El Gamal encryption is public-key cryptosystem which uses asymmetric key encryption for communicating between two parties and encrypting the message.
Let’s understand the idea using a simple example :
Suppose Tommy wants to communicate with Arthur,
- Arthur will generate his public and private keys :
- He will choose a very large number q and a cyclic group Fq.
- From the group, he will choose two elements g and a such that GCD(q , a) = 1.
- Computes h = g^a.
- He then publishes F,h = g^a, q and g as his public key and a as private key.
- Tommy encrypts the data using Arthur’s public key :
- Tommy selects an element k from cyclic group F such that GCD(q,k) = 1.
- Then, he computes p = g^k and s = h^k = g^(ak).
- Multiples s with M.
- Then sends (p,M*s) = (g^k,M*s).
- Arthur decrypts the message :
- Arthur calculates s’ = p^a = g^(ak) .
- He divides M*s by s’ to obtain M as s = s’.
Original Message : How you doing ?
g used : 3363096353293157562289557815414368823473456377149
h = g^a used : 2701504145817056170075118532332297466311764362629
g^k used : 8234195178917799691733309775548171597753240706569
g^(ak) used : 10266653404741035243347135758407606546946688712689
Decrypted Message : How you doing ?
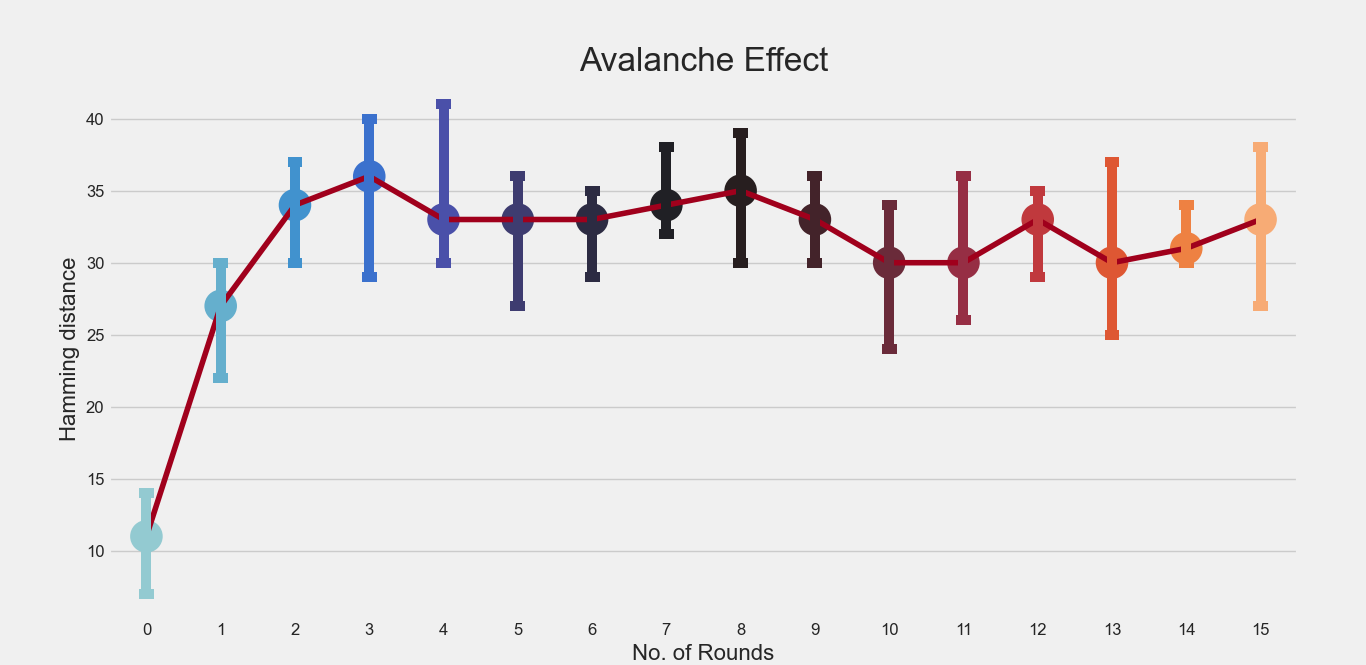
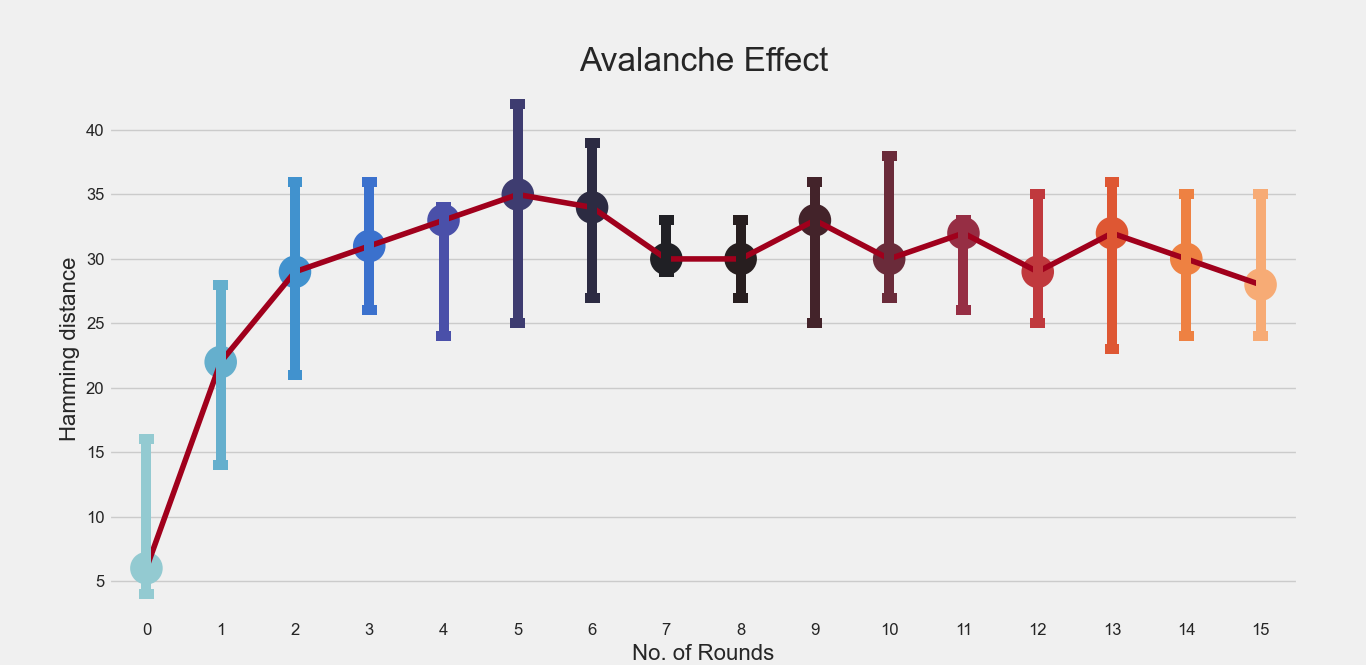
Perform experiments to explore the Avalanche Effect progression across the DES rounds. Use (i) 5 different plaintexts (ii) 5 different Hamming distances (HD) (iii) 5 different secret keys. Report plots of HD against round number.
Avalanche Effect : A desirable property of any encryption algorithm is that a small change in either the plaintext or the key should produce a significant change in the ciphertext. In particular, a change in one bit of the plaintext or one bit of the key should produce a change in many bits of the ciphertext.
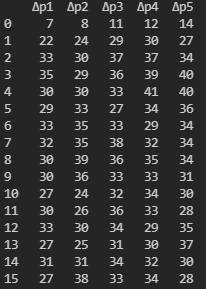
The original plaintext : “10100100” (64 bit string)
The original Key : "00011100" (64 bit string)
text_list = ["±0100100", "ñ0100100", "60100100", "Á0100100", "10É00100"]
The above text_list contains plaintext with hamming distances 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 with respect to original plaintext.
Where column Δp1 denotes the hamming distance observed after a particular round of DES and so on.
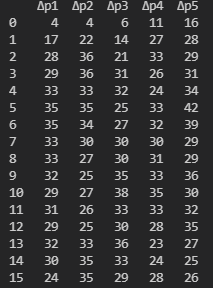
The original plaintext : “10100100” (64 bit string)
The original Key : "00011100" (64 bit string)
key_list = ["p0011100" ,"°0011100" ,"°0451±00" ,"d0451±00" ,"µút11100"]
The above key_list contains keys with hamming distances 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 with respect to original key.
Where column Δp1 denotes the hamming distance observed after a particular round of DES and so on.
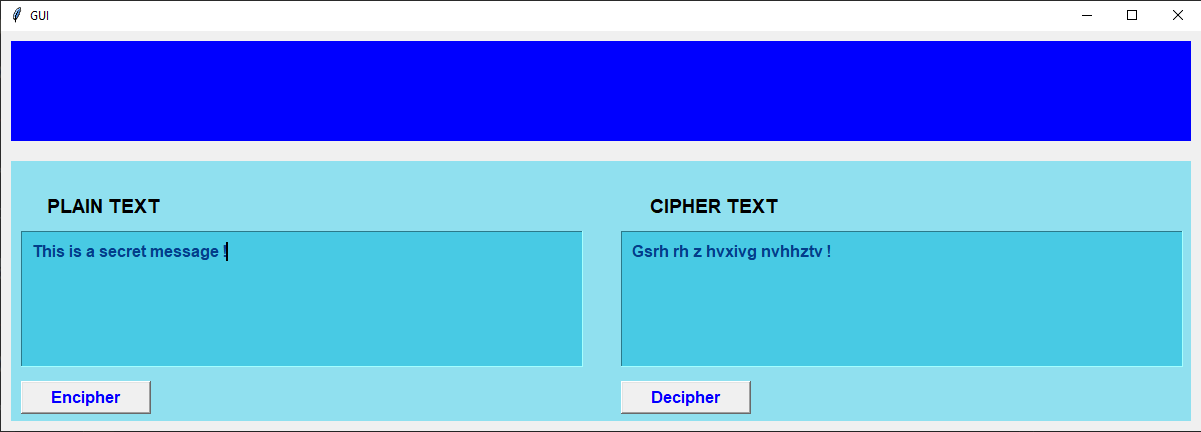
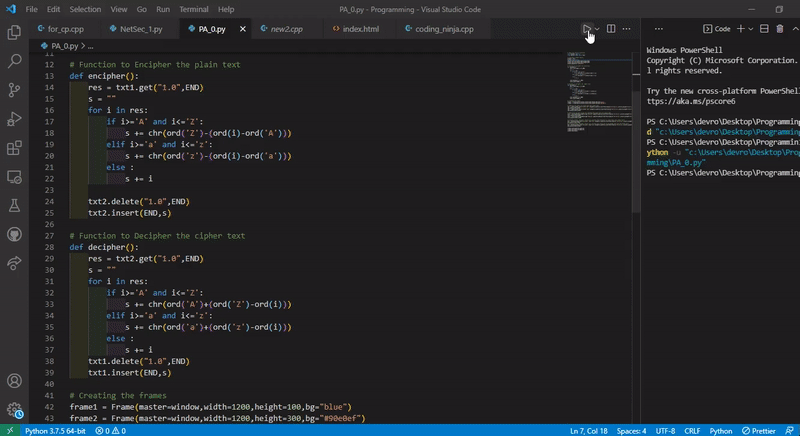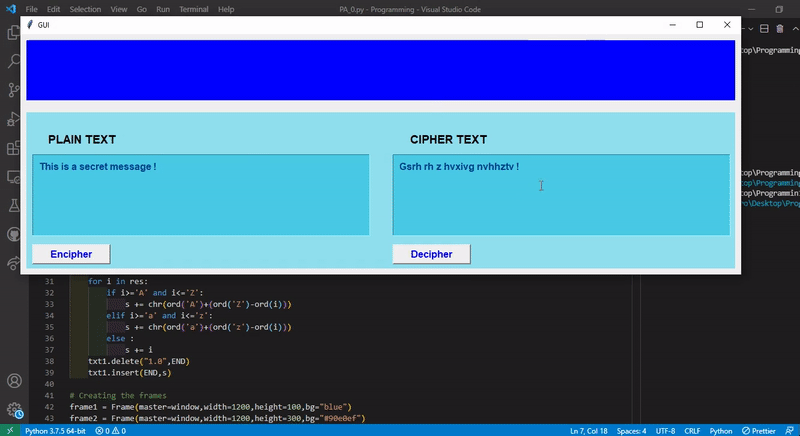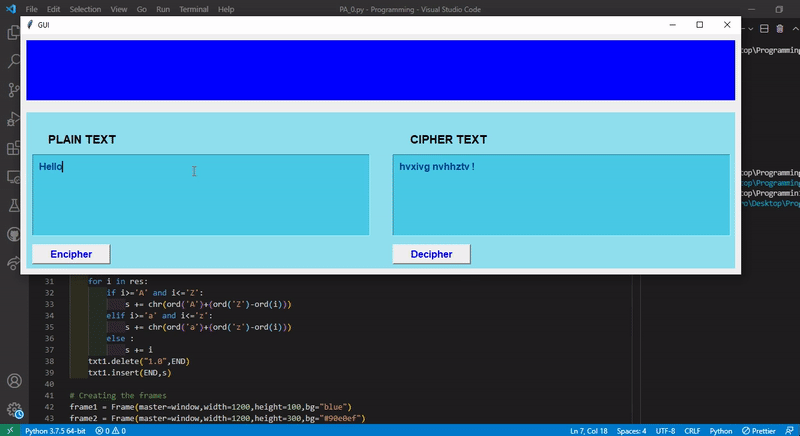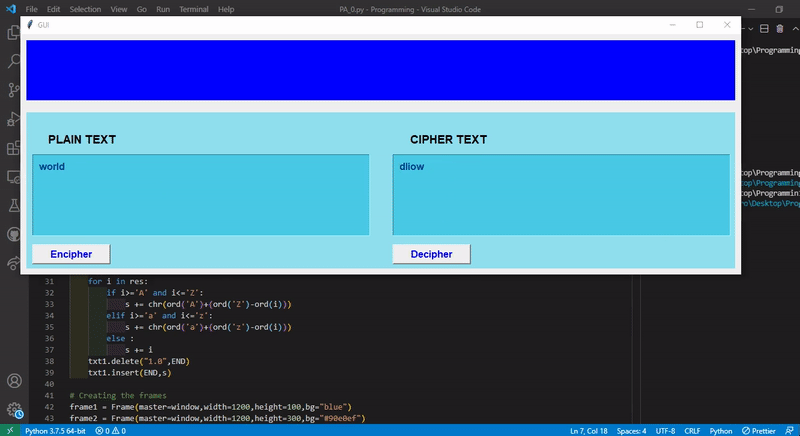
Write a program with a nice UI to Encipher / Decipher with the simple encryption algorithm discussed in the class.
The encryption idea is like :
a -> z || b -> y || c ->x || d -> w || ........................ || y -> b || z -> a
For 'a', since 'a' is the 1st beginning alphabet then the encrypted character of 'a' will be 1st alphabet from last i.e., 'z'.
For 'b', since 'b' is the 2nd beginning alphabet then the encrypted character of 'b' will be 2nd alphabet from last i.e., 'y' and so on.
The encryption algorithm has been mentioned in the code file (PA0.py).