /data/vector/patches_valid.shp -field "fid"
Now use the script provided to build and train the model.
python /path/to/deep-gapfill/model.py \
--s1_t /data/patches/training/s1.tif \
--s2_t_before /data/patches/training/im1.tif \
--s2_t /data/patches/training/im2.tif \
--s2_t_after /data/patches/training/im3.tif \
--valid_s1_t /data/patches/validation/s1.tif \
--valid_s2_t_before /data/patches/validation/im1.tif \
--valid_s2_t /data/patches/validation/im2.tif \
--valid_s2_t_after /data/patches/validation/im3.tif \
--logdir /data/logs/gapfill_log --save_ckpt /data/ckpts/gapfill_model
You can use TensorBoard to follow the training and the validation.
In case the tricks.py is missing, just add to the PYTHONPATH the path of OTBTF python directory.
tensorboard --logdir /data/logs/
Then open yout favorite web browser.
Use OTBTF's ckpt2savedmodel.py to convert the checkpoint into a TensorFlow SavedModel.
Specify what inputs/outputs of the model you need.
python /work/otb/otb/Modules/Remote/otbtf/python/ckpt2savedmodel.py \
--ckpt /data/ckpts/gapfill_model-199 \
--inputs "s1:0" "s2_before:0" "s2_after:0" \
--outputs "gen_fcn:0" \
--model /data/GapFill_SavedModel
Note that you can now use TensorflowModelTrain OTBTF application to do the training of the exported SavedModel.
Let's use TensorflowModelServe to generate the full optical image.
The model has a receptive field of 576x576 pixels and an expression field of 64x64 pixels since we use the exact FCN output ("gen_fcn" tensor).
otbcli_TensorflowModelServe \
-source1.il $s2tA -source1.placeholder "s2_before" -source1.rfieldx 576 -source1.rfieldy 576 \
-source2.il $s2tB -source2.placeholder "s2_after" -source2.rfieldx 576 -source2.rfieldy 576 \
-source3.il $s1t -source3.placeholder "s1" -source3.rfieldx 576 -source3.rfieldy 576 \
-model.dir /data/GapFill_SavedModel/ -model.fullyconv on \
-output.names "gen_fcn" -output.efieldx 64 -output.efieldy 64 \
-out /data/s2_estimated.tif
You can tweak a bit the application to speed ud the process: force the use of large tiles in adding e.g. -optim.tilesizex 2048 -optim.tilesizey 2048 to the former command line.
Use BandMathX to denormalize the s2_estimated.tif generated image.
You can also use BandMathX to keep non polluted values of the s2t image, and replace the polluted ones with s2_estimated.tif.
Please see the license for legal issues on the use of the software.
You can contact Remi Cresson if you have any issues with this remote module at remi [dot] cresson [at] irstea [dot] fr