pip install expedantic
from expedantic import ConfigBase
# Define a config model
class MyConfig(ConfigBase):
device: str = 'cuda:0'
learning_rate: float = 1.0e-3
num_epochs: int = 100
# Save and load from yaml files
my_config = MyConfig()
my_config.save_as_yaml("config.yaml")
my_config = MyConfig.load_from_yaml("config.yaml")
# For a given function or class,
def learn(device: str, learning_rate: float, num_epochs: int):
...
# Consume the config by getting kwargs automatically.
learn(**my_config.compatible_args(learn))
# Or pass manually
learn(my_config.device, my_config.learning_rate, my_config.num_epochs)Find some examples here.
-
Type validation using
pydantic. -
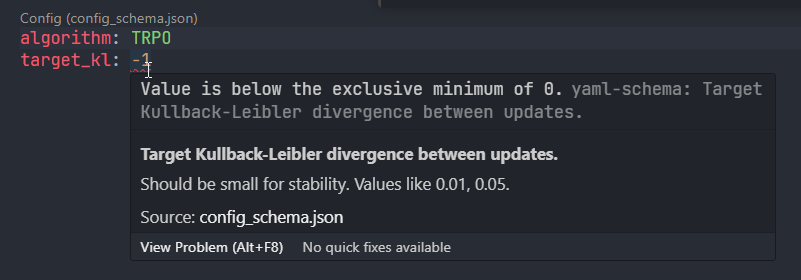
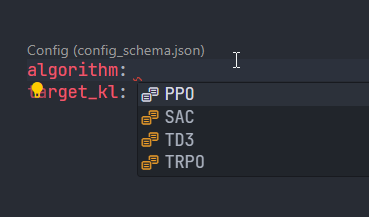
JSON schema generation for autocompletion on yaml files. You can facilitate efficient yaml editing on IDEs such as VS Code.
For the VS Code usage, the following steps enable the autocompletion on yaml files for configuration models.
- Generate a schema.
from pathlib import Path from typing import Annotated, Literal from expedantic import ConfigBase, Field class Config(ConfigBase): algorithm: Literal["TRPO", "PPO", "SAC", "TD3"] = "TRPO" target_kl: Annotated[ float, Field( title="Target Kullback-Leibler divergence between updates.", description="Should be small for stability. Values like 0.01, 0.05.", gt=0.0, ), ] = 0.01 config = Config() Path("configs").mkdir(exist_ok=True) config.save_as_yaml("configs/config.yaml") Config.generate_schema("schemas/config_schema.json")
-
Install the yaml language extension.
-
Associating the schema
.vscode/settings.json yaml.schemas: { "schemas/config_schema.json": "configs/config.yaml", }
Check the further rules for association in the description of the extension.
-
Integrated argument parser with supporting nested key access:
# run.py class MyInnerConfig(ConfigBase): inner_key: str = "inner_value" class MyConfig(ConfigBase): inner_config: MyInnerConfig = MyInnerConfig() outer_key: int = 10 my_config = MyConfig.parse_args()
python run.py --inner_config.inner_key "another inner value" --outer_key 20 -
!includedirective support for yaml files:# base.yaml learning_rate: 3.0e-5 num_epochs: 10 device: cpu
# derived.yaml <<: !include base.yaml device: cuda extra: True
The content of
derived.yamlis equivalent to the following:learning_rate: 3.0e-5 num_epochs: 10 device: cuda extra: True
-
Mutually exclusive configuration groups:
from pydantic import ValidationError class Config(ConfigBase): _mutually_exclusive_sets = [{"make_algorithm_A_obsolete", "use_algorithm_A"}] make_algorithm_A_obsolete: bool = True use_algorithm_A: bool = False try: config = Config(make_algorithm_A_obsolete=True, use_algorithm_A=True) except ValidationError as e: print(e) """ 1 validation error for Config Value error, Mutual exclusivity has broken. (set: {'make_algorithm_A_obsolete', 'use_algorithm_A'}) [type=value_error, input_value={'make_algorithm_A_obsolete': True, 'use_algorithm_A': True}, input_type=dict] """