Lightning App automate the research workflow and production pipeline. Lightning App is composed of Lightning Work and Lightning Flow. Start by wrapping existing scripts as Lightning Works. Lightning Works send state information to Lighting Flows. Lightning Flows send run command to Lightning Works. Distributed states and runs are serialized via event loops in Lightning Flows. Distribute data among Lightning Works with Lightning Drives, Path, and Payload.
graph LR;
AP(App <br><br>Lightning <br>App)
subgraph State Transition via Event Loop
LF((Orchestrate <br><br>Lightning <br>Flow))
LW[Run <br><br>Lightning <br>Work]
AP -- run --> LF
LF -- run --> LW
LW -- state changes --> LF
end
subgraph existing scripts
S[existing .py .sh .. code]
end
LW ---> S
Develop locally on a single box and deploy on distributed on the cloud without any code change
- Develop and test locally
lightning app run app.py- Deploy on the cloud
lightning app run app.py --cloudDistributed state changes are serialized and managed by Lightning Flow.
Lightning Flow then uses run to execute tasks.
Locally, Flow(s) and Work(s) run on a same VM. The diagram below shows state changes. The runs are omitted from this diagram.
graph BT;
subgraph Local VM
LF((App <br><br>Lightning <br>Flow))
T(Train <br><br>Lighting Work) -- state <br>changes --> LF
I(Inference <br><br>Lightning Work) -- state <br>changes --> LF
D(Diag <br><br>Lightning Work) -- state <br>changes --> LF
U(UI <br><br>Lightning FLow) -- state <br>changes --> LF
LF -- run --> T
LF -- run --> I
LF -- run --> D
LF -- run --> U
subgraph existing scripts
TS[train_script.py]
IS[gradio_script.py]
DS[tensorboard]
US[ui_script.py]
end
subgraph wrapper code
T ---> TS
I ---> IS
D ---> DS
U ---> US
end
end
On the cloud, there is one Lightning Flow VM and many Lightning Work VMs.
The diagram below shows run and state changes.
graph TD;
subgraph Cloud
subgraph Flow VM -- Always one VM
LF((Orchestrate <br><br>Lightning Flow))
end
subgraph Train VMs
T(Train <br><br>Lighting Work) <-- state changes --> LF
LF --run --> T
end
subgraph Inference VMs
I(Inference <br><br>Lightning Work) <-- state changes --> LF
LF --run --> I
end
subgraph Diag VM
D(Diag <br><br>Lightning Work) <-- state changes--> LF
LF --run--> D
end
end
Lightning App Drive is available among Lightning Works. Train, Inference, Diag can share files.
graph TD;
LD[Lightning App Drive]
T[Train] <-- push, get --> LD
I[Inference] <-- push, get --> LD
D[Diag] <-- push, get --> LD
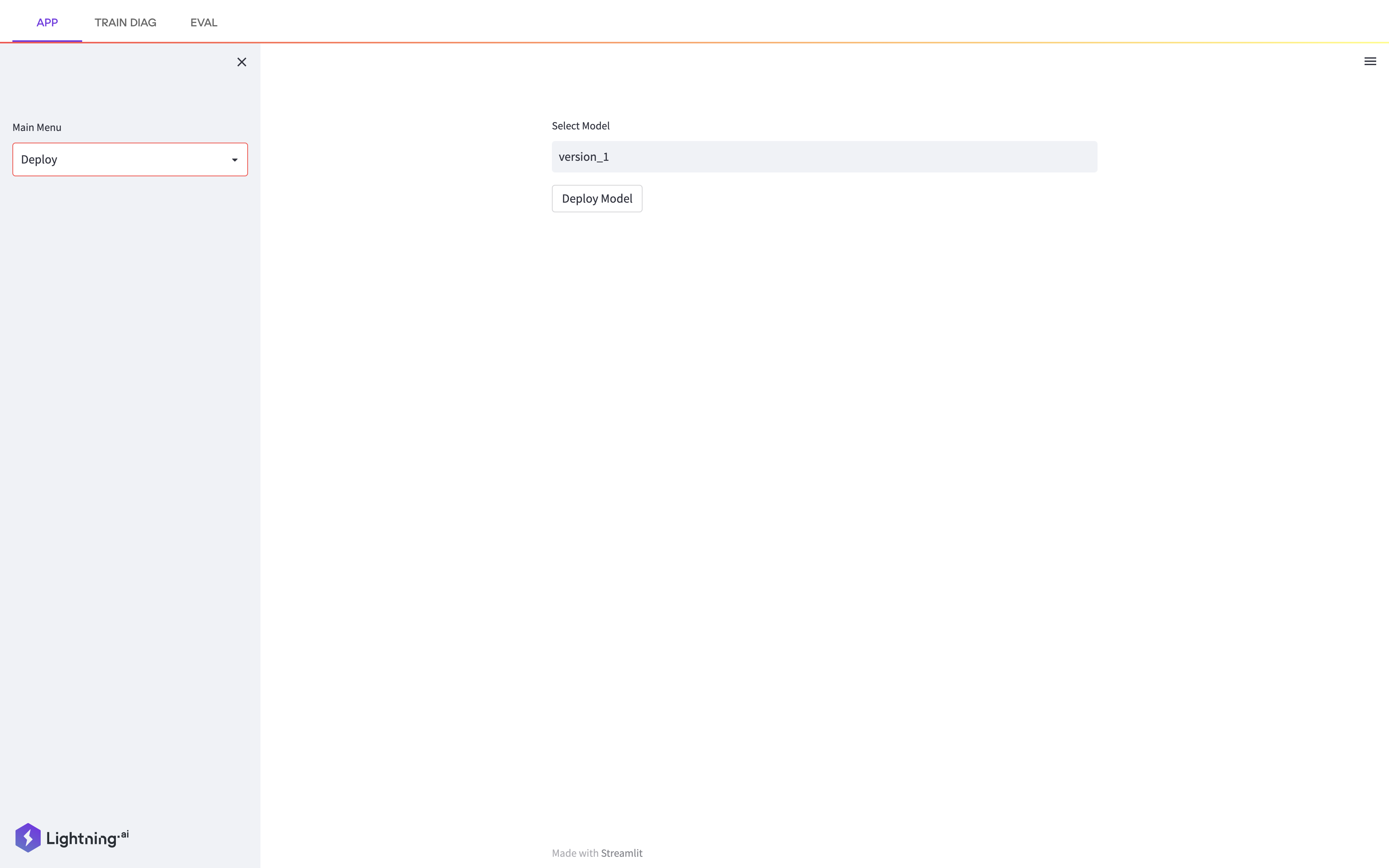
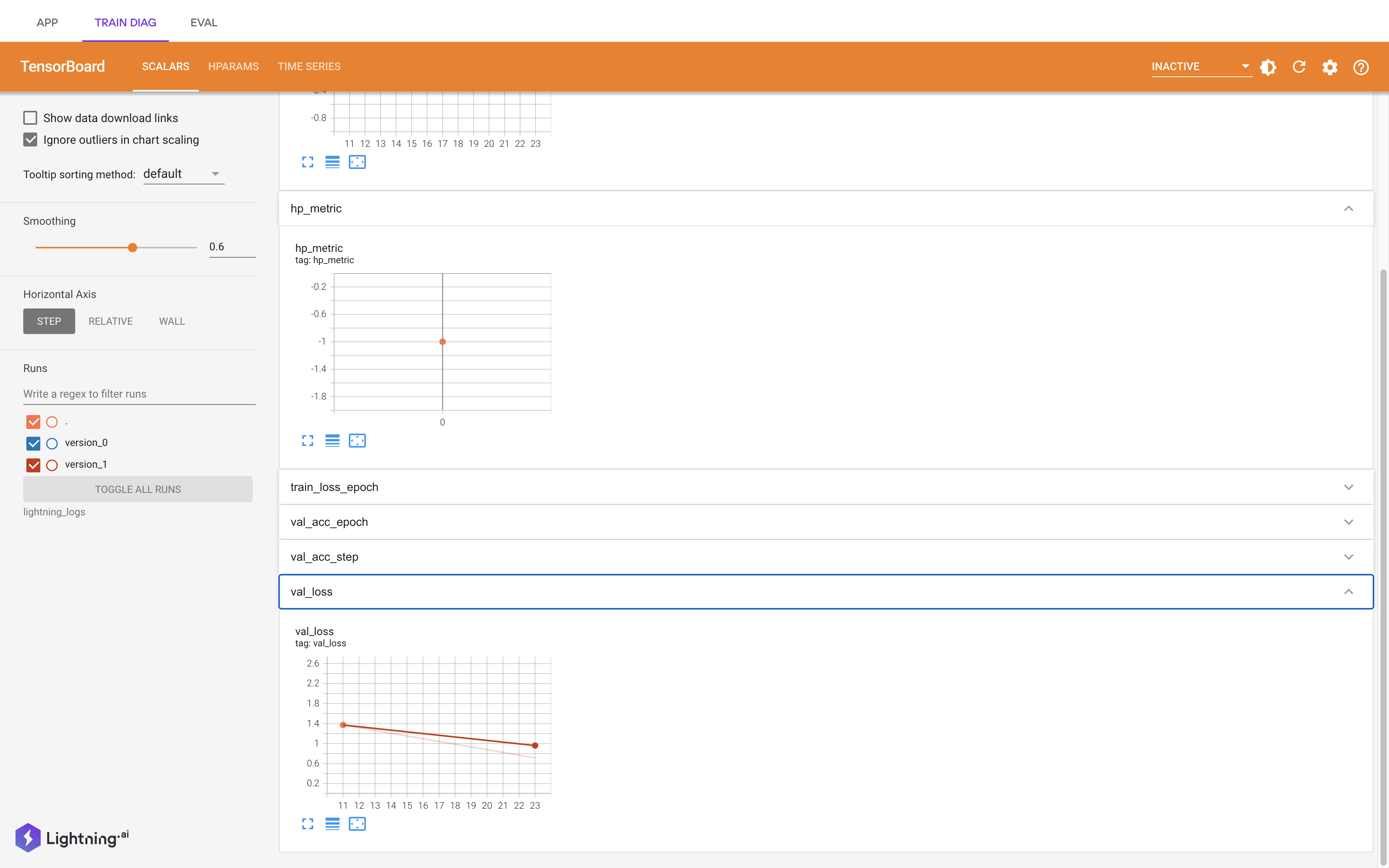
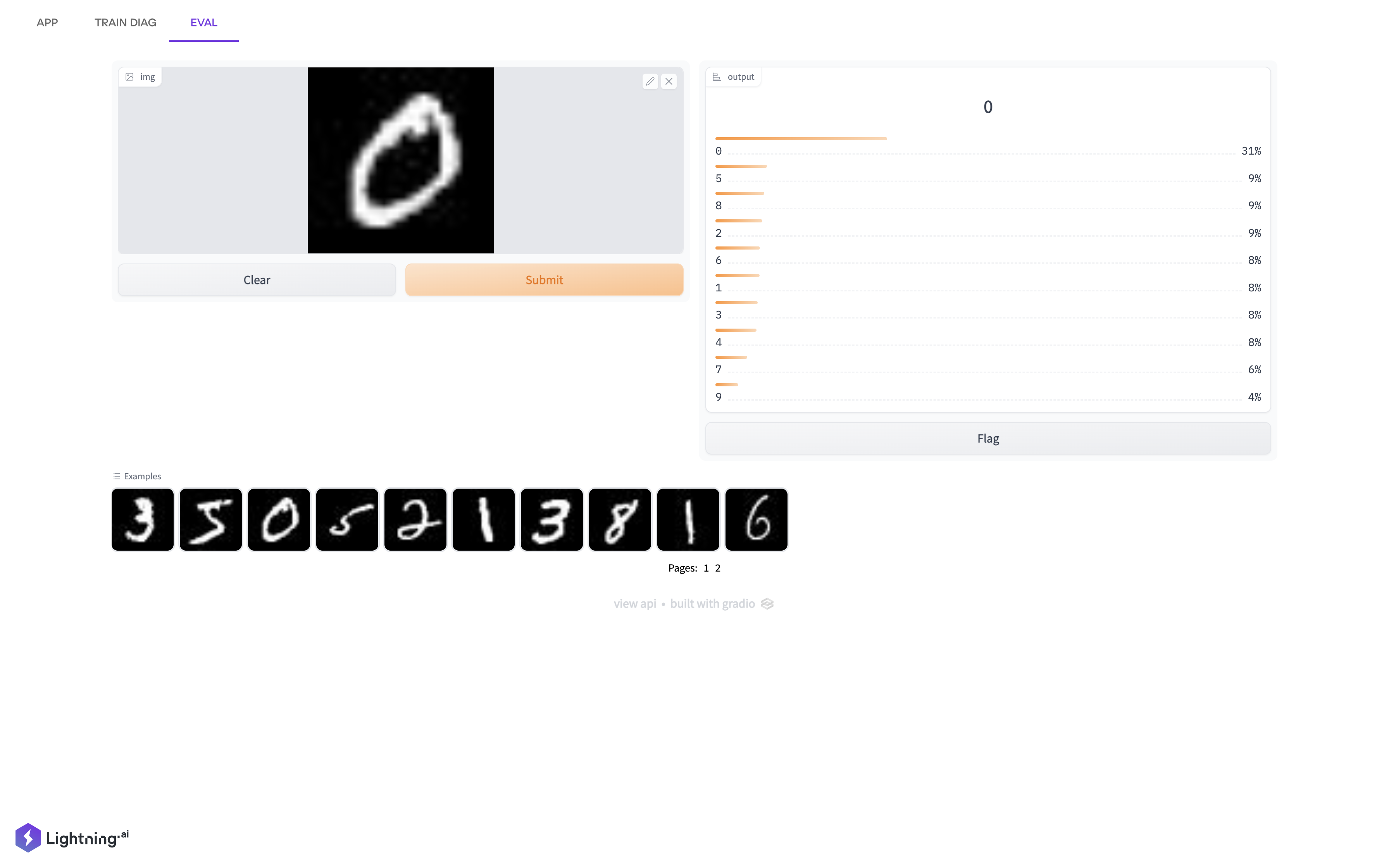
Existing scripts, unchanged, are wrapped in as a Lightning App. Lighting Flow is used to codify orchestration in Python code. Lighting Work is used to run the script. Interactive workflow is enabled with Lightning App.
graph TD;
L[Lightning App] --> U[UI with Streamlit]
U -- start Training --> T[Train with Lighting & Module Trainer];
U -- deploy model --> G[Deploy with Gradio];
T -- Send lightning_log --> D[Diag with Tensorboard];
T -- Send weights.py --> G;
G -- Retrain --> T;