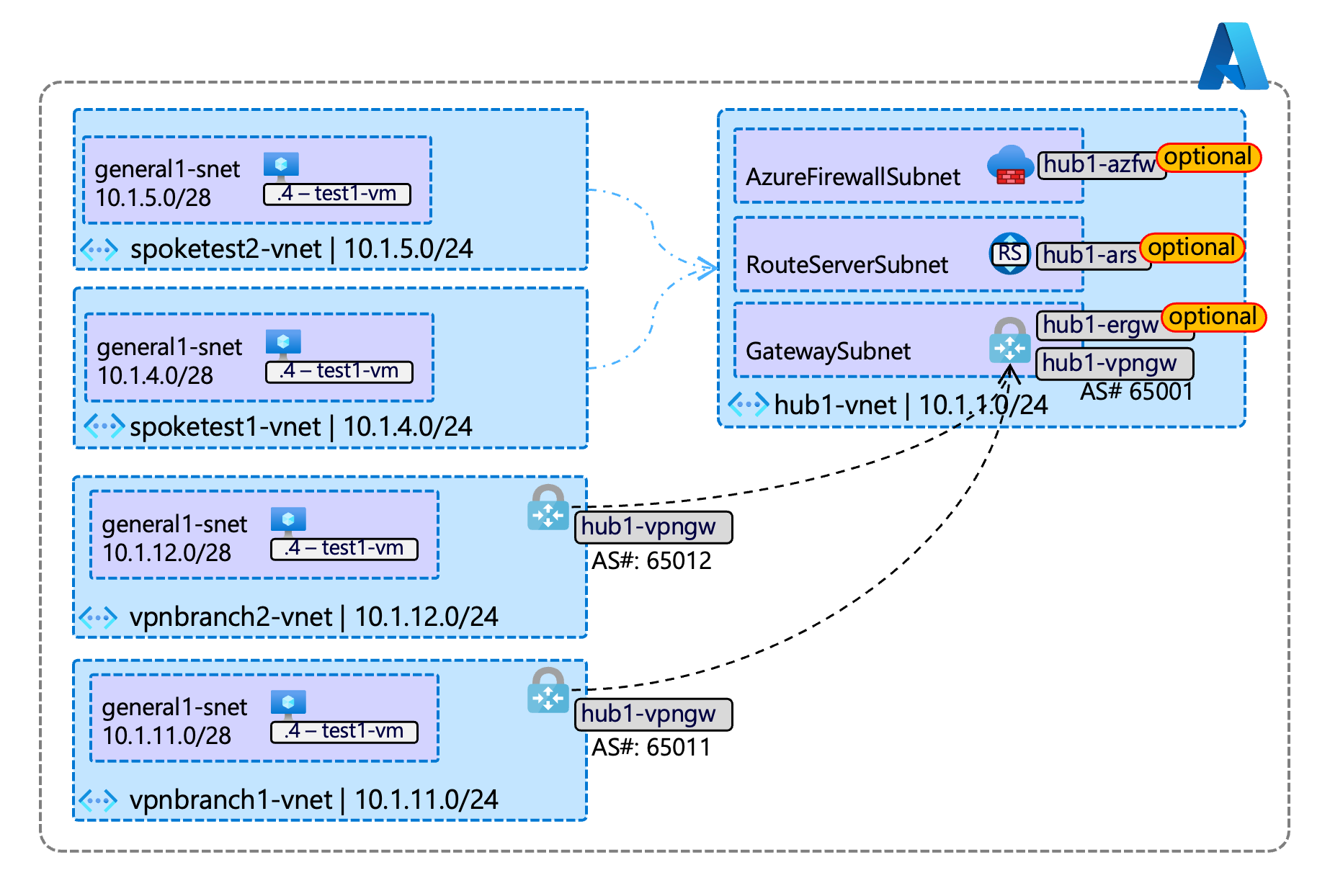
- About this repository
- IaaS components
- Usage note - Terraform directory structure
- Usage note - Github Actions workflow and branches
- Prerequisites and setup procedures
Two main features:
- Terraform code to deploy a common Azure IaaS test environment, based on reference hub-and-spoke architecture.
- Deployment and destroy workflow with Github Actions
Aside from providing a quickly deployable repository, it also serves as a reference of what a CD workflow on Azure could look like.
Development backstory and the whys are provided in DEVNOTES.md for those who are interested.
- Generic hub capable of VPN/ER gateways, Azure Firewall, and Route Servers
- Test VNET-peered spokes with a VM in each to test connectivity
- Test S2S-IPSec spokes to simulate BGP-enabled branches, to study route propagation behaviors (subject to VPN gateway limitations)
Github Actions workflow will only deploy artifacts in [./main] folder.
It contains declarative part of the code and call modules if needed.
Included sample resources are broken into an independent files so user can selectively delete or move unnecessary resources to [./main-nodeploy] folders.
Terraform Deploy workflow deploys the code. It is set to trigger at push for [dev*] branches for rapid development. One can also spin up another set of environment quickly by simply creating another [devN] branch and push - as the workflow uses branch name as part of resource group prefix.
In my use case, [main] branch is being used as a known good code storage.
Terraform Destroy workflows are self-explanatory.
azcli-nukeit destroy the environments by means of using Azure CLI to directly delete resource groups and state blob in case Terraform Destroy workflow fails.
The workflow requires following Github repository secrets. This can be defined in Github repo > Settings > Secrets and variables > Actions > "New repository secrets"
Gather these values as you proceed through below steps
| Secret name | Value | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| ARM_TENANT_ID | Target Entra ID Tenant ID | for Terraform authentication to Azure |
| ARM_CLIENT_ID | Service Principal (appId) | for Terraform authentication to Azure |
| ARM_CLIENT_SECRET | Service Principal secret (password) | for Terraform authentication to Azure |
| ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID | Target subscription ID | |
| TFSTATE_CONTAINER_NAME | Set to 'tfstate' | Container name for Terraform state. |
| TFSTATE_RESOURCE_GROUP | Resource Group name containing Storage Account for Terraform state | |
| TFSTATE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT | Name of the Storage Account containing Terraform state |
This Terraform workflow opt to use Azure blob backend.
- create an Azure Storage Account
- create a container 'tfstate' within the Storage Account
In this step we will create a service principal in your Entra ID tenant for Terraform to authenticate into Azure as.
Below is a sample Azure CLI script to accomplish this setup. Make sure your bash shell is authenticated and Azure CLI is pointing to the target Entra ID tenant.
APPDISPLAYNAME="githubactions1-sp"
SUBSCRIPTIONID="<masked>"
az ad sp create-for-rbac --display-name=$APPDISPLAYNAME --scopes="/subscriptions/$SUBSCRIPTIONID" --role="Contributor"Take note the values [AppId, password, tenant] from these output.
{
"appId": "<masked>",
"displayName": "pngithubactions1-sp",
"password": "<masked>",
"tenant": "<masked>"
}Set shell variables with the Resource Group and Storage Account name created in Step 1.
TFSTATE_RESOURCE_GROUP="resourcegroupname"
TFSTATE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT="storageaccountname"
SPOBJID=$(az ad sp list --display-name=$APPDISPLAYNAME --query="[].id" -o tsv)
az role assignment create \
--role="Storage Blob Data Contributor" \
--assignee-object-id=$SPOBJID \
--assignee-principal-type="ServicePrincipal" \
--scope="/subscriptions/$SUBSCRIPTIONID/resourceGroups/$TFSTATE_RESOURCE_GROUP/providers/Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts/$TFSTATE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT"At this point you should have all of the required value to setup Github secrets.