Use this to rapidly configure kubernetes contexts using combinations of predfined namespaces and clusters.
The end result will be a generated kube config file under ~/.kube/config based on the namespaces and clusters supplied.
I found myself having to remember which namespace I wanted to deploy Kubernetes resources to so I thought why not create contexts that hard code the namespace.
Now with the generated kube config you can switch contexts and make sure you deploy to the right namespaces.
I'm a big fan of VSCode so here's what the end result looks like using the Kubernetes Extension.
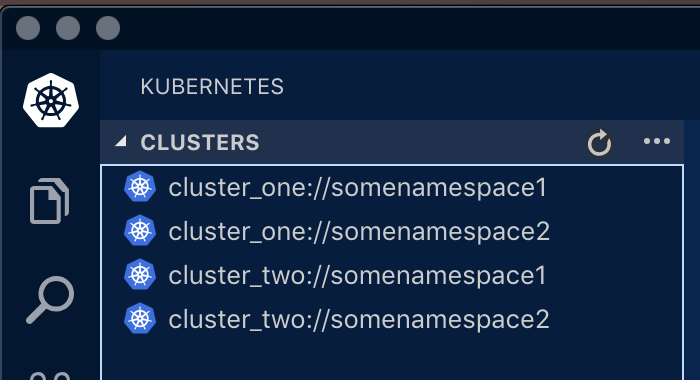
To use the contexts with VSCode you'll need
The extension will install kubectl and Helm Client for you if it can't find them.
We need to several files to be able to configure the Kubernetes contexts.
- JSON Config
- JSON Auth-Cluster Mapping
- GPG encrypted tokens (single file per cluster)
You can use the Example-Run.sh to try it out. The script will
- boilerplate files
- maps.json
- config.json
- Run the docker image as per below
- Delete the docker image
- Save/hack together your config.json (Example below)
- Hack together your maps.json (Example below)
- Run the docker command below to generate a new
~/.kube/configfile in your home directory
Important Note! This will backup your existing config and create a new one. It will not merge the two (To-do list!).
You must substitute your own paths leaving the container paths the same.
docker run --rm \
-v /Users/rhysevans/.kube:/root/.kube \
-v /Users/rhysevans/config.json:/root/config.json:ro \
-v /Users/rhysevans/maps.json:/root/maps.json:ro \
rhysjtevans/k8s-context:latest
The JSON keys must match and must exist for each cluster in the JSON config payload.
{
"cluster_one": {
"Server": "https://api.cluster1.local",
"Token": "<TOKEN/GUID>"
},
"cluster_two": {
"Server": "https://api.cluster2.local",
"Token": "<TOKEN/GUID>"
}
}
{
"kubernetes": {
"cluster_one": [
{
"groups": {
"managed": [
"somenamespace1-somegroup1",
"somenamespace2-somegroup2"
],
"non-managed": [
"somenamespace3-somegroup3"
]
},
"token-ending": "xxxxxx",
"username": "userid"
}
],
"cluster_two": [
{
"groups": {
"managed": [
"somenamespace1-somegroup1",
"somenamespace2-somegroup2"
],
"non-managed": [
"somenamespace3-somegroup3"
]
},
"token-ending": "xxxxxx",
"username": "userid"
}
]
}
}