GbmExplainR is a package to decompose gbm predictions into feature contributions. There is also functionality to plot individual trees from the models and the route for a given observation through the tree to a terminal node. GbmExplainR works with the gbm package.
GbmExplainR is based off the treeinterpreter Python package, there a blog post on treeinterpreter here.
Let's look at the predicted value from a gbm. Note this model is the first example from ?gbm.
predict(gbm1, data[1, ], n.trees = gbm1$n.trees)## [1] 1.575326
For a given prediction from a gbm, the feature contributions can be extracted;
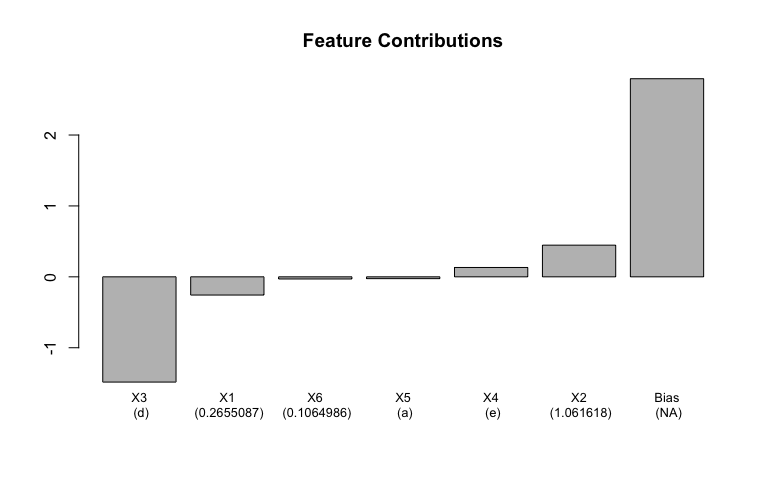
decompose_gbm_prediction(gbm = gbm1, prediction_row = data[1, ])## variable contribution variable_value variable_class
## 1 X3 -1.48439005 d ordered, factor
## 2 X2 0.44671068 1.061618 numeric
## 3 X1 -0.25693447 0.2655087 numeric
## 4 X4 0.13191849 e factor
## 5 X6 -0.03038647 0.1064986 numeric
## 6 X5 -0.02561677 a factor
## 7 Bias 2.79402449 <NA> NA
Notice how the feature contributions sum to give the predicted value.
These can be charted with a simple barchart;
plot_feature_contributions(feature_contributions = decompose_gbm_prediction(gbm1, data[1, ]),
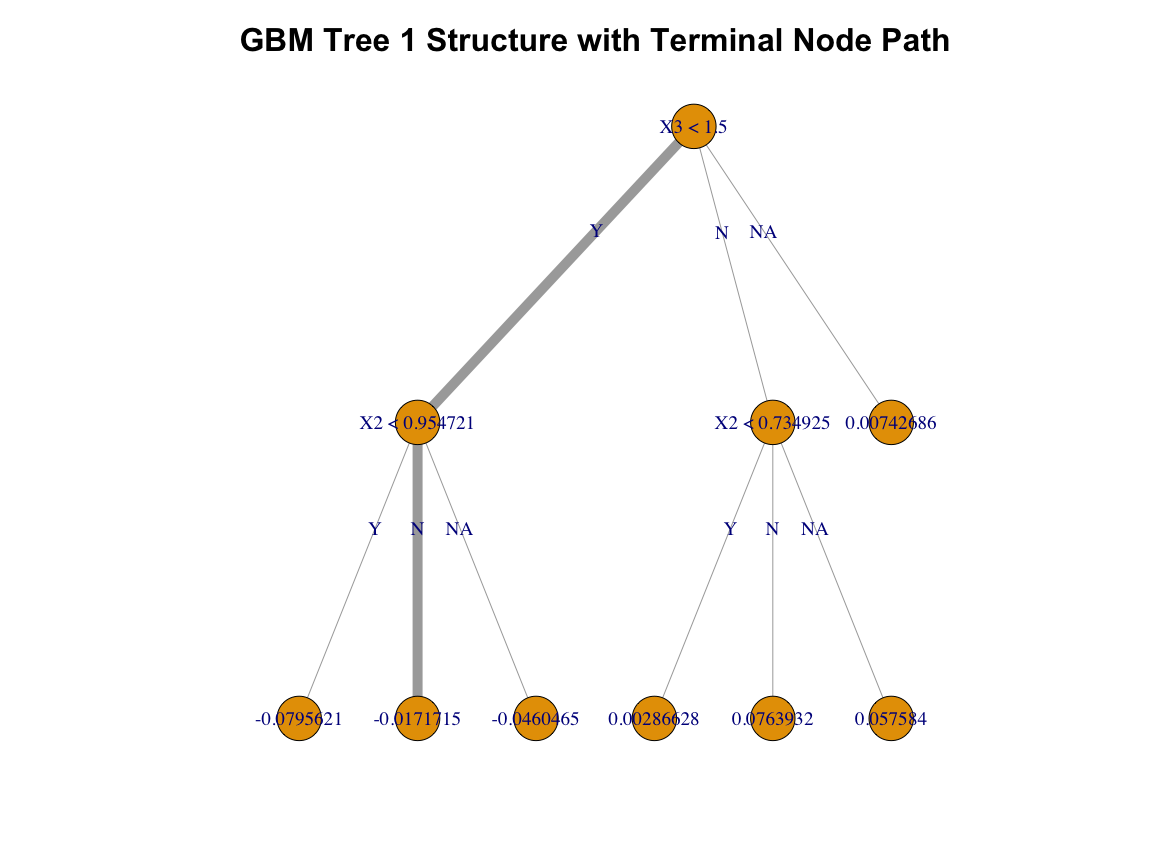
cex.names = 0.8)Individual trees can be plotted, and the route to a terminal node can be highlighted for a given observation;
plot_tree(gbm = gbm1,
tree_no = 1,
plot_path = data[1, ],
edge.label.cex = 1.2,
vertex.label.cex = 1.2) Install form Github with devtools;
library(devtools)
devtools::install_github(richardangell/GbmExplainR)There are other similar packages in R and Python that implement the same method for a variety of tree based models;
- treeinterpreter Python package implements prediction decomposition for decision tree, random forests and extra tree models in scikit-learn
- eli5 Python package contains an explain_predictions function to do prediction decomposition for various models
- xgboostExplainer implements prediction decomposition for xgboost models from R