Here you can find outlines key information and provides instructions for setting up and interacting with the FlightSurety Project, a decentralized application (DApp) built on the Ethereum blockchain. FlightSurety is designed to automate flight insurance, leveraging smart contracts for operational integrity and security.
Explore the FlightSurety smart contracts and transactions via these links on the Sepolia testnet:
FlightSurety leverages the Ethereum blockchain to bring transparency and trust into flight insurance. It allows passengers to purchase insurance for their flights and receive automated payouts if their flights are delayed due to airline faults.
- Smart Contract Logic: Separated into data persistence and application logic for modularity and upgradeability.
- Oracle Simulation: External server application simulates oracle behavior for fetching and updating flight status information.
- User Interaction: Passengers can purchase flight insurance via a user-friendly DApp interface.
Follow these steps to set up and run the FlightSurety DApp:
-
Clone the Repository:
git clone <repository-url> -
Install Dependencies:
- Navigate to the project's root directory:
cd flight-surety - Install the required npm packages:
npm install
- Navigate to the project's root directory:
-
Compile Smart Contracts:
npx hardhat compile
In this project, we've set up a series of npm scripts to streamline the development and deployment process for the FlightSurety DApp. Below, you'll find a brief description of each script, designed to help you understand and efficiently utilize them:
-
server: Launches the backend server application located at./apps/server/src/index.js. Use this to start the server side of the DApp. -
compile: Removes existing compiled artifacts from the project and then compiles the smart contracts using Hardhat. This ensures that your contracts are up-to-date and ready for deployment or testing. -
dapp: Starts the frontend application of the DApp, which is located in the./apps/frontenddirectory. Use this command to launch the user interface in your browser. -
help: Displays a list of available npm scripts in the console. This is useful for getting a quick overview of the scripts you can run. -
Deployment Scripts:
deployLocalhost: Deploys the smart contracts to a local Ethereum network (Hardhat Network) running on your machine. This is useful for local development and testing.deploySepolia: Deploys the smart contracts to the Sepolia test network. Use this for testing your contracts in a live, testnet environment.
-
Composite Scripts:
flightsuretyLocalhost: A composite command that compiles your contracts, starts a local Ethereum node using Hardhat, deploys your contracts to this local node, and finally launches the DApp's frontend. This is your go-to script for quick, local development and testing cycles.flightsuretySepolia: Similar toflightsuretyLocalhost, but instead of deploying to a local node, it deploys the contracts to the Sepolia test network. This script also compiles your contracts and starts the DApp's frontend, making it ideal for testing your application in a live, testnet environment before final deployment.
These scripts are designed to make the development, testing, and deployment process as smooth and efficient as possible. Whether you're working locally or preparing for a live testnet deployment, these commands provide a streamlined workflow for managing your DApp.
npm run <command>
Run Tests:
- Ensure smart contract integrity through comprehensive tests:
npx hardhat test
- Compile Smart Contracts: Initiates the compilation of smart contracts using Hardhat, which generates the necessary artifacts, including the ABI (Application Binary Interface) and bytecode.
- Network Check: Verifies the deployment network to prevent accidental deployments to the ephemeral Hardhat Network, suggesting the use of
--network localhostfor local deployments. - Fetch Signers: Utilizes Hardhat's environment to obtain signer accounts, specifically identifying the deployer and an initial airline account for deployment purposes.
- Deploy Contract: Executes the deployment of the
FlightSuretyAppcontract to the chosen Ethereum network, leveraging the deployer account for the transaction. - Wait for Deployment Completion: Awaits the finalization of the contract deployment process and then captures the contract's deployed address.
- Artifact and Address Distribution:
- Frontend Application: The contract's ABI and address are saved in the
apps/frontend/src/artifacts/contractsdirectory, ensuring the frontend application can properly interact with the deployed contract. - Server Application: Similarly, the artifacts are also placed in the
apps/server/src/artifacts/contractsdirectory, enabling the server-side application to communicate with the contract. - General Artifacts Storage: Additionally, a copy of the contract's artifacts is stored in the general
artifacts/contractsdirectory for reference or other uses.
- Frontend Application: The contract's ABI and address are saved in the
- Error Handling: Manages and logs any errors encountered during the deployment process, facilitating debugging and ensuring smooth deployment operations.
- Purchasing Insurance: Passengers can select flights and purchase insurance through the DApp interface.
- Checking Flight Status: The Oracle server application simulates real-world flight information updates, triggering automatic insurance payouts as applicable.
- Receiving Payouts: In the event of a flight delay due to airline fault, insured passengers are automatically credited with payouts, which they can withdraw through the DApp.
@nomicfoundation/hardhat-toolbox(Version: ^4.0.0)- It provides essential utilities for testing, deployment, and development workflows, making it easier to manage the Ethereum smart contracts in the project.
chai(Version: ^4.4.1)- Chai allows for expressive and readable assertions in contract testing, making it easier to validate contract behavior.
dotenv(Version: ^16.4.5)- It helps manage sensitive information like API keys and mnemonic phrases for Ethereum wallets securely by separating them from the codebase.
hardhat(Version: ^2.22.1)- Hardhat is chosen as the core development tool for Ethereum smart contracts in the project, providing a reliable and extensible development
- @types (packages):
- TypeScript type definitions enhance code quality and help catch type-related errors during development.
@web3-react/core(Version: ^6.1.9)- It abstracts the complexities of connecting to Ethereum wallets, making it easier to handle wallet-related interactions in the frontend.
@web3-react/injected-connector(Version: ^6.0.7)- For connecting to Ethereum wallets that inject the Ethereum provider into the browser, such as MetaMask or other browser extensions.
ethers(Version: ^5.5.2)- Ethers.js simplifies interactions with Ethereum smart contracts and blockchain data, making it easier to build Ethereum-related functionality
react(Version: ^17.0.2) andreact-dom(Version: ^17.0.2)- React is the core library for building the frontend user interface of the application. It offers component-based architecture and efficient rendering.
react-scripts(Version: 5.0.0)- Used as a development dependency in a React project to streamline various development tasks
styled-components(Version: ^5.3.3)- It enables the creation of dynamic and styled components, providing a more maintainable and structured approach to styling React components.
-
express(Version: 4.18.3)- Express is a minimal and flexible Node.js web application framework that provides a robust set of features for web and mobile applications. APIs.
-
ethers(Version: ^5.5.2)- Ethers.js simplifies interactions with Ethereum smart contracts and blockchain data, making it easier to build Ethereum-related functionality
| Feature | Screenshot |
|---|---|
| Deployment |  |
| Oracle Registeration | 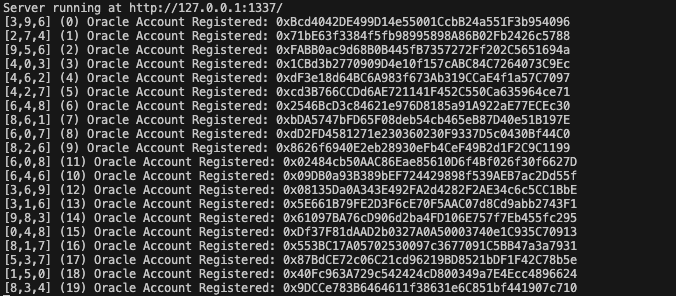 |
| Purchase | 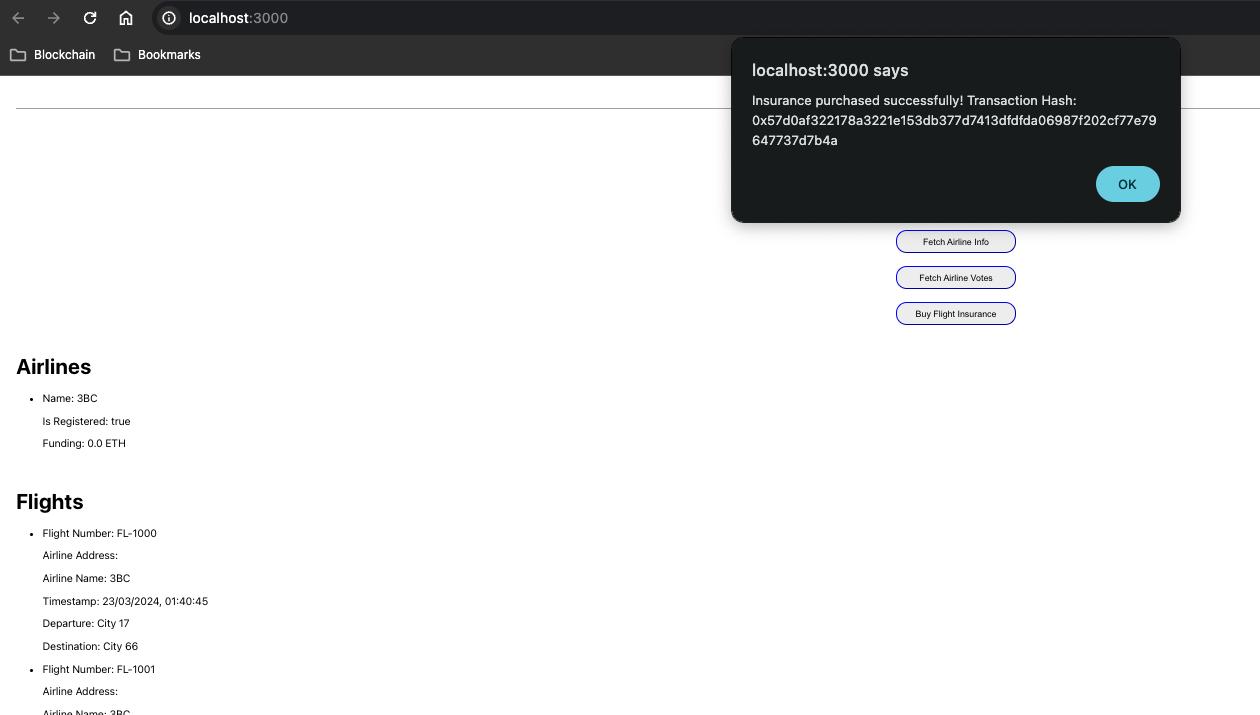 |
| Credit |  |
Contributions to the FlightSurety project are welcome. When contributing, please adhere to the following guidelines:
- Ensure code modifications are well-tested.
- Follow the existing coding style and practices.
- Update documentation as necessary to reflect changes.
Enjoy exploring and contributing to the FlightSurety project. For any queries or assistance, please reach out through the project's issue tracker or discussion forums.