Prolog Virtual DOM
This is a Virtual DOM implementation for Prolog. It is designed to be used with the WebAssembly build of SWI-Prolog.
The implementation keeps the VDOM tree on the Prolog side and serializes the initial tree and modifications through the foreign language interface.
Demo: http://demos.rlaanemets.com/prolog-vdom/examples/wasm/
Overview
Please see examples/wasm/index.html and examples/wasm/app.pl for actual code examples.
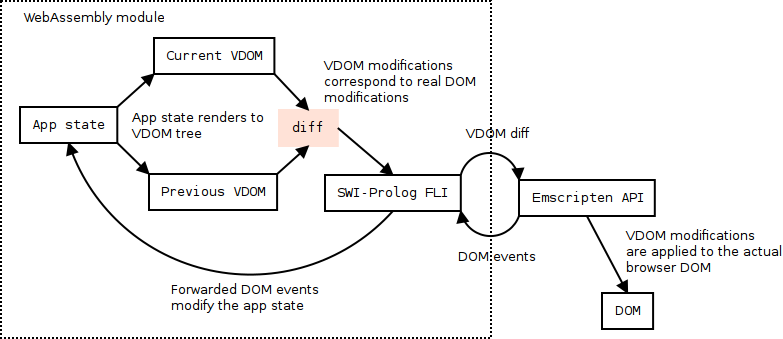
The Prolog code runs inside the WebAssembly module that contains running SWI-Prolog instance. The communication between the page and Prolog is done through the SWI-Prolog Foreign Language Interface (FLI) and the Emscripten API.
The application starts by rendering the initial state into the
initial VDOM tree, passes it to the page side and creates the
actual DOM tree based on it. The glue code in the browser
sets up generic event handlers (currently for events click,
input and submit). Event handlers are set on the body
element and rely on target element id's to differentiate between
targets.
On each event the application renders new VDOM tree, compares it to the previous one and sends diff to the glue code. The JavaScript glue code decodes the diff and applies it to the actual page DOM.
Prolog API
See example:
VIn = div([], [hello]),
VPrev = div([], [world]),
vdom_diff(VIn, VPrev, Diff, VOut).- VIn - current VDOM tree.
- VPrev - previous VDOM tree.
- Diff - serialized updates (
diff(replace(path(0), "hello"))). - VOut - current full VDOM tree.
In this example the first child of the root node is being replaced by the text node containing "hello".
VDOM nodes
VDOM nodes are either atomic terms or tags. Atomic terms are atoms, numbers and strings.
Tags have the general form of name(Attributes, Body) and they
correspond to real DOM tags unless there is a component registered
with the same name.
Components
VDOM components are both an abstraction and optimization tool.
Components are registered using the vdom_component_register(Name, Pred)
predicate. Name refers to the component's name and Pred refers
to the component's rendering predicate.
Components with the same input data at the corresponding VDOM node are not re-rendered during the diff calculation. This allows to skip major parts of the VDOM tree in the algorithm.
Keyed node
Keyed node is a VDOM node where children have distinct key
attributes. This is a common case where a list is rendered into
a list of VDOM nodes. The VDOM diff algorithm is able to:
- Reorder children effectively.
- Add/remove new children in/from the middle.
for a keyed node.
JavaScript (in-page) API
The JavaScript part consist of the following code:
- File
js/prolog.js- Prolog FLI bound using Emscripten. - File
js/patcher.js- Helper that applies patches onto the real DOM and forwards DOM events.
Construct a new Prolog FLI instance:
const prolog = new Prolog(module, args);where module is a Emscripten module object and
args is an array or arguments for PL_initialise function.
With the semi-official SWI-Prolog WebAssembly build, args is:
[
'swipl',
'-x', 'wasm-preload/swipl.prc',
'--nosignals'
]Construct a new Patcher instance:
const patcher = new Patcher(prolog, root);where prolog is a Prolog instance and root is the
application's root DOM element (it does not have to be document.body).
DOM serialization
Atomic terms are serialized as strings.
Attribute terms:
attrs(name1(Value1), name2(Value2))where Value1 and Value2 are strings.
Tags:
name(Attrs, body(Child1, Child2)).where Attrs is an attribute term and Child1 and Child2 are serialized DOM subtrees.
DOM patch serialization
Node rebuild:
replace(Path, Dom)where Path is a path term and Dom is a serialized DOM tree as described in "DOM serialization".
Set/unset attributes:
set_attrs(Path, Attrs)where Path is a path term and Attrs an attributes term.
Reorder-or-create:
roc(Path, actions(Action1, Action2))where Path is a path term and Action1 and Action2 are terms in the form:
Reuse term (reuses DOM node from the old index):
reuse(Index)Create term (creates a new DOM node):
create(Dom)where Dom is a serialized DOM tree for the node as described in "DOM serialization".
Path term:
path(0, 2)Path term represents path from the root element down to
the element that is being modified. For example, path(0, 2)
refers to 1st child of the root, and 3rd subchild of the child.
TODO
- Style updates.
- Special
eachnode.
License
The MIT license. See the LICENSE file.