The purpose of this document is to provide instructions on how to use the Azure Automation to execute scripts inside Linux Virtual Machines. In this lab scenario, the Linux VM will be runing on Azure and the connection from the Azure Automation to the VM will be done through the public IP of the VM. The script to be executed will be a simple command to stop the Nginx service.
First of all, you need to have an Automation Account. In order to have this, follow those steps:
- Create a resource group called rg-automation;
- Create an automation account on the resource group previously created;
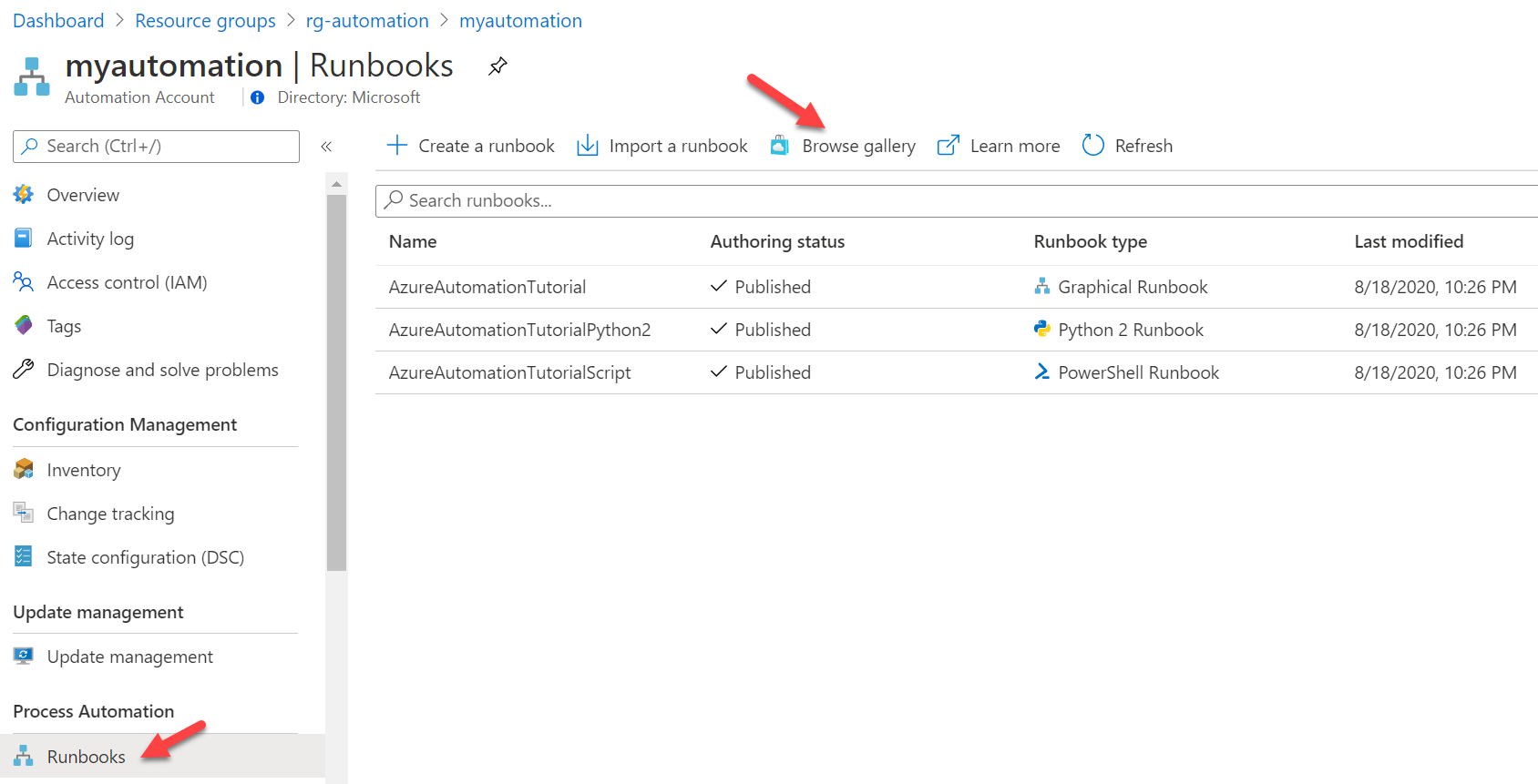
Now you have your automation account created, go to Process Automation > Runbooks > Browse gallery and lets import a Runbook:
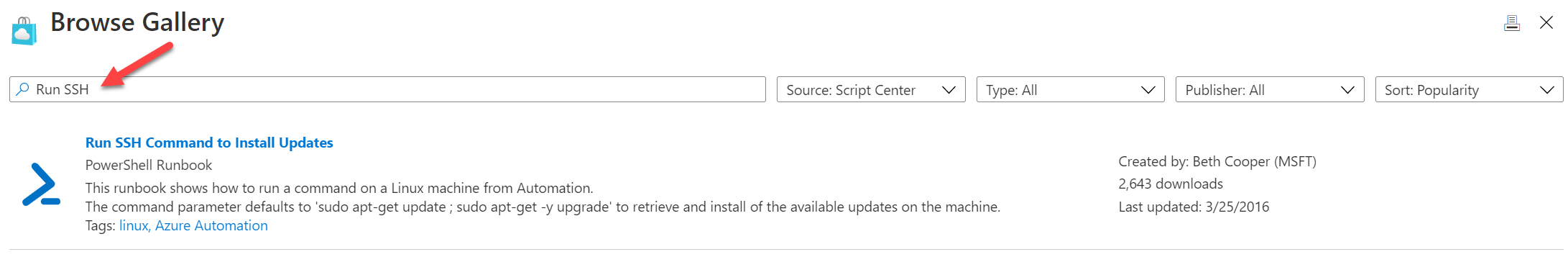
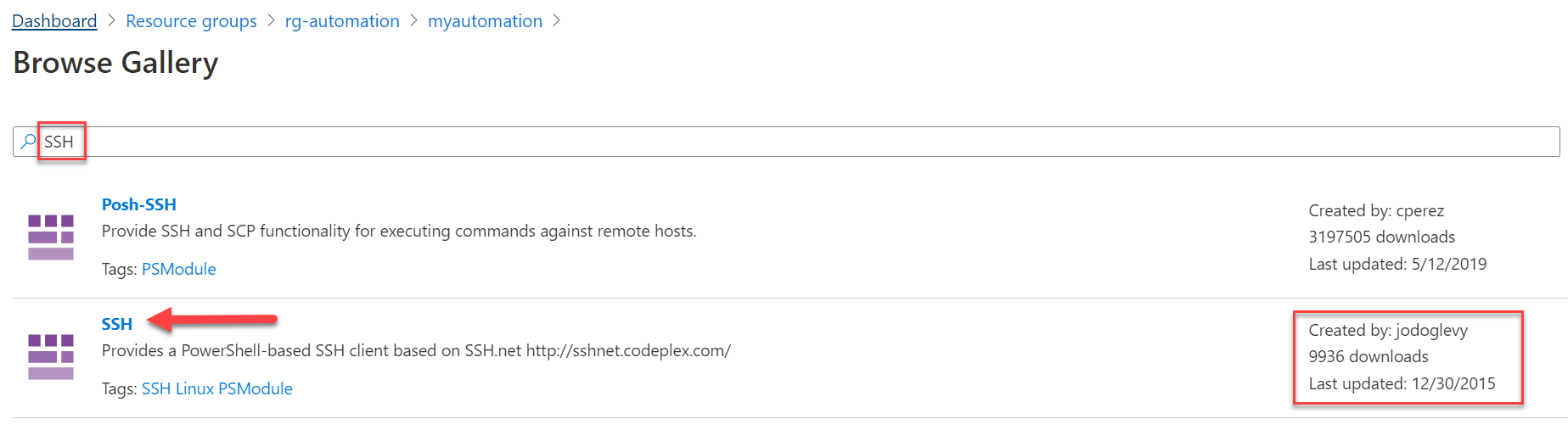
Then search by Run SSH:
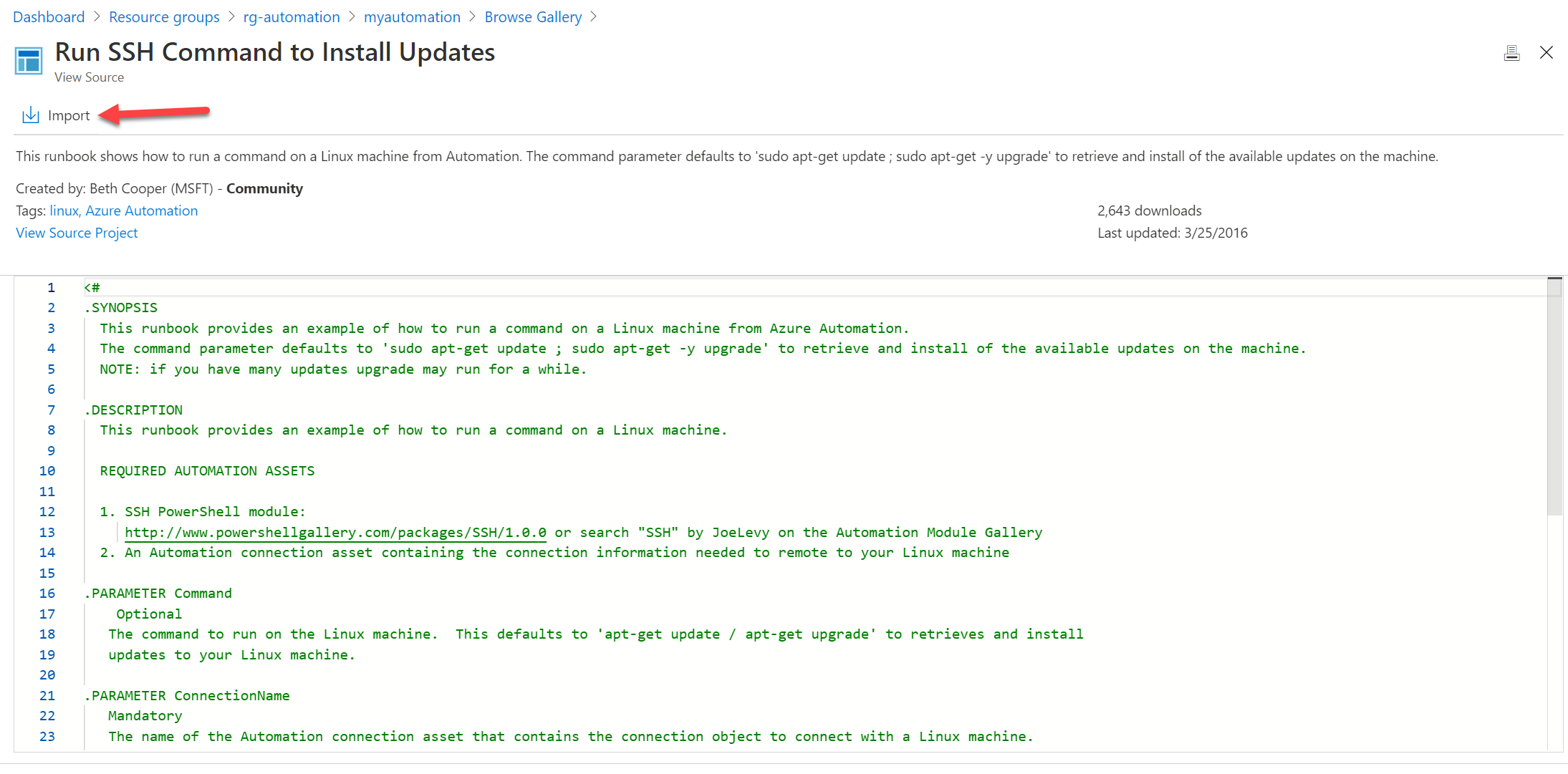
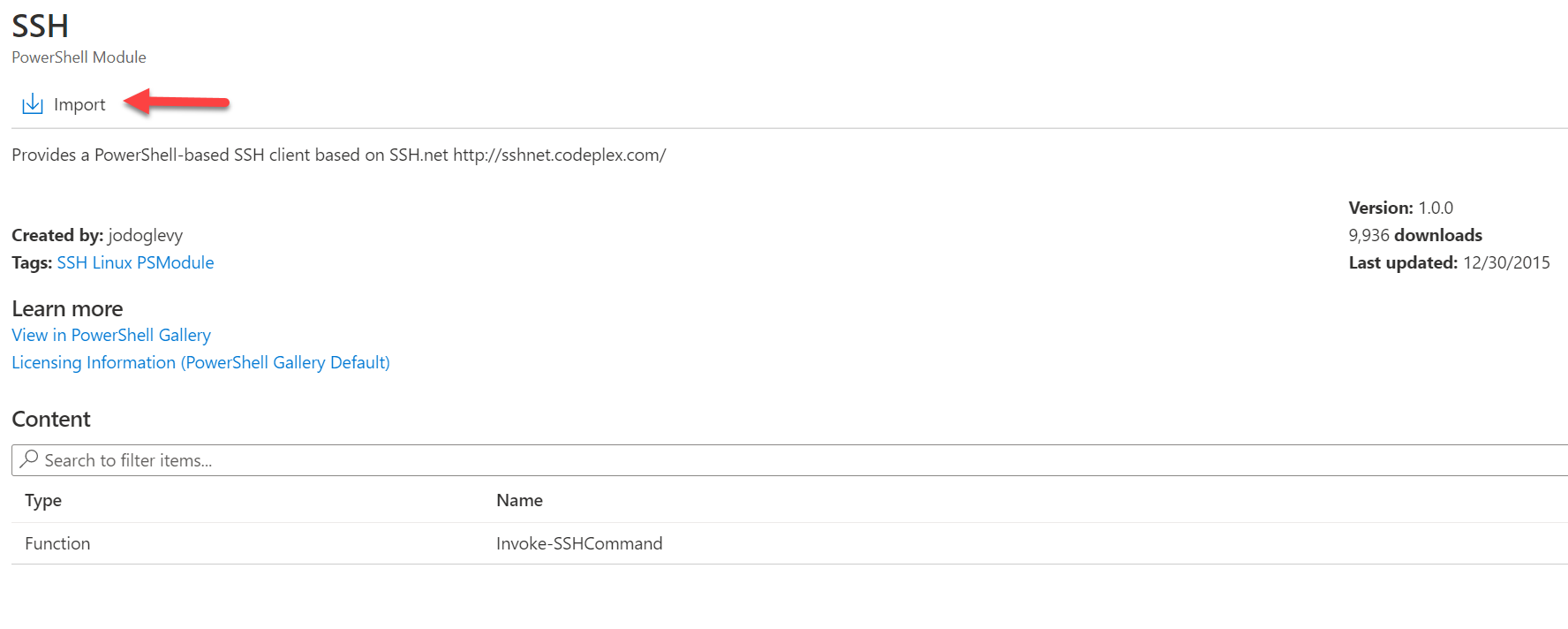
Click to import:
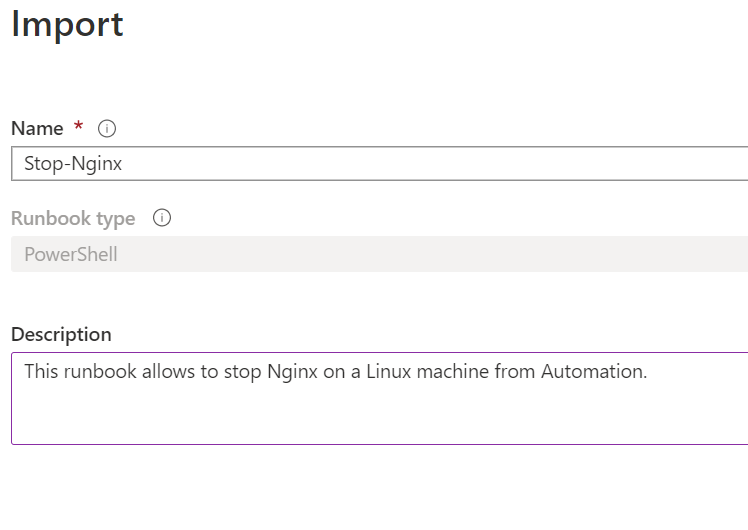
Now let's start with some changes. I'll change the name in order to be more acurated with the function desired (command or script to be executed). I'll rename the name to Stop-Nginx and create an appropriated description:
Finishing the importing:
Now we have a new runbook available:
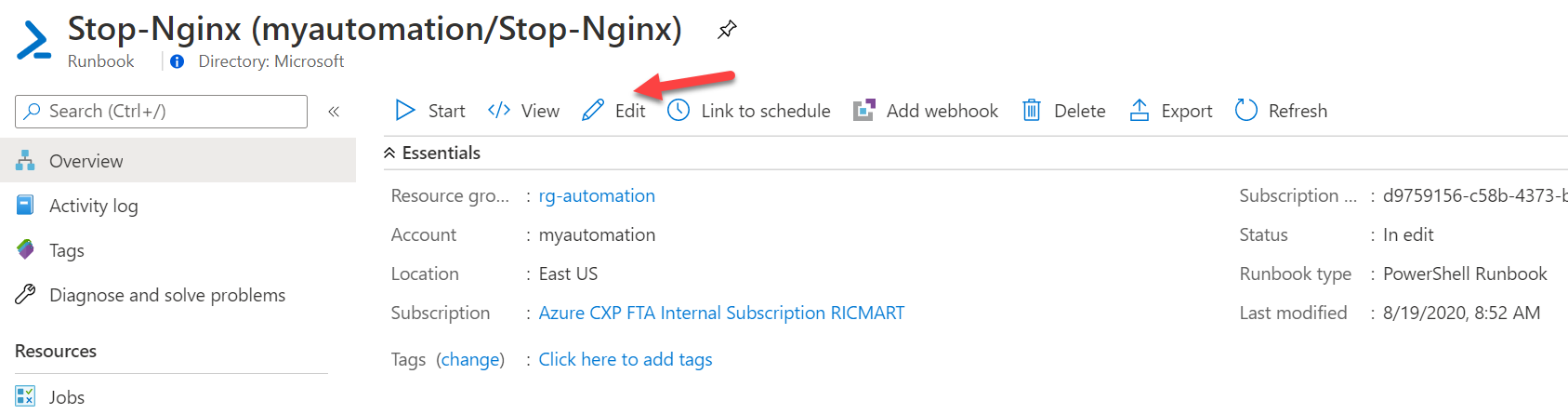
Let's go to Overview > Edit and click:
And so we'll customize the runbook. Change the original content to this one:
<#
.SYNOPSIS
This runbook provides an example of how to run a command on a Linux machine from Azure Automation.
The command parameter defaults to 'sudo /bin/systemctl stop nginx' to stop the Nginx service on the machine.
.DESCRIPTION
This runbook provides an example of how to run a command on a Linux machine.
REQUIRED AUTOMATION ASSETS
1. SSH PowerShell module:
http://www.powershellgallery.com/packages/SSH/1.0.0 or search "SSH" by JoeLevy on the Automation Module Gallery
2. An Automation connection asset containing the connection information needed to remote to your Linux machine
.PARAMETER Command
Optional
The command to run on the Linux machine. This defaults to 'sudo /bin/systemctl stop nginx' to stop the Nginx service on the machine.
.PARAMETER ConnectionName
Mandatory
The name of the Automation connection asset that contains the connection object to connect with a Linux machine.
.NOTES
LASTEDIT: August 19, 2020
#>
Param (
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)]
[string] $Command = "/bin/systemctl stop nginx.service",
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[string] $ConnectionName
)
$Conn = Get-AutomationConnection -Name $ConnectionName
$CommandScriptBlock = [scriptblock]::Create($Command)
Invoke-SSHCommand `
-Connection $Conn `
-ScriptBlock $CommandScriptBlock
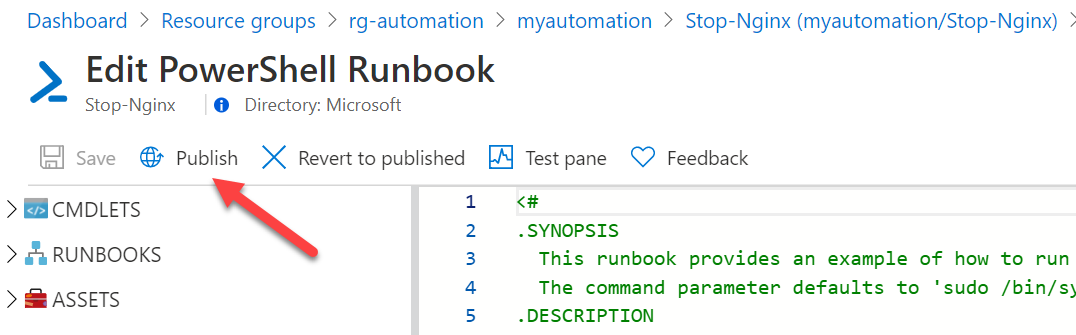
Then click to save:
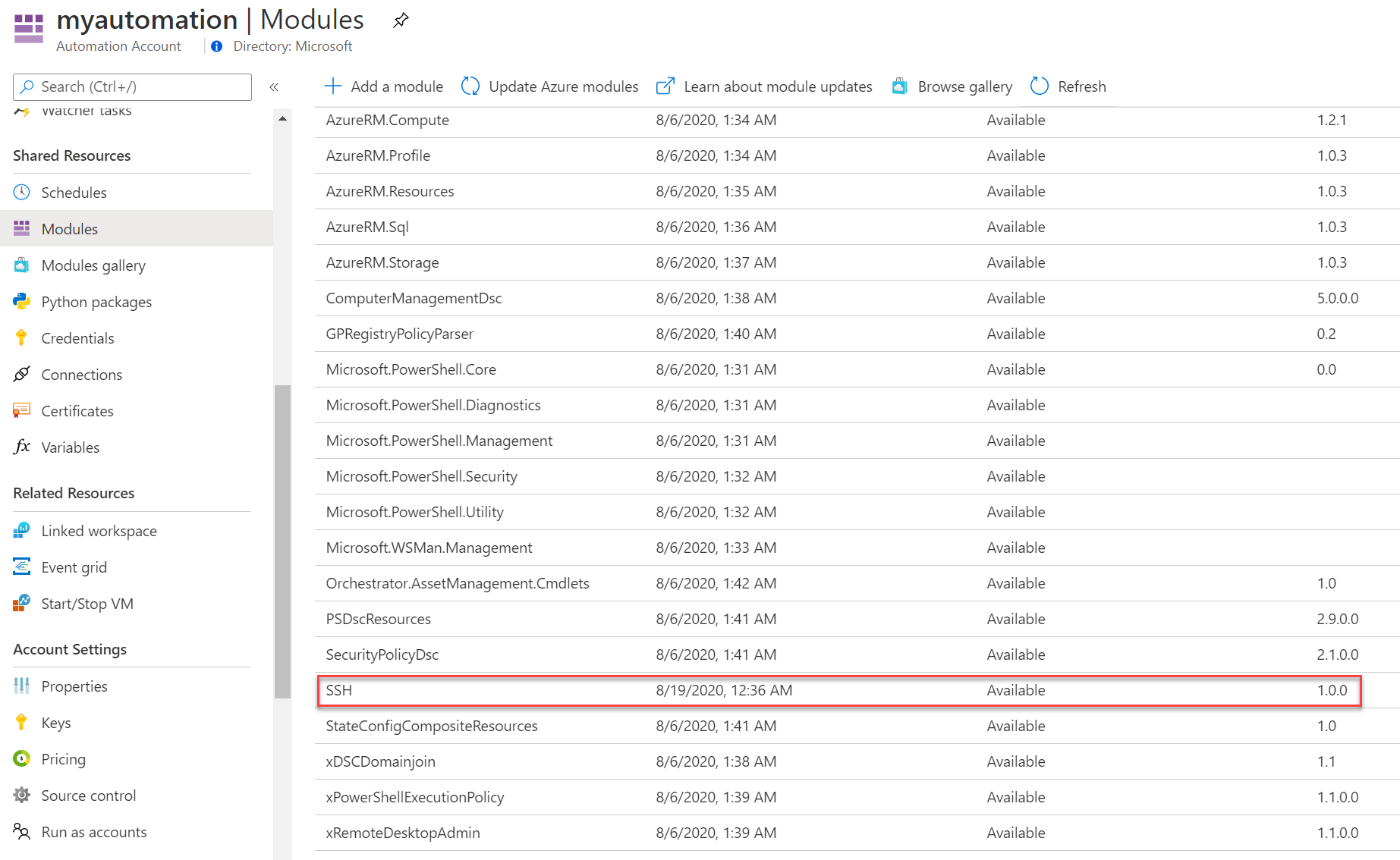
Now, the next step is to add the SSH Module to Stop-Nginx runbook. Go to Automation Account menu, then Shared Resources > Modules. Then click at Browse Gallery and type SSH:
Now click to import this PowerShell SSH Module:
Click to OK so in a few moments the PowerShell SSH Module will be available:
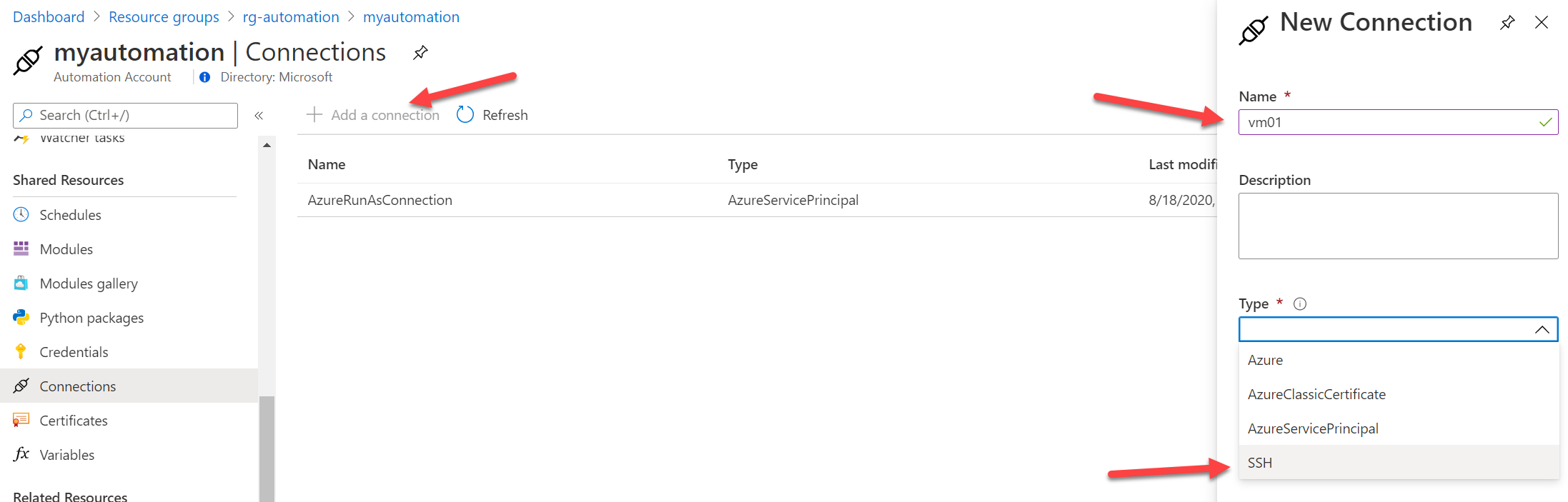
Now we need to create the SSH connection for the Automation Account. So on the Automation Account menu, under Shared Resources go to Connections then click to + Add a connection, set a name and choose *SSH:
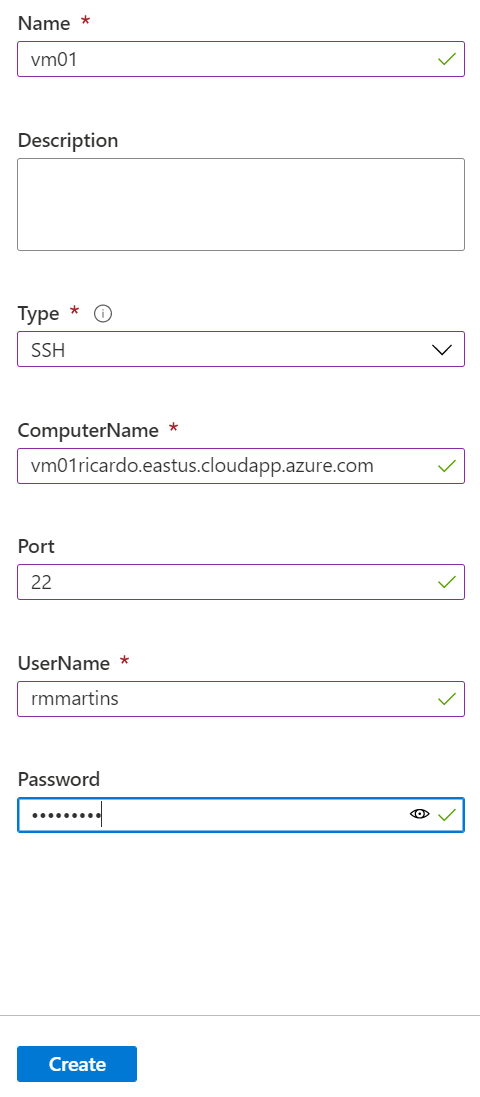
Now you have to set the connection parameters and click to Create
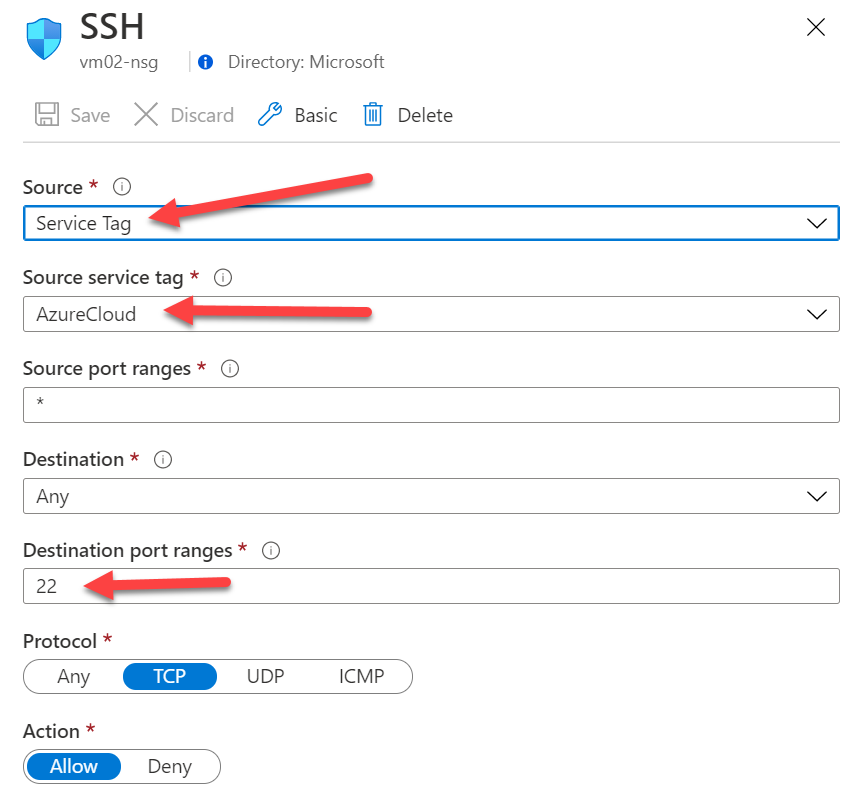
Now we need to create a rule to allow the VM be accessed through SSH using the port 22 from the Azure Cloud, in this case, from the Azure Automation running on Azure. To do this, you can go to the Network Security Group attached to the VM network interface or VM subnet then create a rule as below:
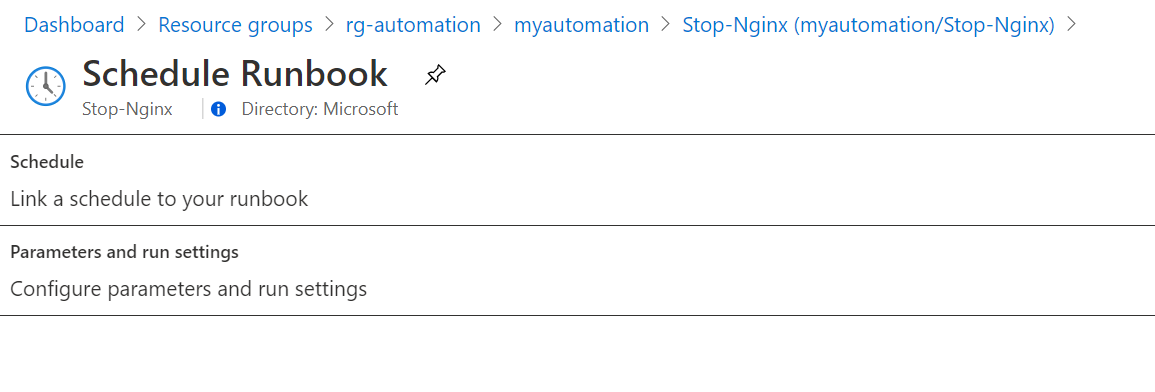
Now let's publish the runbook so we will be able to set their schedule. Go to the Automation Account > Process Automation > Runbooks. Then select the runbook called Stop-Nginx then click to edit:
Then click to Publish:
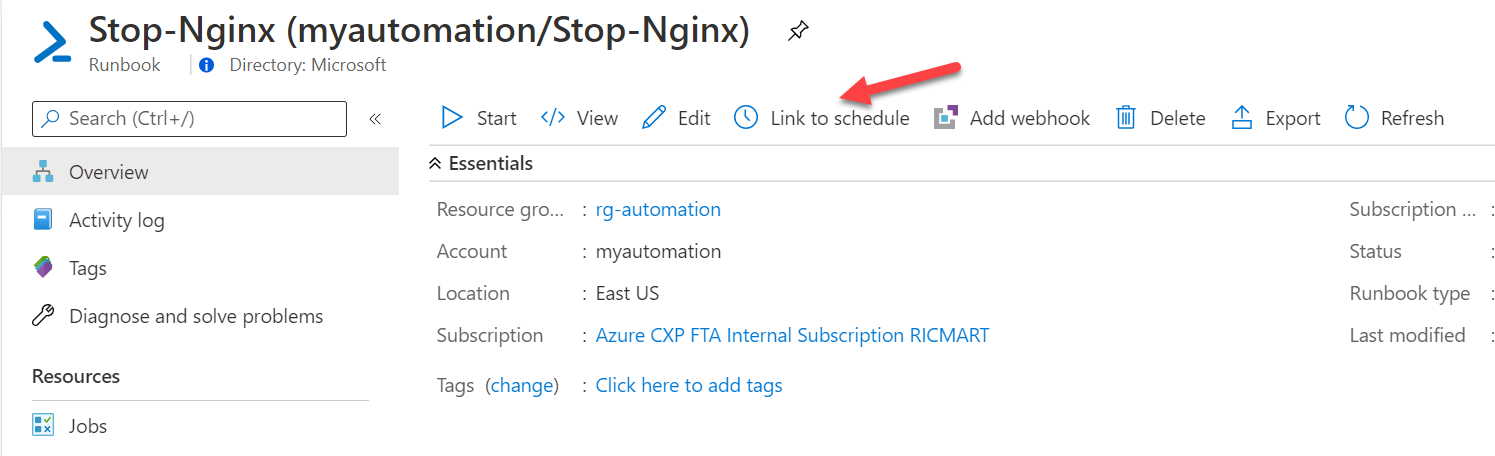
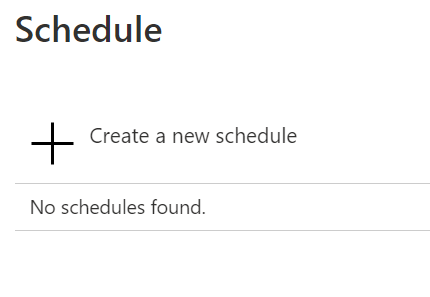
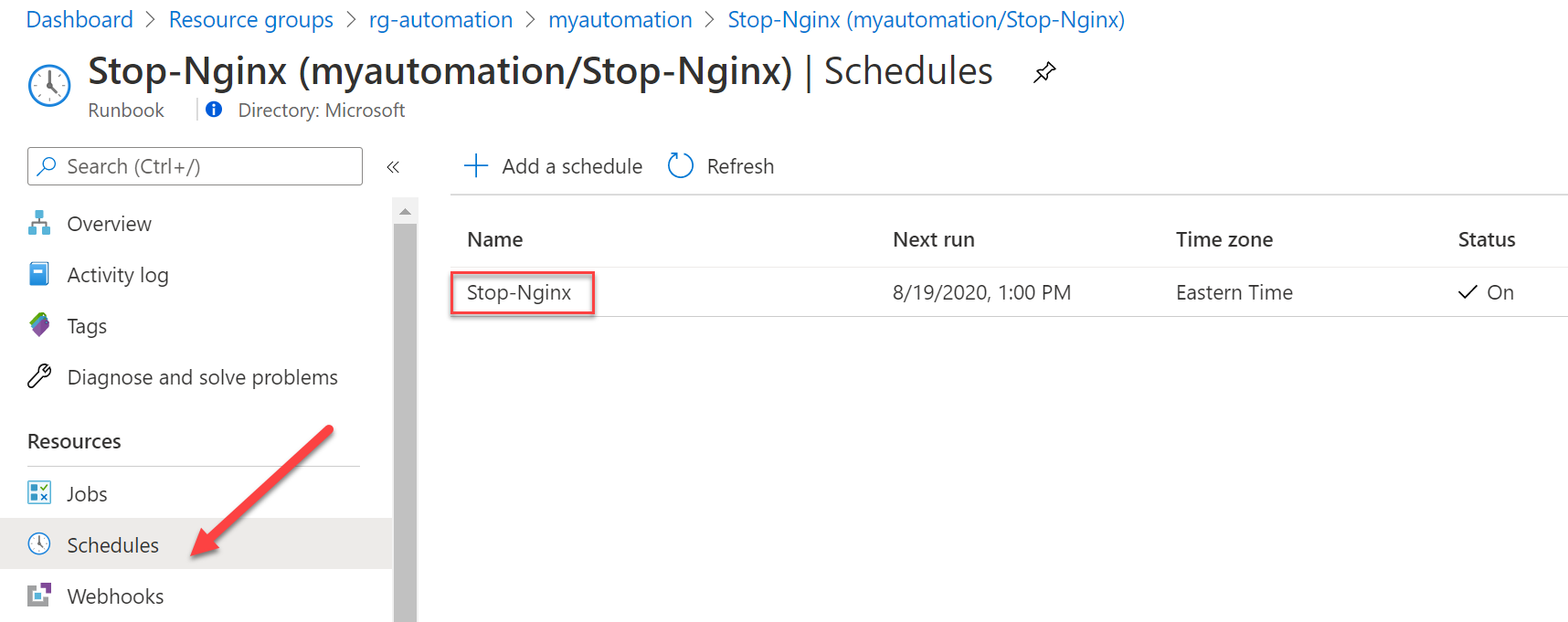
Now let's set the schedule. Click at Link to schedule:
And in the next screen we'll have something like this:
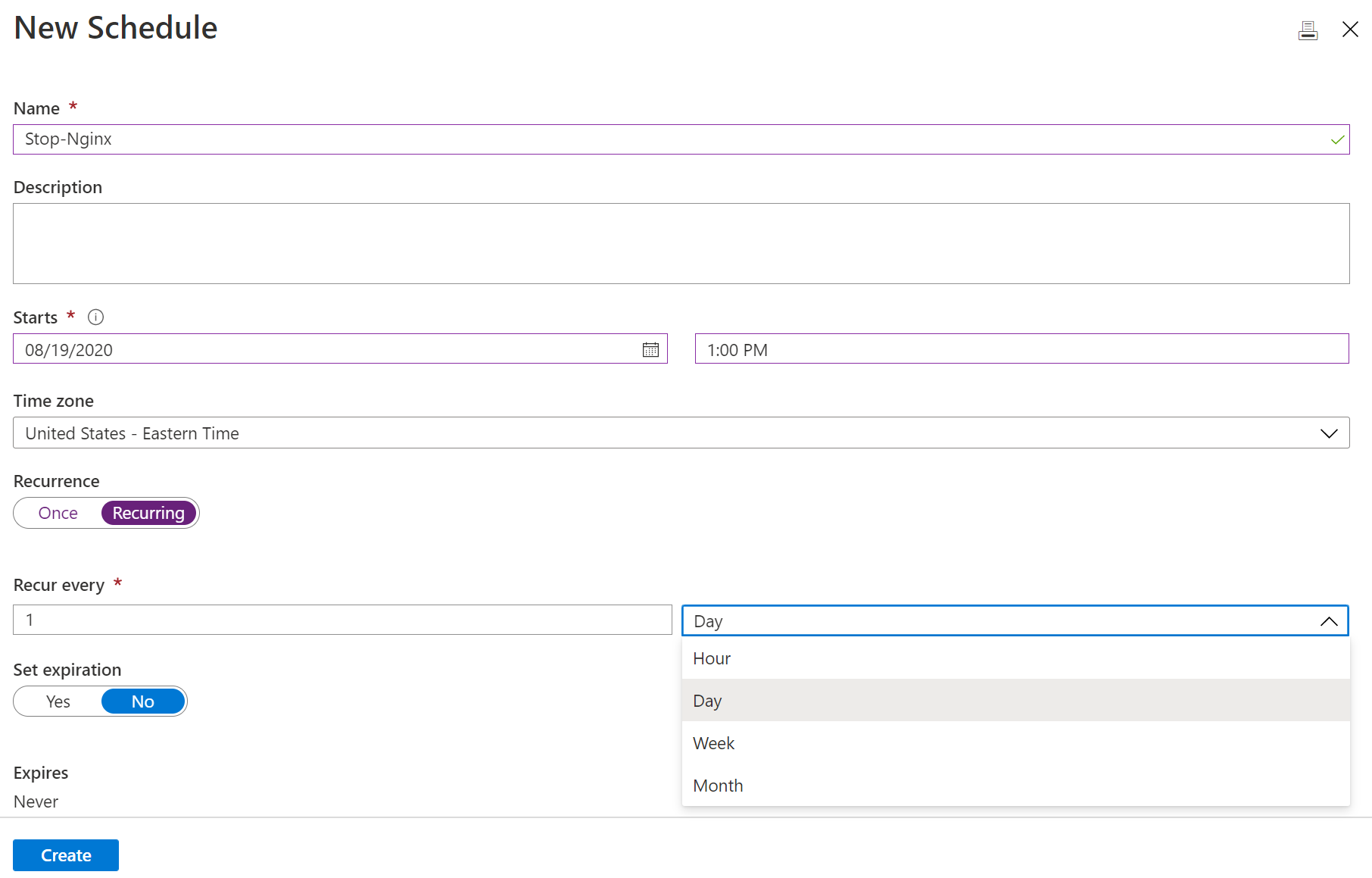
So click at Create a new schedule:
And you must define the schedule details and then click to Create:
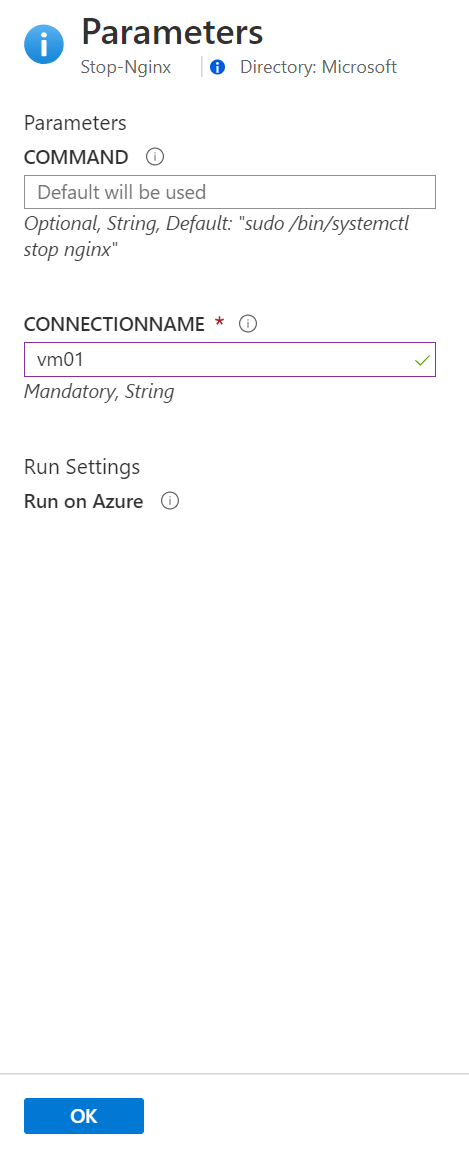
For the next step, we will define the runbook parameters and the execution settings. By default will be running the default command already present at the runbook, so you can leave the COMMAND field in blank. At the field CONNECTIONNAME you must type the name of the connection created earlier with the VM Name, SSH port to be used, username and password.
Now you can execute the runbook manually to validate the execution, or, wait until the runbook be executed at the schedule.
There are some Linux distributions where in the /etc/ssh/sshd_config is missing the KexAlgorithms to describe which methods are supported by the SSH daemon. On those scenarios when trying to execute the runbook, the execution can fail presenting some message litke this:
Exception calling "Connect" with "0" argument(s): "An established connection was aborted by the software in your host
machine."
At C:\Modules\User\SSH\SSH.psm1:68 char:5
+ $SSHConnection.Connect()
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : NotSpecified: (:) [], MethodInvocationException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : SshConnectionException
Exception calling "RunCommand" with "1" argument(s): "Client not connected."
At C:\Modules\User\SSH\SSH.psm1:69 char:5
+ $ResultObject = $SSHConnection.RunCommand($ScriptBlock.ToString() ...
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : NotSpecified: (:) [], MethodInvocationException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : SshConnectionException
You can check also on the /var/log/messages of the VM some kind of mesage like this
ssh_dispatch_run_fatal: Connection from XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX port XXX: DH GEX group out of range [preauth]
To solve, you need to
- Add the following at the end of /etc/ssh/sshd_config:
KexAlgorithms=diffie-hellman-group14-sha1
- Restart the SSHD:
sudo systemctl restart sshd
This sample was created based on the following SSH module for PowerShell: https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/scriptcenter/SSH-PowerShell-Module-17616e1a