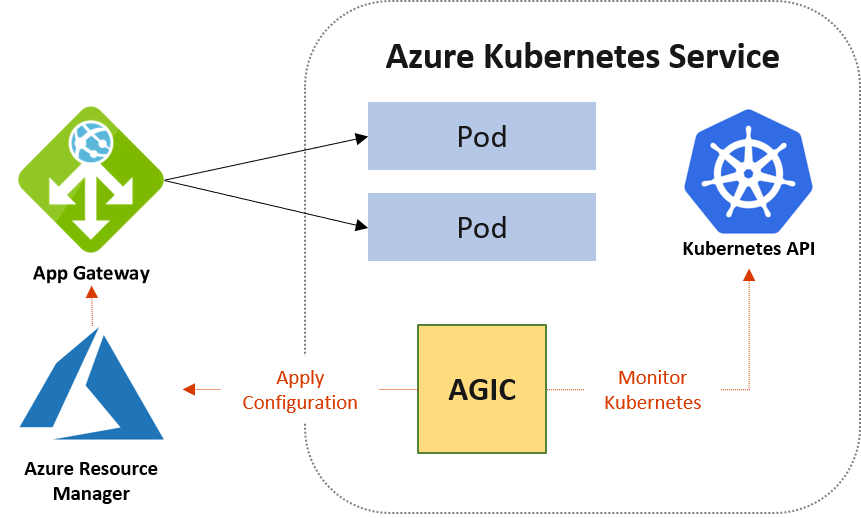
This project illustrates how
- a docker image based on a Camunda BPM Spring Boot project is built,
- the Azure CLI is used to create an Azure Container Reqgistry (ACR) and to push the image to it
- a Kubernetes Cluster on AKS is created using the Azure CLI
- an image is deployed on the Kubernetes cluster as a service and
- the service is exposed to the internet via a public IP using a LoadBalancer or Ingress)
The project assume local installations Maven, Docker, PowerShell and Azure CLI are accessible via the command line.
The sub folder .\vanilla-spring-boot contains a standard Camunda Spring Boot Maven project, created using the Camunda BPM Initializr. This project can be adjusted as needed to created the desired Camunda deployment.
Inside the .\vanilla-spring-boot folder run
mvn clean install
to clean the project, then build the Camunda Spring Boot jar (in
.\vanilla-spring-boot\target\camunda-vanilla-boot-7.14.0.jar) and build and publish a Docke rimage based on it to your local Docker registry named robsacr.azurecr.io/camunda/camunda-vanilla-boot:7.14.0 (adjust docker.image.tag in pom.xml line 15 as desired).
In .\createACRandPush.ps1 adjust resource group name, container registry name and image tag as desired.
$rgName = "rgaks"
$acrName = "robsacr"
...
docker push robsacr.azurecr.io/camunda/camunda-vanilla-boot:7.14.0
then run .\createACRandPush.ps1 to create the resource group and container registry and push your image to the Azure container registry.
In .\createCluster.ps1 adjust resource group, container registry and cluster names as desired.
$rgName = "rgaks"
$acrName = "robsacr"
$clusterName = "camundaCluster" then run
.\createCluster.ps1to create a new Kubernetes cluster and apply pod, service and ingress definitions to it.
You can check the results of the scripts via Azure CLI or in the Azure portal
The external IP will become visible in the console when the script and Azure proivisioning are completed. The EXTENRAL IP column will at first show pending, then a new row with the external IP will appear. This may take a few seconds or rarely even minutes.
Check if you can access the Camunda Web application via the public IP of your load balancer.
In the Kubernetes services section of the Azure portal you can check the configured workloads, services and ingresses and their status. The services and ingresses also contains a link to the external IP under which the Camunda web application should be accessible.
Remove-AzResourceGroup -Name <resource group name>
Camunda BPM Spring Boot documentation
Azure Kubernetes Sevrice (AKS) documentation
Quickstart: Create a private container registry using Azure PowerShell
Quickstart: Create an Azure container registry using the Azure portal
Tutorial: Deploy an Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster
Use a public Standard Load Balancer in Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Exposing an External IP Address to Access an Application in a Kubernetes Cluster
Kubernetes Nginx ingress: traffic redirect using annotations demystified
Create an HTTPS ingress controller on Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Application Gateway Ingress Controller for Azure Kubernetes Service
Application Gateway Ingress Controller
Use kubenet networking with your own IP address ranges in Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS)
Application Gateway configuration overviewhttps://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/application-gateway/configuration-overview