Kernel Sidecar
Overview
kernel-sidecar provides the building blocks for creating applications that run alongside Jupyter Kernels, keeping the Notebook document model in memory and acting as a middle-man between the Kernel and all other clients. There are many potential features that can be built into a Sidecar application:
- Persisting Outputs for cell execution even when no clients are connected (e.g. run a cell, close your browser, come back later and see the output)
- Code Cell Linting such as
blackorisort - Variable Explorer that can be sent to newly connected clients without needing to execute code in the Kernel
- Custom Execution Managers to handle DAG/dependent cell execution or to dequeue queued cells without sending an interrupt to the Kernel which dequeues all queued cells
Installation
pip install kernel-sidecarKey Concepts
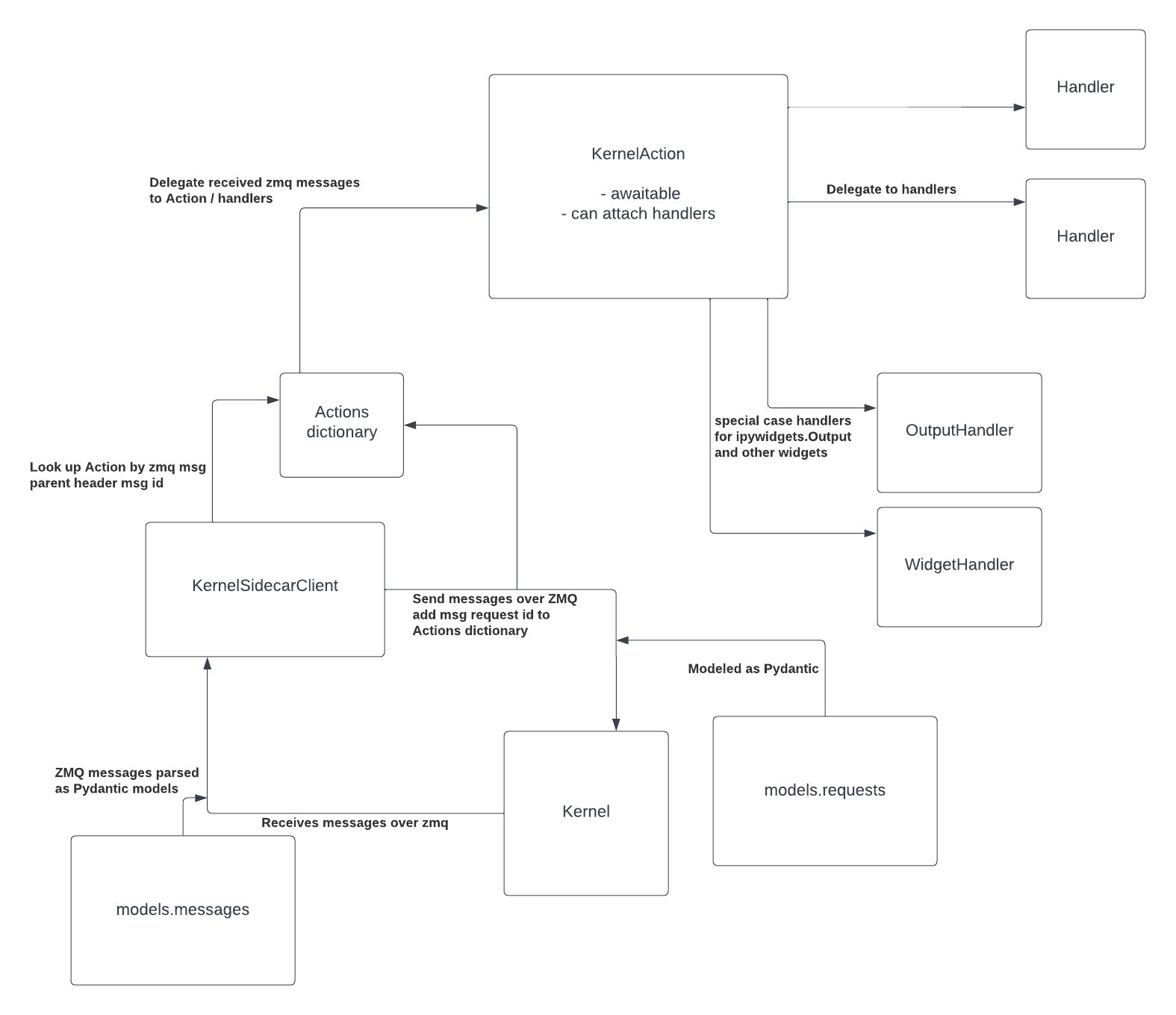
KernelSidecarClient
The KernelSidecarClient class manages the ZMQ connections to the Kernel, sending execute request or other messages to the Kernel, and processing messages coming back from the Kernel on iopub, shell, control, and stdin channels. All messages sent and received are modeled with Pydantic. When preparing to send a request to the Kernel, it's structured as a KernelAction which connects the request with zero-to-many callbacks for responses to that specific request.
KernelAction
KernelAction connects three key pieces of the request-reply flow between the sidecar application and the Kernel:
- Store the sent Request message
- Delegate messages to callbacks based on the request message
- Make the flow "awaitable" based on the Request type, e.g. an
execute_requestis done whenexecute_replyorerroris received andstatushas gone toidle.
Handlers
When the KernelSidecarClient receives a message over ZMQ, parses it into a Pydantic model, and delegates it to the appropriate Action to be handled, it passes on that message to every Handler attached to the Action and awaits all of them to handle that message. Handler objects can define handling different message types by creating methods named for the message type, e.g. async def handle_display_data. See handlers.DebugHandler or cli.OutputHandler for examples of custom Handlers.
Comms
Comms are a flexible way for a client and the Kernel to send messages outside of the execute_request format. The most widely used package that utilizes Comms is probably ipywidgets, but Comms in general are a very powerful tool for a Sidecar application. A Comm can be opened by either the Sidecar or the Kernel. A target for that Comm should be registered on the other side before the open happens. It's probably most typical to register a Comm target in the Kernel by sending an execute_request, then sending a comm_open from the Sidecar side. See tests/test_comms.py for examples.
Once a Comm is open, it has a unique comm_id. KernelSidecarClient will automatically route all comm_msg messages to a CommHandler instance by comm_id in the comm_msg content. That routing pattern is a bit confusing as it overlaps the Handler / Action pattern, but it's necessary because comm_msg can come in as a result of execute_request's or comm_msg's or potentially other messages. So the CommManager -> CommHandler routing basically needs to be applied to every message the KernelSidecarClient receives over ZMQ.
Models
kernel-sidecar has Pydantic models for:
- The Jupyter Notebook document (
models/notebook.py), which should be consistent withnbformatparsing / structure - Request messages sent to the Kernel over ZMQ (
models/requests.py) - Messages received over ZMQ from the Kernel (
models/messages.py)
CLI
kernel-sidecar ships a small CLI for testing a connection to a Kernel.
❯ sidecar --help
Usage: sidecar [OPTIONS]
Options:
-f FILE Kernel connection file [required]
--debug / --no-debug Turn on DEBUG logging [default: no-debug]
--execute TEXT Execute code string instead of sending
kernel info request
--tail / --no-tail Continue tailing ZMQ after connecting or
executing code [default: no-tail]
--install-completion [bash|zsh|fish|powershell|pwsh]
Install completion for the specified shell.
--show-completion [bash|zsh|fish|powershell|pwsh]
Show completion for the specified shell, to
copy it or customize the installation.
--help Show this message and exit.Try it out by starting an IPython kernel in one terminal and using the CLI in another.
python -m ipykernel_launcher --debug -f /tmp/kernel.jsonkernel-sidecar on release-0.3.2 [$?] is 📦 v0.3.1 via 🐍 v3.11.0 (kernel-sidecar-py3.11)
❯ sidecar -f /tmp/kernel.json
2023-03-10T14:31:59.992235Z [info ] Attempting to connect:
{'control_port': 34897,
'hb_port': 49821,
'iopub_port': 40577,
'ip': '127.0.0.1',
'kernel_name': '',
'key': '615bcebc-baf2e28abad1f6c017dc71dc',
'shell_port': 37421,
'signature_scheme': 'hmac-sha256',
'stdin_port': 41405,
'transport': 'tcp'} [kernel_sidecar.cli] filename=cli.py func_name=main lineno=62
2023-03-10T14:32:00.026503Z [info ] {'banner': 'Python 3.11.0 (main, Nov 7 2022, 09:38:45) [GCC 9.4.0]\n'
"Type 'copyright', 'credits' or 'license' for more information\n"
"IPython 8.10.0 -- An enhanced Interactive Python. Type '?' for "
'help.\n',
'debugger': None,
'help_links': [{'text': 'Python Reference',
'url': 'https://docs.python.org/3.11'},
{'text': 'IPython Reference',
'url': 'https://ipython.org/documentation.html'},
{'text': 'NumPy Reference',
'url': 'https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/'},
{'text': 'SciPy Reference',
'url': 'https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/reference/'},
{'text': 'Matplotlib Reference',
'url': 'https://matplotlib.org/contents.html'},
{'text': 'SymPy Reference',
'url': 'http://docs.sympy.org/latest/index.html'},
{'text': 'pandas Reference',
'url': 'https://pandas.pydata.org/pandas-docs/stable/'}],
'implementation': 'ipython',
'implementation_version': '8.10.0',
'language_info': {'codemirror_mode': {'name': 'ipython', 'version': 3},
'file_extension': '.py',
'mimetype': 'text/x-python',
'name': 'python',
'nbconvert_exporter': 'python',
'pygments_lexer': 'ipython3',
'version': '3.11.0'},
'protocol_version': '5.3',
'status': 'ok'} [kernel_sidecar.cli] filename=cli.py func_name=connect lineno=44❯ sidecar -f /tmp/kernel.json --execute "print('Hello, World'); 1/0"
2023-03-10T14:33:27.394935Z [info ] Attempting to connect:
{'control_port': 34897,
'hb_port': 49821,
'iopub_port': 40577,
'ip': '127.0.0.1',
'kernel_name': '',
'key': '615bcebc-baf2e28abad1f6c017dc71dc',
'shell_port': 37421,
'signature_scheme': 'hmac-sha256',
'stdin_port': 41405,
'transport': 'tcp'} [kernel_sidecar.cli] filename=cli.py func_name=main lineno=62
2023-03-10T14:33:27.629630Z [info ] Hello, World
[kernel_sidecar.cli] filename=cli.py func_name=handle_stream lineno=23
2023-03-10T14:33:27.702700Z [error ] division by zero [kernel_sidecar.cli] filename=cli.py func_name=handle_error lineno=31