The ubiquitous UITableView, with its required data source and delegate, is one of the main sources of badly architected solutions in the iOS platform. SDK classes, as UITableViewController, enforce bad design practices, and lead you to the problem of the Massive View Controller, where the single responsibility principle is completely missed.
RLDTableViewSwift is a set of ready-to-use Swift classes that will get you back in track, helping you to refine the shape of your app. They enforce the SOLID principles, with an adaptation of the Model-View-Presenter pattern.
Objective-C version also available.
These are reusable components for the data source and delegate of all your table views. With them, you won't need to write the same boilerplate code again and again –they will just use your table view model and event handlers to be able to manage any UITableView.
They fully implement the UITableViewDataSource and UITableViewDelegate protocols, and keep synchronized between themselves, giving you all the UITableView features with little effort from your side:
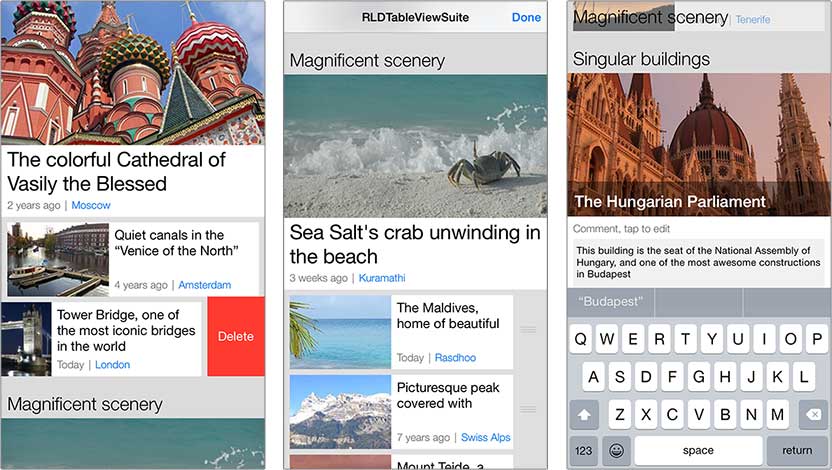
- Display customization
- Variable height support
- Sections, with headers and footers
- Sections index titles
- Cell accessories (disclosures)
- Highlighting and selection of cells
- Editing, moving and reordering cells
- Indentation
- Copy and Paste
The table view model defines the state, look and feel of the views in your table view, and the relationships between them. You can use the provided generic implementations, or subclass them to tailor them to yor needs:
RLDTableViewCellModel, for cells,RLDTableViewSectionModel, for table sections,RLDTableViewSectionAccessoryViewModel, for section headers and footers, andRLDTableViewModel, for the table view itself.
Every view in your table view (like cells, section headers and section footers) should be managed by an event handler. It will receive all the view related actions from the table view delegate and react to user generated events on the view.
Event handlers are short-lived objects that will be instantiated on demand and destroyed once the event that caused its creation has been handled or when the view they manage is deallocated. They should not store state (because we have a model, right?) and they can either configure the look of the view by themselves, or pass the view model to the view, so it can autoconfigure. The provided sample app uses the latest approach.
You have two event handlers classes that you can subclass:
RLDTableViewCellEventHandler, for table view cells, andRLDTableViewSectionAccessoryViewEventHandler, for section headers and footers.
Although it is not mandatory, if the handled view conforms to the RLDHandledViewProtocol it will receive an event handler just before the view is displayed for the first time. The view will retain this event handler during all its lifecycle to be able to react to the user generated events on the view. This retained event handler will be reused together with the cell, improving the performance.
In order to create the best suited event handler on demand, RLDTableViewDelegate will need an event handler provider to find the first event handler which supports a certain combination of table view, view and view model.
To make your event handlers available to the provider, you must register them using their register() class method.
The best way to make sure all your classes are ready when needed is registering them in the same place. You can use a registar class with a function that is called once when the application has finished launching, or register them just before their first use. The included sample app uses this approach.
This class is a drop-in replacement of UITableViewController. It just requires a table view model to be able to configure your table view. Internally, it uses the default implementations of RLDTableViewDataSource, RLDTableViewDelegate and RLDTableViewEventHandlerProvider, so it's the easiest way to use RLDTableViewSwift without worrying about its internals, while getting the most of having a proper architecture.
To use the latest stable release of RLDTableViewSwift, just add the following to your project Podfile:
pod 'RLDTableViewSwift', '~> 0.2.1'
If you like to live on the bleeding edge, you can use the master branch with:
pod 'RLDTableViewSwift', :git => 'https://github.com/rlopezdiez/RLDTableViewSwift'
- Clone, add as a submodule or download.
- Add all the files under
Classesto your project. - Enjoy.
RLDTableViewSwift is available under the Apache License, Version 2.0. See LICENSE file for more info.
This README has been made with (GitHub-Flavored) Markdown Editor