This is a set of supplementary (ruby language) tools for use with Andrew Goldberg's CSA weighted bipartite matching solver.
Included here are the following:
-
generate_matching - The main driver script. Take a DIMACS-format graph file containing a weighted bipartite graph, augment the graph, run the CSA solver, and deaugment the resulting matching. I.e., solve a matching, doing whatever you have to do behind the scenes.
-
generate_augmented_graph - command-line tooling to take a weighted bipartite graph, contained in a Dimacs-format graph file, and produce an augmented graph in another Dimacs-formatted graph file. The augmented graph is guaranteed to have a perfect matching.
-
deaugment_matching - command-line tooling to take a CSA matching on an augmented graph and convert that matching to the analogous matching on the original (unaugmented) graph.
$ git clone https://github.com/rick/CSA
$ cd CSA
$ script/setup
$ export CSA_PATH=`pwd` # used by generate_matching
$ cd ..
$ git clone https://github.com/rick/CSA-tools
$ cd CSA-tools
$ gem install bundler
$ bundle install
$ bundle exec bin/generate_matching spec/fixtures/10-node-graph.txt solution-to-10-node-matching.txt
Wrote augmented graph file: /var/folders/r3/60vtc6hx3yq29ny76xms5bym0000gp/T/d20160604-36664-155kjni/augmented_graph.txt
===== Precise costs; Stack ordering; Quick minima; NUM_BEST = 3 =====
==========================================================================
|> n = 20, m = 50, sc_f = 10
|> cost -1100, time 0.000 seconds
|> 11 refines: 0% 290 relabelings
|> 180 double pushes, 470 pushes
|> 110 list rebuilds, 0 full scans, 180 avoided scans
==========================================================================
Processing matching file [/var/folders/r3/60vtc6hx3yq29ny76xms5bym0000gp/T/d20160604-36664-155kjni/output.flow]. Original problem had 5 source nodes and 10 total nodes...
Keeping match [1, 13, 18] -> [1, 8, 18]
Keeping match [2, 14, 29] -> [2, 9, 29]
Keeping match [3, 11, 36] -> [3, 6, 36]
Keeping match [4, 15, 410] -> [4, 10, 410]
Keeping match [5, 12, 57] -> [5, 7, 57]
Discarding match [6, 16, 16]
Discarding match [7, 20, 57]
Discarding match [8, 18, 38]
Discarding match [9, 17, 29]
Discarding match [10, 19, 410]
generated output file in [solution-to-10-node-matching.txt]
$ cat solution-to-10-node-matching.txt
f 1 8 18
f 2 9 29
f 3 6 36
f 4 10 410
f 5 7 57
$ bundle install
$ rake
CSA presumes that the graph provided as input contains a perfect matching. If no such matching exists the solver will either not terminate, or can produce a non-optimal matching. (There are notes in the code to the effect that it would be possible to modify the solver to deal with this case, but that work was apparently never undertaken.)
In conversations with Andrew V. Golberg, he provided an algorithm for converting a bipartite graph which might not have a perfect matching into a graph which will have a perfect matching, and from which a solution to the perfect assignment problem on the augmented graph can be transformed into a maximum cardinality minimum cost matching on the original graph.
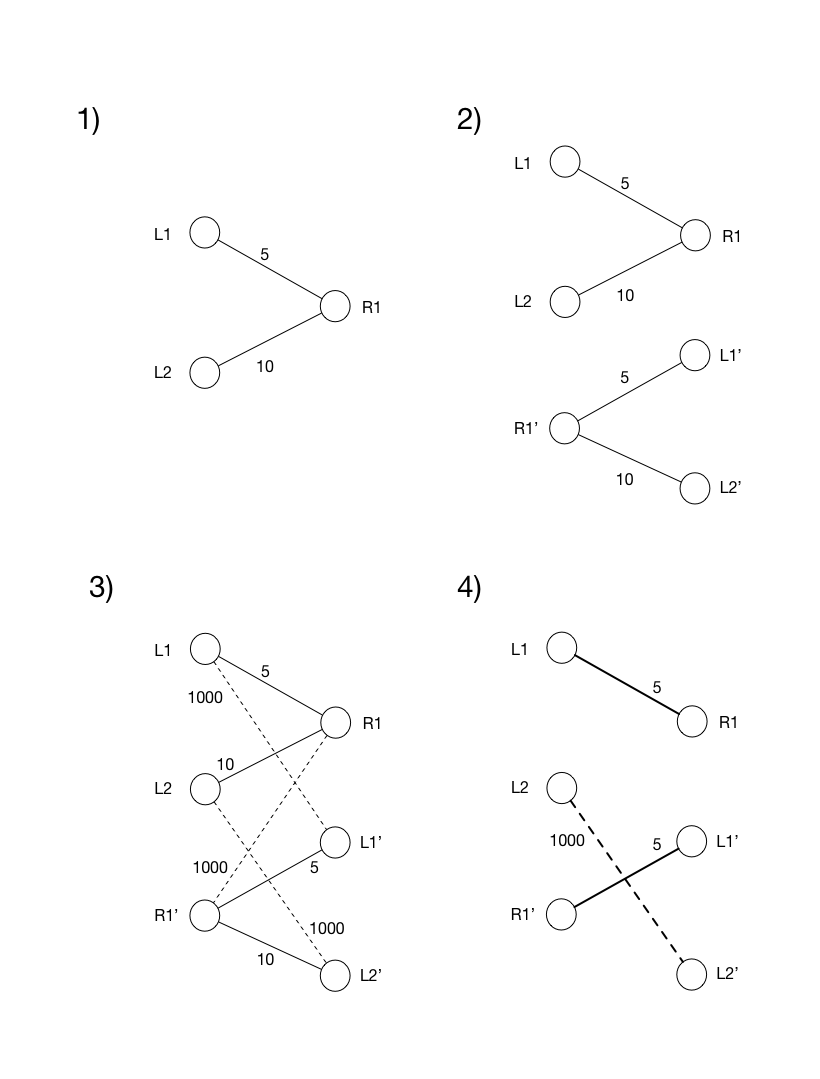
The algorithm is as follows.
Given a weighted bipartite graph G, with n vertices and m weighted edges, construct an augmented graph G' with 2n vertices and 2m+n edges:
- Take the vertices and edges of the original graph
G, and add a flipped copy ofG: vertices on the left side copied to the right side, and vice versa. Copy the edges with weights. - Add high-cost edges between each original node and its flipped copy.
An illustration may help:
From the matching on the augmented graph, we can take those original nodes from G which matched with other original nodes from G as the desired matching. Note that nodes from G which matched via high-cost edges (necessarily with their complement nodes in the flipped graph) are unmatched nodes in the solution.
The generate_augmented_graph script creates an augmented graph from an input weighted bipartite graph, while deaugment_matching will take a matching for an augmented graph, and translate it back to a matching on the original input graph. The generate_matching script automates the process of augmenting, running the solver, and deaugmenting the final matching.