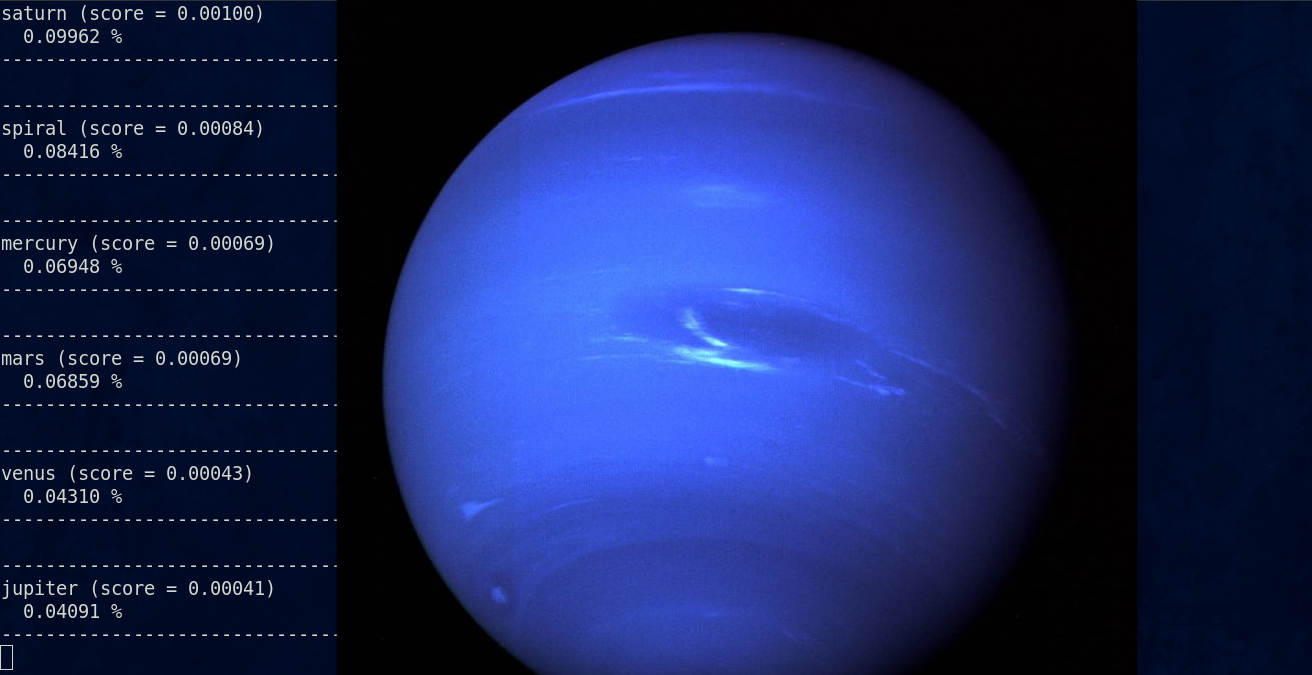
Transfer learning with an Inception v3 architecture model using TensorFlow used to classify images from Planet (Earth, Mercury, Mars, etc), Galaxy (Spiral, Elliptical, Irregular), Satellites, Comets, Etc
Create a virtual environment (recommended)
Python virtual environments are used to isolate package installation from the system.
Create a new virtual environment by choosing a Python interpreter and making a ./venv directory to hold it:
virtualenv --system-site-packages -p python3 ./venv
Activate the virtual environment using a shell-specific command:
source ./venv/bin/activate # sh, bash, ksh, or zsh
Install Tensorflow
pip install tensorflow
Downloaded automatically while training
python retrain.py --bottleneck_dir=bottlenecks --how_many_training_steps=500 --model_dir=inception --summaries_dir=training_summaries/basic --output_graph=retrained_graph.pb --output_labels=retrained_labels.txt --image_dir=./training_data
python /home/riya/git/celestial_body_detection/hub/examples/image_retraining/label_image.py /home/riya/git/celestial_body_detection/hub/examples/image_retraining/test_data/uranus.jpg
The Inception network was an important milestone in the development of CNN classifiers. Prior to its inception (pun intended), most popular CNNs just stacked convolution layers deeper and deeper, hoping to get better performance.
The Inception network on the other hand, was complex (heavily engineered). It used a lot of tricks to push performance; both in terms of speed and accuracy. Its constant evolution lead to the creation of several versions of the network.
The below image is the “naive” inception module. It performs convolution on an input, with 3 different sizes of filters (1x1, 3x3, 5x5). Additionally, max pooling is also performed. The outputs are concatenated and sent to the next inception module.
An astronomical object or celestial object is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. [1] In astronomy, the terms object and body are often used interchangeably. However, an astronomical body or celestial body is a single, tightly bound, contiguous entity, while an astronomical or celestial object is a complex, less cohesively bound structure, which may consist of multiple bodies or even other objects with substructures.
Examples of astronomical objects include planetary systems, star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies, while asteroids, moons, planets, and stars are astronomical bodies. A comet may be identified as both body and object: It is a body when referring to the frozen nucleus of ice and dust, and an object when describing the entire comet with its diffuse coma and tail.
A galaxy is a gigantic collection of interstellar dust, gas, stellar remnant, stars along with their own solar systems. All held together by the force of gravity. Earth is located in a galaxy called the Milky Way. The Milky Way is a spiral shaped galaxy that has a diameter between 100,000 and 180,000 light years across. We used to think that our galaxy contained all the stars in the universe until in 1920, observations by Edwin Hubble showed that Milky Way is just one of many galaxies in the universe and that each galaxy contains billions or even trillions of stars within it.
There are so many galaxies out there in the universe that there could be as many as tens of billions of undiscovered galaxies and we have only discovered a fraction of that. In recent years, with numerous digital sky surveys across a wide range of wavelengths, astronomy has become an immensely data-rich field. For example, the Sloan Digital Sky Survey will produce more than 50,000,000 images of galaxies in the near future. Studying the viimorphology of galaxies is one of the most important aspects of answering many of the questions that mankind does not know the answer to yet and that is the creation of the universe. By classifying galaxies into different groups in terms of their structure appearance, scientists will be able to understand the origin and formation of galaxies as well as the evolution process of the universe. Galaxy morphological classification on a large-scale database is important to help astronomers reduce classification errors and to help them produce collections of statistical and observational purposes as well as discovering the mystery of nature at large.
With the help of space telescopes that are much more powerful than our eyesight, astronomers are able to look into time and space as far as billions of light years away from Earth and explore millions of galaxies far away from our own.
 Figure 1: Three classes of galaxy morphological. From left to right: Elliptical Shaped Galaxy, Spiral
Shaped Galaxy and Irregular Shaped Galaxy (en.Wikipedia.org, 2006)
Figure 1: Three classes of galaxy morphological. From left to right: Elliptical Shaped Galaxy, Spiral
Shaped Galaxy and Irregular Shaped Galaxy (en.Wikipedia.org, 2006)
There are different types of galaxies:
-
ELLIPTICAL
An elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy having an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless image.
Unlike flat spiral galaxies with organization and structure, elliptical galaxies are more three-dimensional, without much structure, and their stars are in somewhat random orbits around the center. -
SPIRAL
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, form part of the Hubble sequence. Most spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as the bulge.
-
IRREGULAR
An irregular galaxy is a galaxy that does not have a distinct regular shape, unlike a spiral or an elliptical galaxy. Irregular galaxies do not fall into any of the regular classes of the Hubble sequence, and they are often chaotic in appearance, with neither a nuclear bulge nor any trace of spiral arm structure.
A planet is an astronomical body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals. There are total of 8 planets in our solar system:
- Mercury: the closest to the sun and the second smallest planet in our solar system, Mercury has a rotation of only 88 days around the sun. Because of its close proximity to the celestial giant, the surface of the planet reaches temperatures as high as 840°F during the day and hundreds of degrees below the freezing point at night. There is no atmosphere due to the intense temperatures so the planet's surface is covered with pock marks and craters from meteor impacts.
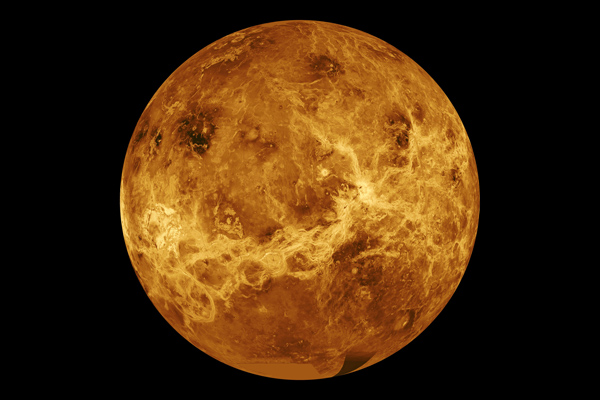
- Venus: this toxic planet, primarily consisting of carbon dioxide, is next in line from the sun and contains a pressure index that would crush anyone who landed on its surface. Though it is further away from the sun then Mercury, Venus is the hottest planet in the solar system and is able to be seen by the naked eye from Earth. A thick cloud shrouds the planet, making it difficult to see its surface which attributes to its brilliance.
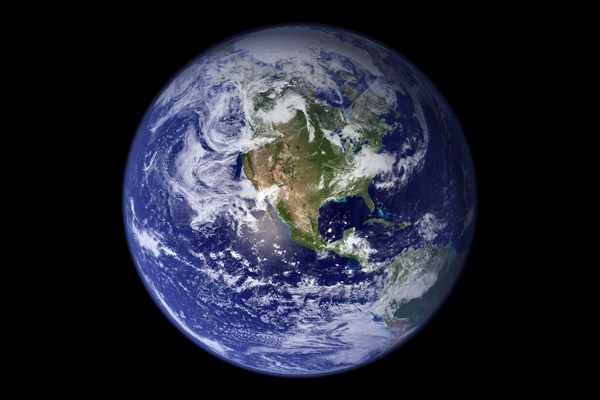
- Earth: is the planet in which we live on and is the 3rd planet from the sun. Also known as "Terra" the Earth is the only planet within our solar system that is capable of sustaining advanced life forms, such as humans. The Earth's rotation around the sun is approximately 365 days and it is believed that the Earth is approximately four thousand million years.
- Mars: the fourth planet from the sun the "red planet", so named for its reddish color due to the high iron content in its soil, has a rotation around the sun of 686 days. Its thin atmosphere, consisting primarily of carbon dioxide, makes it unsuitable for sustaining life, but is believed to have at one time been capable of it and might still be able in the future.
- Jupiter: the largest planet in our system, the mysteries of Jupiter has fascinated astronomers and non-astronomers alike for centuries. Poisonous gases completely cover its surface, hiding what lies beneath and violent storms prevent any landings of probes onto or images taken of the giant planet. Jupiter's atmosphere has been determined to be similar to that of the sun containing elements of hydrogen and helium.
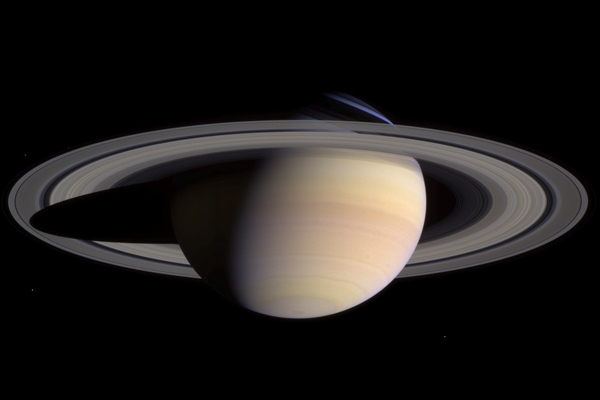
- Saturn: first viewed via telescope in 1610 by Galileo Galilei, is the 6th planet in our solar system from the sun. Like Jupiter, its atmosphere is composed primarily of helium and hydrogen and it is the only planet discovered so far that has a lower density than water, approximately 30% lower. It is surrounded by a set of 9 whole rings and 3 broken rings that are comprised mainly of ice, rock, and space "dust".
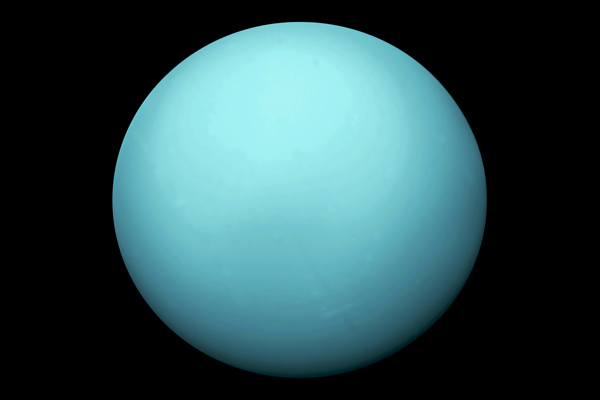
- Uranus: also known as the "sideways planet" because of its awkward rotation, is the 7th planet in our solar system from the sun. Its North and South poles are located where other planets equators are, given to its strange rotation and its 20 years long seasons. The level of methane gases in its atmosphere account for its bluish color, but the main elements in Uranus' atmosphere is helium and hydrogen.
- Neptune: is known as the windiest planet in our solar system and 8th furthermost known "planet" from our sun. It has a revolution around the sun of 165 Earth years. Like Uranus, Neptune has high traces of methane in its atmosphere, which contributes to its blue color. It is believed there is a second "unknown" element, though, that makes it a much brighter blue than Uranus.