- Reduces the risk of losing production assets because of intended or unintended damage (deletion) of assets by people or resources with legitimate access to production AWS Account.
- Encourages thinking about DR and understanding of environments through documentation
- Increased confidence and realigns business expectations around recovery of resources critical to Business Continuity
- Increased knowledge of AWS RDS Service and what it has to offer on Cross Account backups
Disaster recovery (DR) is often thought of in terms of handling massive failures of infrastructure - the loss of a whole data centre for example. In AWS, these kinds of failures are usually mitigated by architectures that allow technical solutions to span multiple Availability Zones and Regions. However, there are other kinds of 'disasters' including the accidental or intentional mass deletion of resources by people who have legitimate access to an AWS account. < br /> This kind of 'disaster' can be mitigated by saving copies of key resources - AMIs, CloudFormation templates, encryption keys and instance & RDS snapshots - to a second 'Failsafe' account to which there is limited and carefully controlled access. Such control could be maintained by splitting the password and the MFA device across multiple members of staff, requiring two to be present before access is possible.
The AWS Serverless Application Model Stack provided here offers a way of taking a daily copy of the most recent Automated RDS Snapshots. This could be from one or more RDS instances in a Live AWS Production Account to an AWS 'Failsafe' Account. The 'Failsafe' Account is assumed to have restricted / limited access granted to People and Services.
The target RDS Database is tagged with a special tag {Key:"Failsafe", Value:"True"}. Apart from invoking AWS SAM via AWS CLI to deploy the Stack across AWS Accounts, this is the only manual work required to enable 'Failsafe' backups. Once the stack is up and running developers will only need to add the Failsafe tags to the RDS Instance.
The target RDS Database should have automatic snapshot creation enabled via the AWS console. AWS RDS creates automated backups of the DB instance during the backup window. AWS RDS saves the automated backups of the DB instance according to the backup retention period that is specified.
When an automated backup is run, a payload is sent to an SNS Topic by the RDS Event Subscription. This event kicks off the Lambda function to Copy and Share the RDS Snapshot across accounts.
The Copy Lambda function in the target Account checks whether the "failsafe" tagged RDS has automated snapshots that have not been backed-up to the 'Failsafe' account yet.
If there are then a manual copy of the automated snapshot is created. The manual snapshot is shared to the Failsafe account. The Save Lambda function in the Failsafe account will then copy this snapshot and keep it for the specified retention period.
The illustration below demonstrates how this approach is tied together:
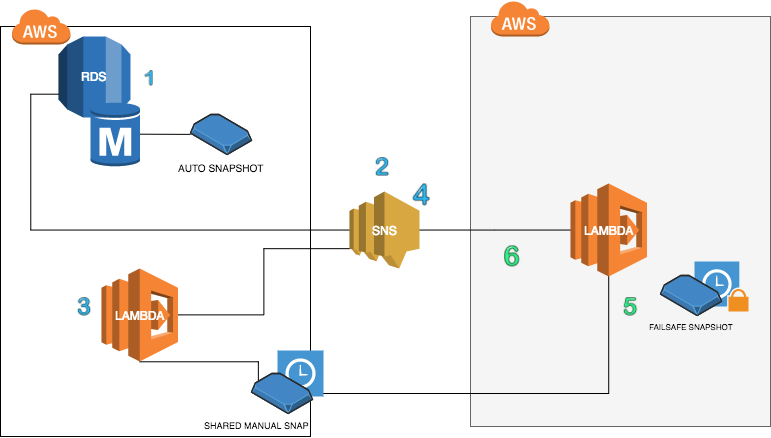
- Amazon RDS in a production AWS Account is configured to create and save automated backup snapshots of DB instances
- There is an SNS Topic configured in the production AWS Account that receives an event when RDS automated backup starts & ends. The event triggers the Lambda function to Copy the Automated Snapshot to a manual Snapshot within the production AWS Account.
- The Copy Lambda function copies the Automated Snapshot to a Manual Snapshot and shares it with the FailSafe account
- The Copy Lambda function sends an SNS Event to trigger the Save Lambda function in the FailSafe account
- The Save Lambda function in the FailSafe account copies the shared Snapshot and saves it to the Failsafe account
- An SNS Event for notification and to clean up…
Note: still considering how to make this step less chatty hence not implemented yet
-
Polling. How can we reliably tell the
Save Lambda functionthat the Manual snapshot is ready? This opportunity arose from the realisation that waiting for any RDS event to complete using polling is bad practice. Events are sent in succession and developers are forced to write a polling functions for the Lambda functions so as to have some control on the process flow. -
Cross Account Copy. There is no possibility to share AWS RDS Automated snapshots straight up when they are created. This is also complicated by the fact that Manual Snapshots have to be available before they are shared. This forces the developer to think up complicated means of managing Automated Snapshot sharing procedure Cross Accounts.
-
Cross Account Access Maturity Working with RDS (any AWS Infrastructure) Cross-Accounts is not mature enough at the time of writing this readme. Orchestration of infrastructure setup across accounts is hard. The only option at the moment is to use tools that are currently Beta versions. We tried using AWS SAM, AWS StackSets, but these require granting cross account global access which is not inline with our restricted Backup account policy.
-
Cross Account API Maturity Cross accounts creation of stacks is also limited by API definitions e.g. for RDS
copy_db_snapshotscannot be used to copy snapshots Cross Accounts. A feature request has been raised with AWS to look into this. We Investigated Stack-Sets which was launched a month ago and it has its own limitations. -
Testing We found that testing Lambda functions locally is a painful task. We looked at SAM local and were impressed at how easy it made testing functionality of Lambda functions. Unfortunately, this meant creating real AWS Resources and interrogating real API endpoints. This means managing clean-ups and incurring undesirable costs.
- AWS to fix the “Event Category Bug” which has been reported to AWS RDS Team
- Review the Category and events for Automated Backups such that:
- SNS notifications can have split events
- Make it easier to manipulate individual events via Event IDs
- Requested a functionality that will allow immediate sharing of the RDS Automated Backups with accounts of choice
- Give more Cross Account definitions to the current RDS APIs
Backing up the RDS Snapshot from AWS production account to FailSafe production Account. In order to perform cross account actions Amazon SNS deliveries to Lambda, we have authorised the Lambda function to be invoked from Amazon SNS in the AWS production Account. In turn, Amazon SNS needs to allow the Lambda account to subscribe to the Amazon SNS topic.
Target Account - means execute the AWS CLI commands in the context of the target account
Failsafe Account - means execute the AWS CLI commands in the context of the FailSafe account
-
Target Account: RDS Instance has automated snapshot configured
-
Target Account: Create an SNS Topic that the RDS will subscribe;
SNSCopyTopic.- An event will be fired via SNS to begin the backup process once an auto-backup is complete.
SNSTopicRDSAutoSnap
Because of the “Event Category Bug” we are using an event trigger at 4AM] - check if this is still true #1
- An event will be fired via SNS to begin the backup process once an auto-backup is complete.
-
Target Account: RDS Event Subscription to SNS Topic is created
-
Target Account: Create an SNS Topic for the
Save Lambda Functionto Subscribe to -SNSSaveTopic
The step described here will be generic for 2. 3. 4.
Note: Using the Backup source type of RDS causes two events to be sent to the Lambda function. These have to be handled by the Lambda function - backup (RDS-EVENT-0001) - An automated backup of the DB instance has started. - backup (RDS-EVENT-0002) - An automated backup of the DB instance is complete.
- Create an SNS Topic for
Some Lambda Functionto Subscribe toSNSSomeTopicbash aws sns create-topic --name <SNSSomeTopic> Response: { "TopicArn": "arn:aws:sns:ap-southeast-2:<some_account_id>:<SNSSomeTopic>" }
-
Target Account: Create a Lambda Function
rdscopysnapshotsthat will:- copy Automated RDS snapshot to a Manual snapshot
- share the Manual Snapshot with the Failsafe account
- trigger an SNS event once copy of RDS automated snapshot is complete.
Pre-requisite:
- Create Role and attach policies to execute Lambda as well as work with RDS Snapshot... See: rdscopysnapshots-role-policy.json - might need to restrict access to a particular RDS instance
$ aws iam create-role --role-name <rdscopysnapshots> \ --assume-role-policy-document <file://rdscopysnapshots-role-policy.json>
- Command to create Lambda function
$ aws lambda create-function \ --function-name <rdscopysnapshots> \ --runtime python2.7 \ --role arn:aws:iam::<target_account_id>:<role/rdscopysnapshots-role-policy> \ --handler <handler> \ --description "lambda function to save and share automated rds snapshot" \ --timeout 60 \ --memory-size 128 \ --zip-file <rds_backup/rdscopysnapshots.zip>
NOTE: We pushed the file (rds_backup/rdscopysnapshots.zip) to AWS S3 and we were able to create Lambdas. AWS SAM is elegant since it does this for us automatically.
-
Failsafe Account: Subscribe the
Save Lambda Functionto anSNSSaveTopicthat is cross Account capable
STEP 1.- Tell the Lambda function in Failsafe account about the SNS topic in the Target account. Ran this in the Failsafe Account AWS CLI context.
$ aws sns subscribe \ --topic-arn arn:aws:sns:ap-southeast-2:<target_account_id>:<SNSSaveTopic> \ --protocol lambda \ --notification-endpoint arn:aws:lambda:ap-southeast-2:<failsafe_account_id>:function:<rdssavesnapshots> response: { "SubscriptionArn": "arn:aws:sns:ap-southeast-2:<target_account_id>:<SNSSaveTopic>:fb93-21fc-4577-9ab1-0c4cc5a1" }STEP 2.
- Allow the Failsafe account Lambda function to subscribe, list subscriptions by topic and to receive notifications from the Target SNS Topic
# run in the aws cli context of the target account ➜ $ aws sns add-permission \ --topic-arn "topic-arn arn:aws:sns:ap-southeast-2:<target_account_id>:<SNSSaveTopic>" \ --label "some-unique-identifier" \ --aws-account-id "<failsafe_account_id>" \ --action-name "Receive" "Subscribe"
Example policy result { "Sid": "some-unique-identifier", "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "AWS": [ "arn:aws:iam::<failsafe_account_id>:root", ] }, "Action": [ "SNS:Subscribe", "SNS:Receive" ], "Resource": "arn:aws:sns:ap-southeast-2:<target_account_id>:<SNSSaveTopic>" }
-
Target Account: Allow the Failsafe account resources to subscribe, list subscriptions by topic and to receive notifications from the
SNSSaveTopic.# run from the Failsafe account context to create a trust policy on the lambda in the failsafe account ➜ aws lambda add-permission \ --function-name <rdssavesnapshot> \ --statement-id <rdssavesnapshot> \ --action "lambda:InvokeFunction" \ --principal sns.amazonaws.com \ --source-arn arn:aws:sns:ap-southeast-2:<target_account_id>:<SNSSaveTopic> The response below confirms that SNS from target account will be able to trigger the lambda function in Failsafe account { "Statement": "{\"Sid\":\"rdssavesnapshot\",\"Effect\":\"Allow\",\"Principal\":{\"Service\":\"sns.amazonaws.com\"},\"Action\":\"lambda:InvokeFunction\",\"Resource\":\"arn:aws:lambda:ap-southeast-2:<failsafe_account_id>:function:rdssavesnapshot\",\"Condition\":{\"ArnLike\":{\"AWS:SourceArn\":\"arn:aws:sns:ap-southeast-2:target_account_id:SNSSaveTopic\"}}}" }
NOTE: Do not use the --source-account parameter to add a source account to the Lambda policy when adding the policy. Source account is not supported for Amazon SNS event sources and will result in access being denied. This has no security impact as the source account is included in the source ARN.
To get the above output run
➜ aws lambda get-policy --function-name <rdssavesnapshot>
-
Failsafe account: Create a Lambda Function
rdssavesnapshotsthat will:- copy shared manual RDS snapshots to manual snapshots in the Failsafe account
- Delete previously saved snapshots in the Failsafe account according to the retention period
- Notify all subscribers that the snapshots have been saved in the Failsafe account
# run in the context of the backup account ➜ $ aws sns subscribe \ --topic-arn arn:aws:sns:ap-southeast-2:<target_account_id>:SNSSaveTopic \ --protocol lambda \ --notification-endpoint arn:aws:lambda:ap-southeast-2:<failsafe_account_id>:function:rdssavesnapshot { "SubscriptionArn": "arn:aws:sns:ap-southeast-2:<target_account_id>:SNSSaveTopic:fb92e3-21fc-4577-9ab1-0ca0c5a1" }
-
Failsafe account: Allow the Lambda function to accept invocations from Target
SNSSaveTopic -
Failsafe account: subscribe the Lambda function to the topic in Target Account.
By virtue of the Stack being across accounts it is tedious to manually deploy. Considering that, at the time of writing, tools are not mature enough to securely deploy the stack across accounts with varied access requirements, we used SAM (Beta) to automate as much of the deployment as we could. The developer would still have to run SAM on two accounts to get the full stack deployed. Hence we have cosercutively named the two sides of the stack RDS Copy Snapshot Stack and RDS Save Snapshot Stack. This however, makes rigorous testing even harder.
-
Create a template
rds_copy_snap_template.yaml -
Package the
RDS Copy Snapshot Stackfor deployment to AWS account# run in the target account context ➜ $ aws cloudformation package \ --template-file /workdir/rds_copy_snap_template.yaml \ --output-template-file /workdir/readme_artefacts/rds_copy_serverless-output.yaml \ --s3-bucket <reptileinx.aws> --- Response will look something like below:- Uploading to 3cbscdsee8bc225d61ss1ee9ccdd848a92f0 60480 / 60480.0 (100.00%) Successfully packaged artefacts and wrote output template to file /workdir/readme_artefacts/rds_copy_serverless-output.yaml. Execute the following command to deploy the packaged template aws cloudformation deploy --template-file /workdir/readme_artefacts/rds_copy_serverless-output.yaml --stack-name <YOUR STACK NAME>
NOTE: The package command will zip our code, upload it to S3, and add the correct CodeUri property to the output template. This is why the CodeUri is empty in our template, or is set to a dot, in our original template. Each time we run the package command, it will generate a different ID for our package and will fill the CodeUri field with the correct address. In this way, we can deploy new versions of our Lambda function or roll back to a previous version.
- Deploying the
RDS Copy Snapshot Stack➜ $ aws cloudformation deploy \ --template-file /workdir/readme_artefacts/rds_copy_serverless-output.yaml \ --stack-name ReptileinxCOPYRDSSnap \ --capabilities CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM --parameter-overrides FailsafeAccountIdParam=failsafe_account_id
NOTE: We are adding the --capabilities CAPABILITY_IAM parameter because the AWS::Serverless::Function resource is going to create a role with the permissions to execute our Lambda function, and we want CloudFormation to be able to create it for us. The failsafe account is being passed on to the function as follows:
--parameter-overrides FailsafeAccountIdParam=<failsafe_account_id>
-
If the stack is successfully created its output will be as shown below:
Waiting for changeset to be created.. Waiting for stack create/update to complete Successfully created/updated stack - ReptileinxCOPYRDSSnap
-
Go to the Lambda function and test it by running the test with default payload:
# sample CloudWatch logs START RequestId: 76d906ba-9ed0-11e7-8cdd-031cef4ef44f Version: $LATEST Found database with Failsafe tag reptileinxDB--instanceDate Deleting previously created manual snapshots for reptileinxDB--instanceDate Ignoring manual snapshot mingbreaks Ignoring manual snapshot sameaccountcopy Deleting manual snapshot failsafe-reptileinxDB--snapshot-date Creating manual copy of the most recent automated snapshot of database instance - reptileinxDB--instanceDate Waiting for copy of failsafe-reptileinxDB--snapshot-date to complete. failsafe-reptileinxDB--snapshot-date: creating... failsafe-reptileinxDB--snapshot-date: creating... failsafe-reptileinxDB--snapshot-date: creating... failsafe-reptileinxDB--snapshot-date: creating... failsafe-reptileinxDB--snapshot-date: creating... failsafe-reptileinxDB--snapshot-date: creating... failsafe-reptileinxDB--snapshot-date: available... Snapshot rds:reptileinxDB--snapshot-date copied to failsafe-reptileinxDB--snapshot-date Sharing snapshot... failsafe-reptileinxDB--snapshot-date to account ... <target_account_id> Security Notice: DB Snapshot will remain shared to <target_account_id> until when snapshot is deleted Sending SNS alert to failsafe topic END RequestId: 76d906ba-9ed0-11e7-8cdd-031cef4ef44f REPORT RequestId: 76d906ba-9ed0-11e7-8cdd-031cef4ef44f Duration: 75206.69 ms Billed Duration: 75300 ms Memory Size: 128 MB Max Memory Used: 40 MB
To run stacks in production account the following special policies are required for Cloudformation.
delete policy, detach role policy, update, create, deletestack
Log on to the Target account AWS console and run the test on the Lambda function. The default test payload will work just fine as the Lambda is not using any Event Object.
- Manual Approach: This involves following steps in "Manual Deployment of Cross Accounts RDS Failsafe Stack " process. Then in the target account invoke the test with default test payload.
Note: the target DB Instance should be tagged as a precursor for the approach to work 'Failsafe:True'
Once the RDSCopySnapshot Lambda function completes, check the CloudWatch events in both the Target account and the Backup account.
To test end to end, leave the stacks running overnight and then check the Backup account for Failsafe Snapshots created (would have been around 4am)
-
Automated AWS Tests using SAM. Documented herein 'Solving the testing problem using AWS SAM Local' TODO: 🐒
-
Moto Testing To remove dependencies on the AWS infrastructure we decided to run Moto in standalone server mode. See documentation here: https://github.com/spulec/moto
- Installing and Testing with Moto
pip install pytest
pip install coverage
# we recommend setting up moto by pulling down the github repository and running the docker install
docker build -t motoserver .
# In the moto dir runrun tests like so
py.test --cov-report term --cov=rdssavesnapshots test_save_manual_failsafe_snapshot_standalone.py- select the RDS snapshot that has been shared with the Failsafe account
- under snapshot actions select
share snapshot - there should be the intended account under
Manage Snapshot Permissionse.g.failsafe_account_id
TODO: 🐒
We want to deploy a stack that spans across accounts... one half of the stack is for copying rds snapshots and the other half will save the RDS snapshots to failsafe account.
AWS CloudFormation enables users to create infrastructure based on templates specified in YAML or JSON. Rather than setting up an environment manually, a CloudFormation template can be used to create all of the necessary resources. Until recently, this functionality was limited to a single account and a single region.
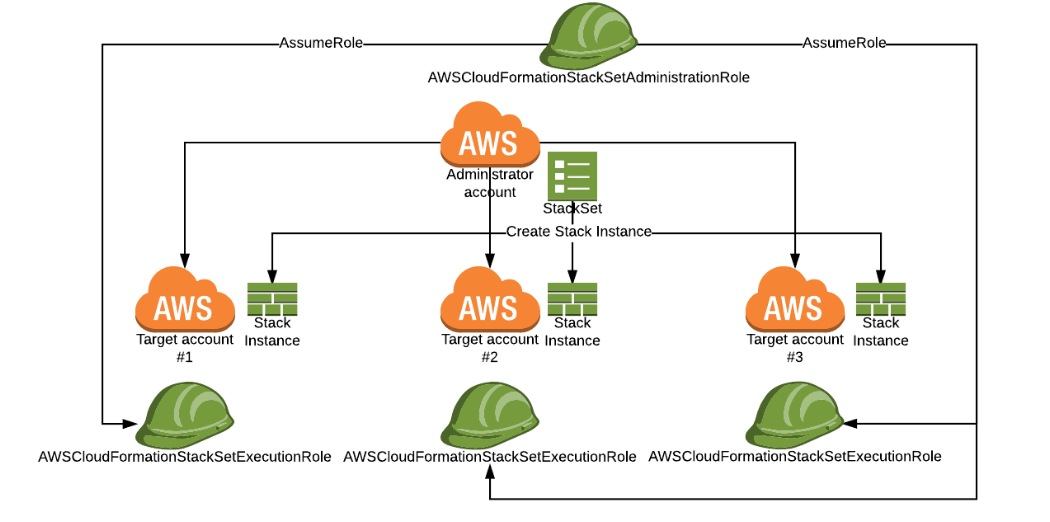
A StackSet is a set of CloudFormation stacks that can easily be deployed to multiple AWS accounts and/or multiple AWS regions. We will use the AWS CLI to create a StackSet with the CloudFormation stacks defined by our templates.
In a nut shell there are two resources that are managed
- StackSet - the container in which the set of CloudFormation stack instances will live
- Stack - the actual instantiation of the template we provided to the StackSet
CloudFormation needs some very specific permissions to get a StackSet up and running.
- In the Administrator Account we will need
AWSCloudFormationStackSetAdministrationRole - In each of the Target accounts will need the IAM role
AWSCloudFormationStackSetExecutionRolewhich will be assumed by theAWSCloudFormationStackSetAdministrationRoleRole (see http://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSCloudFormation/latest/UserGuide/stacksets-prereqs.html)
The picture bellow shows how then StackSet will be able to orchestrate to different accounts.
- What will happen if the 5 databases save snapshots at exactly the same time? Consider the fact that the Lambda function will die after 5 min.
- How can we stop the need to re-run both Stacks if we recreate the any of the stacks 'Copy or Save stack'? see issue #2
- How can we remove the waits from our Lambda functions without degrading the level of control we have on the process flow?
- Why is using event trigger bad for our solution?
Imagine a scenario where 10 database instances create snapshots at exactly the same time. The event trigger will wake up only 1 single lambda function to process all these snapshots. The lambda function has a timeout period of 5min. After which the error "...Task timed out after 300.09 seconds" is thrown. This means our solution is bound to fail. The situation would have been different if we used the RDS automatic notification. AWS would automatically - we hope - trigger multiple Lambda functions to finish the job.