This plugin allows to integrate a frontend Node/NPM/Yarn build into Gradle. It is inspired by the frontend-maven-plugin. See the quick start guide below to install/configure the plugin, and build your frontend application.
The plugin supports:
The plugin is built and tested on Linux, Mac OS, Windows. For a full list of build environments used, see the contributing notes.
2 options are available.
Using Gradle DSL
This is the modern and recommended approach.
// build.gradle
plugins {
id 'org.siouan.frontend' version '1.2.1'
}This approach is the legacy way to resolve and apply plugins.
// build.gradle
buildscript {
repositories {
url 'https://plugins.gradle.org/m2/'
}
dependencies {
classpath 'org.siouan:frontend-gradle-plugin:1.2.1'
}
}
apply plugin: 'org.siouan.frontend'All settings are introduced hereafter, with default value for each property.
// build.gradle
frontend {
// NODE SETTINGS
// Node version, used to build the URL to download the corresponding distribution, if the 'nodeDistributionUrl'
// property is not set.
nodeVersion = '10.16.0'
// [OPTIONAL] Sets this property to force the download from a custom website. By default, this property is
// 'null', and the plugin attempts to download the distribution compatible with the current platform from
// Node's website. The version of the distribution is expected to be the same as the one set in the
// 'nodeVersion' property, or this may lead to unexpected results.
nodeDistributionUrl = 'https://nodejs.org/dist/vX.Y.Z/node-vX.Y.Z-win-x64.zip'
// [OPTIONAL] Install directory where the distribution archive shall be exploded.
nodeInstallDirectory = "${projectDir}/node"
// YARN SETTINGS
// [OPTIONAL] Whether Yarn shall be used instead of NPM when executing frontend tasks. Consequently, a Yarn
// distribution will be downloaded and installed by the plugin. If <true>, the 'yarnVersion' version property
// must be set.
yarnEnabled = false
// [OPTIONAL] Yarn version, used to build the URL to download the corresponding distribution, if the
// 'yarnDistributionUrl' property is not set. This property is mandatory when the 'yarnEnabled' property is
// true.
yarnVersion = '1.16.0'
// [OPTIONAL] Sets this property to force the download from a custom website. By default, this property is
// 'null', and the plugin attempts to download the distribution compatible with the current platform from
// Yarn's website. The version of the distribution is expected to be the same as the one set in the
// 'yarnVersion' property, or this may lead to unexpected results.
yarnDistributionUrl = 'https://github.com/yarnpkg/yarn/releases/download/vX.Y.Z/yarn-vX.Y.Z.tar.gz'
// [OPTIONAL] Install directory where the distribution archive shall be exploded.
yarnInstallDirectory = "${projectDir}/yarn"
// OTHER SETTINGS
// Name of the NPM/Yarn scripts (see 'package.json' file) that shall be executed depending on the Gradle
// lifecycle task. The values below are passed as argument of the 'npm' or 'yarn' executables.
// [OPTIONAL] Use this property to customize the command line used to install frontend dependencies. This
// property is used by the 'installFrontend' task.
installScript = 'install'
// [OPTIONAL] Use this property only if frontend's compiled resources are generated out of the
// '${project.buildDir}' directory. Default value is <null>. This property is used by the 'cleanFrontend' task.
// The task is also executed when the Gradle built-in 'clean' task is executed, if this property is set.
cleanScript = 'run clean'
// [OPTIONAL] Script called to build frontend's artifacts. Default value is <null>. This property is used by
// the 'assembleFrontend' task.
// The task is also executed when the Gradle built-in 'assemble' task is executed, if this property is set.
assembleScript = 'run assemble'
// [OPTIONAL] Script called to check the frontend. Default value is <null>. This property is used by the
// 'checkFrontend' task. The task is run when the Gradle built-in 'check' task is run.
// The task is also executed when the Gradle built-in 'check' task is executed, if this property is set.
checkScript = 'run check'
}// build.gradle
frontend {
nodeVersion = '<X.Y.Z>'
cleanScript = 'run clean'
assembleScript = 'run assemble'
checkScript = 'run check'
}// build.gradle
frontend {
nodeVersion = '<X.Y.Z>'
yarnEnabled = true
yarnVersion = '<X.Y.Z>'
cleanScript = 'run clean'
assembleScript = 'run assemble'
checkScript = 'run check'
}Now that the plugin is correctly installed and configured, open a terminal, and execute the following command in the project's directory:
gradlew buildIf the frontend application is packaged with a Java backend into a single artifact, take a look at this guide to assemble the frontend and the backend together.
Note: the package.json file is expected to be in the project's root directory.
If you plan to use the downloaded distributions of Node/NPM/Yarn apart from Gradle, apply the following steps:
- Create a
NODEJS_HOMEenvironment variable containing the real path set in thenodeInstallDirectoryproperty. - Add the Node/NPM executables' directory to the
PATHenvironment variable:- On Unix-like O/S, add the
$NODEJS_HOME/binpath. - On Windows O/S, add
%NODEJS_HOME%path.
- On Unix-like O/S, add the
Optionally, if Yarn is enabled and you don't want to enter Yarn's executable absolute path on a command line:
- Create a
YARN_HOMEenvironment variable containing the real path set in theyarnInstallDirectoryproperty. - Add the Yarn executable's directory to the
PATHenvironment variable:- On Unix-like O/S, add the
$YARN_HOME/binpath. - On Windows O/S, add the
%YARN_HOME%\binpath.
- On Unix-like O/S, add the
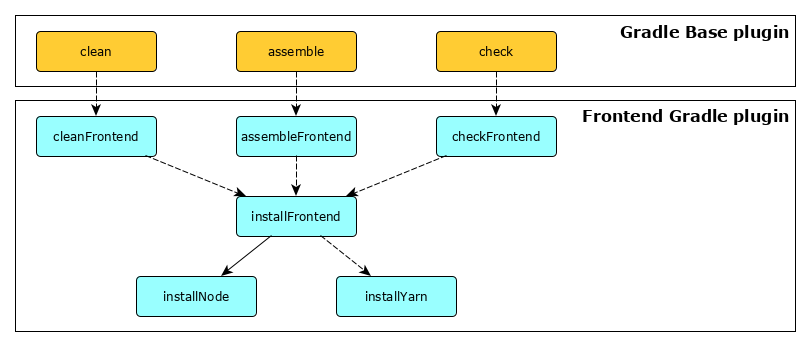
The plugin registers multiple tasks, some having dependencies with other, and also with Gradle lifecycle tasks defined in the Gradle base plugin.
The installNode task downloads a Node distribution and verifies its integrity. If the distributionUrl property is
ommitted, the URL is guessed using the version property. Use the property nodeInstallDirectory to set the directory
where the distribution shall be installed, which, by default is the ${projectDir}/node directory.
This task should not be executed directly. It will be called automatically by Gradle, if another task depends on it.
The installYarn task downloads a Yarn distribution, if yarnEnabled property is true. If the distributionUrl
property is ommitted, the URL is guessed using the version property. Use the property yarnInstallDirectory to set
the directory where the distribution shall be installed, which, by default is the ${projectDir}/yarn directory.
This task should not be executed directly. It will be called automatically by Gradle, if another task depends on it.
Depending on the value of the yarnEnabled property, the installFrontend task issues either a npm install command
or a yarn install command, by default. If a package.json file is found in the project's directory, the command shall
install dependencies and tools for frontend development. Optionally, this command may be customized (e.g. to run a
npm ci command instead of a npm install command). To do so, the installScript must be set to the corresponding
NPM/Yarn command. This task depends on the installNode task, and optionally on the installYarn task if the
yarnEnabled property is true.
This task may be executed directly, especially if the Node distribution and/or the Yarn distribution must be downloaded again.
The cleanFrontend task does nothing by default, considering frontend generated resources (pre-processed Typescript
files, SCSS stylesheets...) are written in the ${project.buildDir} directory. If it is not the case, this task may be
useful to clean the relevant directory. To do so, a clean script must be defined in the project's package.json file,
and the cleanScript property must be set to the corresponding NPM/Yarn command. This task depends on the
installFrontend task if the cleanScript property is set.
The assembleFrontend task shall be used to integrate a frontend's build script into Gradle builds. The build script
must be defined in the project's package.json file, and the assembleScript property must be set to the corresponding
NPM/Yarn command. This task depends on the installFrontend task if the assembleScript property is set.
The checkFrontend task shall be used to integrate a frontend's check script into Gradle builds. The check script must
be defined in the project's package.json file, and the checkscript property must be set with the corresponding
NPM/Yarn command. A typical check script defined in the project's package.json file may lint frontend source files,
execute tests, and perform additional analysis tasks. This task depends on the installFrontend task if the
checkScript property is set.
The plugin provides the task type org.siouan.frontendgradleplugin.tasks.RunNodeTask that allows creating a custom
task to launch a frontend script. The script property must be set with the corresponding Node command. For
instance, the code below added in the build.gradle file allows to run a JS my-custom-script.js with Node:
tasks.register('myCustomScript', org.siouan.frontendgradleplugin.tasks.RunNodeTask) {
// Choose whether Node only is required, or if additional dependencies located in the package.json file should
// be installed: make the task either depends on 'installNode' task or on 'installFrontend' task.
// dependsOn tasks.named('installNode')
// dependsOn tasks.named('installFrontend')
script = 'my-custom-script.js'
}The plugin provides the task type org.siouan.frontendgradleplugin.tasks.RunScriptTask that allows creating a custom
task to launch a frontend script. The script property must be set with the corresponding NPM/Yarn command. For
instance, the code below added in the build.gradle file allows to run frontend's end-to-end tests in a custom task:
tasks.register('e2e', org.siouan.frontendgradleplugin.tasks.RunScriptTask) {
dependsOn tasks.named('installFrontend')
script = 'run e2e'
}If you plan to serve your frontend with a Java backend (e.g. a Spring Boot application), you will probably use other Gradle plugins, such as the Gradle Java plugin, the Gradle Spring Boot plugin, or other ones of your choice.
In this configuration, you may package your full-stack application as a JAR/WAR artifact. To do so, the frontend must be
assembled before the backend, and generally provided in a special directory for the backend packaging task (e.g.
jar/war/bootJar/bootWar... tasks).
Assembling the frontend before the backend shall not be difficult to setup in Gradle. Below is the task tree of the
assemble task when this plugin is used with the Gradle Java plugin or a plugin depending on it:
gradlew taskTree --no-repeat assemble
:assemble
+--- :assembleFrontend
| \--- :installFrontend
| +--- :installNode
| \--- :installYarn
+--- :jar
\--- :classes
+--- :compileJava
\--- :processResources- Considering the frontend assembling script generates the frontend artifacts (HTML, CSS, JS...) in the
${frontendBuildDir}directory, these artifacts must be copied, generally in the${project.buildDir}/resources/main/publicdirectory, so as they can be served by the backend.
Let's create a custom task for this. Add the following lines in the build.gradle file:
tasks.register('processFrontendResources', Copy) {
description 'Process frontend resources'
from "${frontendBuildDir}"
into "${project.buildDir}/resources/main/public"
dependsOn tasks.named('assembleFrontend')
}Finally, you should:
- Replace the
${frontendBuildDir}variable by any relevant directory, depending on where the frontend artifacts are generated by your assembling script. - Adapt the target directory under
${project.buildDir}/resources/main, depending on the Java artifact built.
- The frontend must be assembled and the generated resources must be copied before the backend packaging task.
Our recommendation is the processResources task depends on the processFrontendResources task.
tasks.named('processResources').configure {
dependsOn tasks.named('processFrontendResources')
}The resulting task tree shall be as below:
gradlew taskTree --no-repeat assemble
:assemble
+--- :jar
\--- :classes
+--- :compileJava
\--- :processResources
+--- :processFrontendResources
+--- :assembleFrontend
\--- :installFrontend
+--- :installNode
\--- :installYarnThe checkFrontend task is attached to the lifecycle check task. The Gradle official documentation states that the
check task shall be used to attach [...] verification tasks, such as ones that run tests [...]. It's enough vague to
let you consider any verification task. The script mapped to the checkFrontend task may run either automated unit
tests, or functional tests, or a linter, or any other verification action, or even combine some or all of them. Every
combination is even possible, since you can define a script in your package.json file that executes sequentially the
actions of your choice.