According to official documentation,we can use the below cmd to start up minikube,but the dfault value of CPU (2 core) is not enough .
$ minikube delete && minikube start --kubernetes-version=v1.24.11 \
--cpus=4 \
--memory=6g \
--bootstrapper=kubeadm \
--extra-config=kubelet.authentication-token-webhook=true \
--extra-config=kubelet.authorization-mode=Webhook \
--extra-config=scheduler.bind-address=0.0.0.0 \
--extra-config=controller-manager.bind-address=0.0.0.0cd kube-prometheus-v0.12.0
kubectl apply --server-side -f manifests/setup
kubectl wait \
--for condition=Established \
--all CustomResourceDefinition \
--namespace=monitoring
kubectl apply -f manifests/
cd ..- Access UIs
- Grafana:
Then access via http://localhost:3001
$ kubectl --namespace monitoring port-forward svc/grafana 3001:3000
- Prometheus
Then access via http://localhost:9090
$ kubectl --namespace monitoring port-forward svc/prometheus-k8s 9090
- Grafana:
According to the official documentation.
cd activemq-artemis-operator-v1.0.7
kubectl create namespace activemq-artemis-operator
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace activemq-artemis-operator
kubectl create -f deploy/installAt this point you should see the activemq-artemis-operator starting up and if you check the logs you should see something like
$ kubectl get pod -n activemq-artemis-operator
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
activemq-artemis-controller-manager-5ff459cd95-kn22m 1/1 Running 0 70m
Now that the operator is running and listening for changes related to our crd we can deploy one of our basic broker custom resource examples which looks like
apiVersion: broker.amq.io/v1beta1
kind: ActiveMQArtemis
metadata:
name: ex-aao
spec:
env:
- name: TZ
value: 'Asia/Taipei'
deploymentPlan:
size: 1
enableMetricsPlugin: true
image: placeholder
messageMigration: true
resources:
limits:
cpu: "500m"
memory: "1024Mi"
requests:
cpu: "250m"
memory: "512Mi"
acceptors:
- name: all-acceptors
protocols: all
port: 61616
connectionsAllowed: 100
console:
expose: trueNote in particular the spec.image which identifies the container image to use to launch the AMQ Broker. If it's empty or 'placeholder' it will get the latest default image url from config/manager/manager.yaml where a list of supported broker image are defined as environment variables.
To deploy the broker simply execute
kubectl create -f examples/artemis-basic-deployment.yaml -n activemq-artemis-operatorIn a mement you should see one broker pod is created alongside the operator pod:
$ kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
activemq-artemis-controller-manager-5ff459cd95-kn22m 1/1 Running 0 128m
ex-aao-ss-0 1/1 Running 0 23mNow that the broker is running that we can deploy privilege about prometheus which looks like
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: prometheus
app.kubernetes.io/instance: k8s
app.kubernetes.io/name: prometheus
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: kube-prometheus
app.kubernetes.io/version: 2.41.0
name: prometheus-k8s
namespace: activemq-artemis-operator
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: prometheus-k8s
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: prometheus-k8s
namespace: monitoring
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/component: prometheus
app.kubernetes.io/instance: k8s
app.kubernetes.io/name: prometheus
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: kube-prometheus
app.kubernetes.io/version: 2.41.0
name: prometheus-k8s
namespace: activemq-artemis-operator
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- services
- endpoints
- pods
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- extensions
resources:
- ingresses
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- apiGroups:
- networking.k8s.io
resources:
- ingresses
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
---
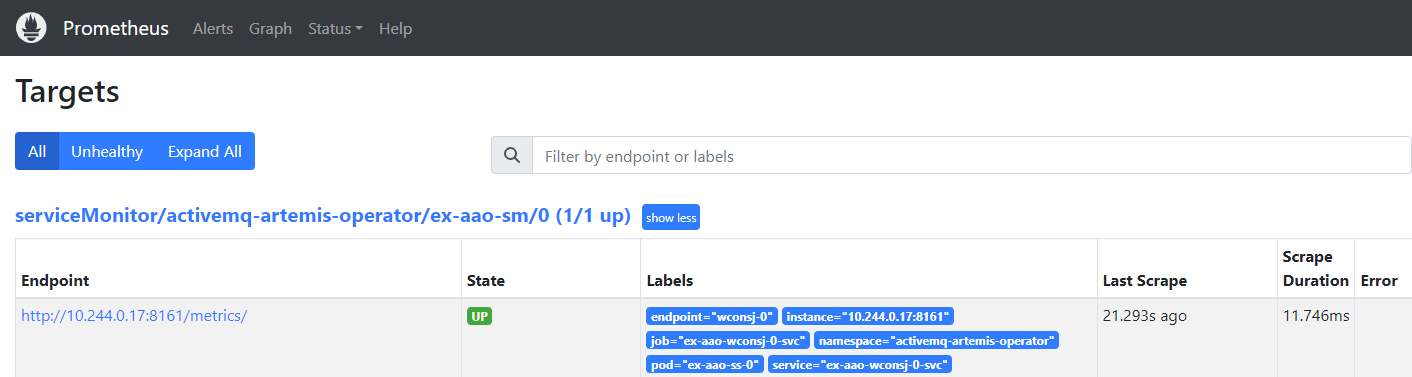
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: ServiceMonitor
metadata:
name: ex-aao-sm
labels:
team: frontend
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
application: ex-aao-app
endpoints:
- path: /metrics/
port: wconsj-0
--- - Test Objective: test monitoring activemq artemis integrated with wildfly application** .
cd helloworld-mdb
kubectl create namespace helloworld-mdb
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace helloworld-mdb
mvn clean package
eval $(minikube docker-env)
docker build -t helloworld-mdb:latest .
kubectl create -f k8s-yaml/- Test Objective: test monitoring the custom metrics wildfly application .
cd helloworld-anthos
kubectl create namespace helloworld-anthos
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace helloworld-anthos
mvn clean package
eval $(minikube docker-env)
docker build -t helloworld-anthos:latest .
kubectl create -f helloworld-anthos/k8s-yaml/
kubectl create -f helloworld-anthos/k8s-yaml/prometheus- Test Objective: test monitoring the normal metrics wildfly application .
cd wildfy-26.1.3.Final-sample-todo-backend
kubectl create namespace wildfly-ex-app
kubectl config set-context --current --namespace wildfly-ex-app
mvn clean package
eval $(minikube docker-env)
docker build -t wildfly-todo-backend:latest .
kubectl create -f wildfy-26.1.3.Final-sample-todo-backend/k8s-yaml/
kubectl create -f wildfy-26.1.3.Final-sample-todo-backend/k8s-yaml/prometheusecho "Add the loki helm chart"
helm repo add grafana https://grafana.github.io/helm-charts
helm repo update
helm install loki-stack grafana/loki-stack --values $BASE/loki-stack-values.yaml -n monitoring we can see the below loki-stack-values.yaml:
# https://github.com/grafana/helm-charts/blob/loki-stack-2.9.10/charts/loki-stack/values.yaml
# Enable Loki with persistence volume
loki:
enabled: true
size: 1Gi
promtail:
enabled: true
grafana:
enabled: false
sidecar:
datasources:
enabled: true
image:
tag: 8.3.4
fluent-bit:
enabled: true Once you are logged in Grafana, we can add Loki as a data source.
- Step1. From the Left side-panel, select Configuration -> Data Sources .
- Step2. In the Data sources view, click Add data source and then select Loki .
- Step3. Give the datasource a name and then set the Loki URL (
loki-stack:3100). - Step4. Click Save & Test. You should see a confirmation message like Data source connected and labels found .