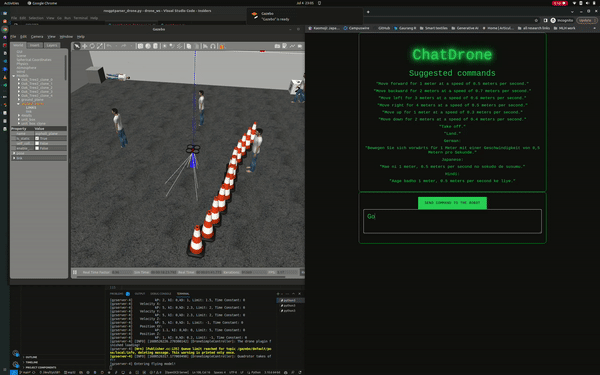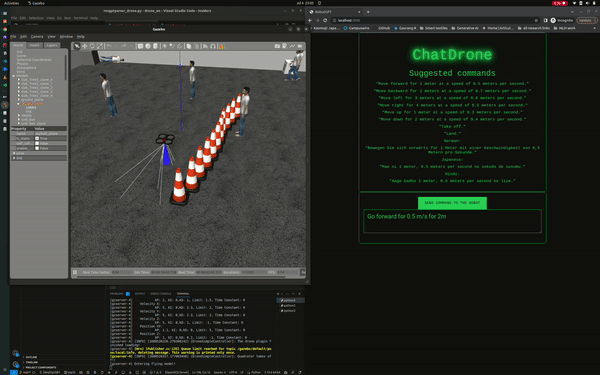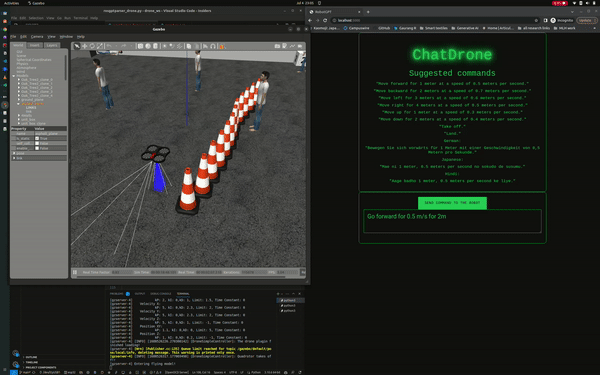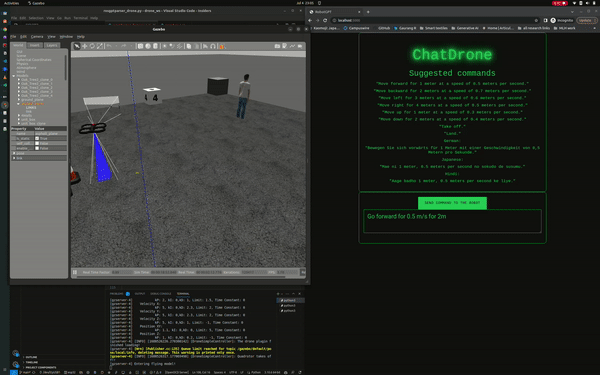
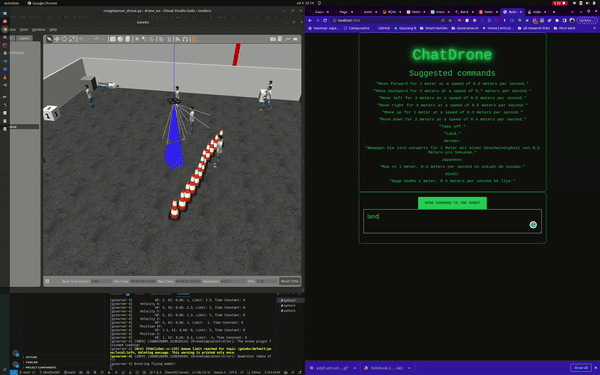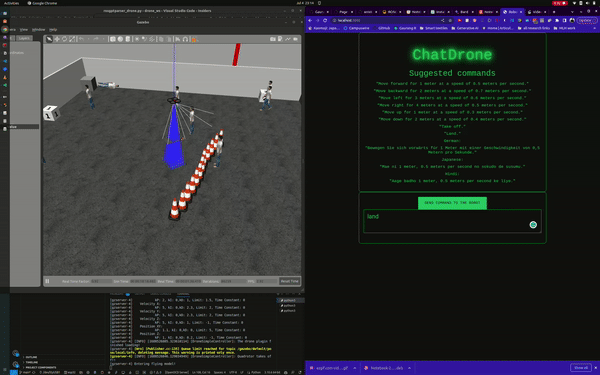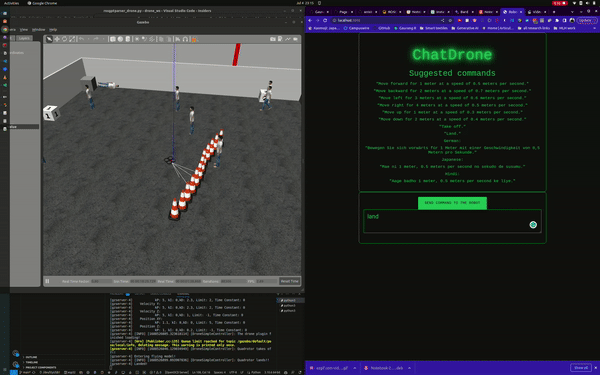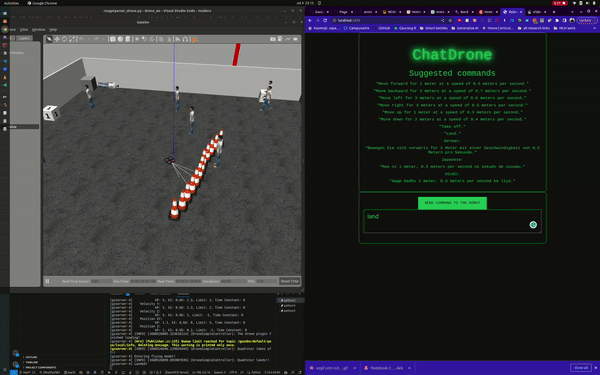
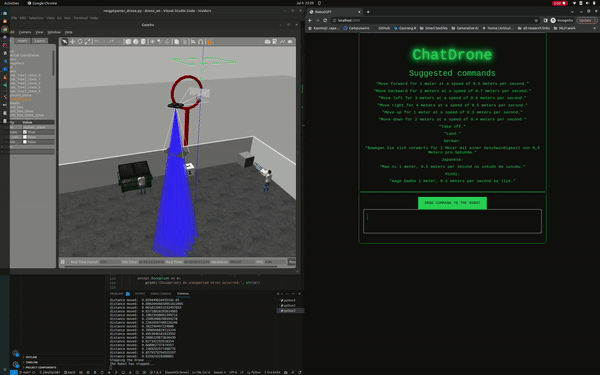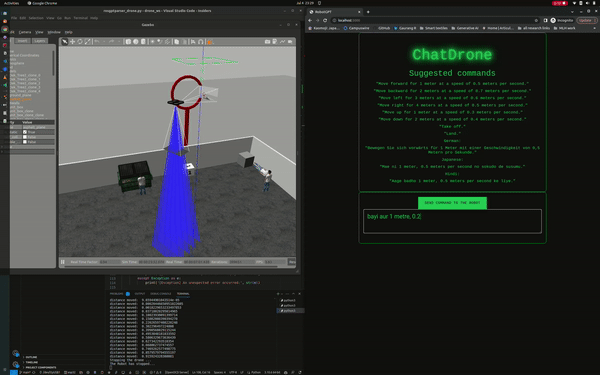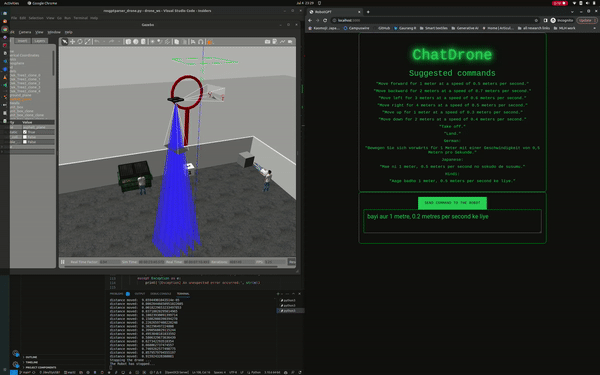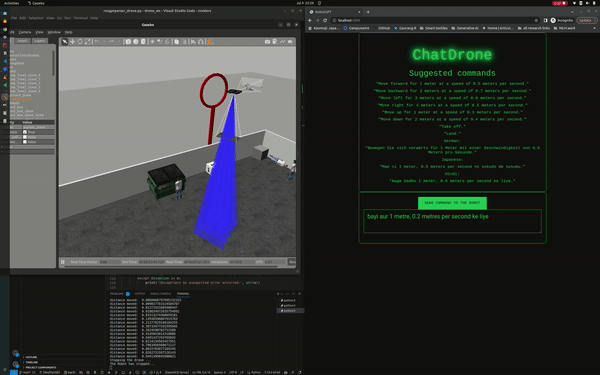
ChatDrones is a project that integrates Language Logic Models (LLMs) with drone control. This setup allows users to command drones using simple, everyday language. The project uses the ROS2 (Robot Operating System) Humble and runs simulations in the Gazebo environment, providing a reliable platform for drone behavior.
ChatDrones also includes a web application with a user-friendly interface, making it easy for users to input commands. This combines the benefits of advanced technology with a simple and easy-to-use design.
Currently, ChatDrones operates within a simulated environment, serving as a practical platform for testing and development. However, it's also designed to work with real drones, translating natural language instructions into actual drone commands.
Key features include:
- A user-friendly web application that provides an interactive interface for drone control
- Ability to initiate drone landing and takeoff through simple natural language commands
- Full control over the drone's directional movement, including forward, backward, left, and right commands
- Support for commands in multiple languages
-
The first component, "rosgpt.py", serves as the primary translator. As a REST server in a ROS2 node, it receives instructions in the form of POST requests, then processes these instructions into structured JSON commands using the ChatGPT API. Once the translation is complete, the commands are published on the /voice_cmd topic, ready for the next stage.
-
The next component is "rosgpt_client_node.py", a ROS2 client node that acts as a liaison between the user and rosgpt.py. It sends POST requests with the user's commands to the ROSGPT REST server and awaits the transformed JSON commands, displaying them upon receipt.
-
Another key component is "rosgpt_client.py", which fulfills a similar role to rosgpt_client_node.py. The main difference is that this script functions solely as a REST client for ROSGPT, without the ROS2 node involvement.
-
Once the commands are translated, they are received by "rosgptparser_drone.py". This script, dubbed the ROSGPTParser, executes the commands. It subscribes to the /voice_cmd topic, receives the JSON commands, parses them, and then carries out the necessary drone maneuvers.
Clone the repository
mkdir ros_ws
cd ros_ws
git clone <repo_url>
Install rosgpt libraries from the rosgpt folder
cd ~/src/rosgpt
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
Install ROS requirements
sudo apt-get install python-rosdep
sudo rosdep init
rosdep update
cd ~/ros_ws
rosdep install --from-paths src --ignore-src --rosdistro=<rosdistro> -y
Add your OpenAI API Key in your .bashrc as an environment variable
echo 'export OPENAI_API_KEY=your_api_key' >> ~/.bashrc
First, navigate to the root directory of your workspace and build the project
cd ~/ros_ws
colcon build --symlink-install
Now run each of these commands on new terminals
source install/setup.sh
ros2 run rosgpt rosgpt
source install/setup.sh
ros2 run rosgpt rosgpt_client_node
source install/setup.sh
ros2 run rosgpt rosgptparser_drone
source install/setup.sh
ros2 launch sjtu_drone_bringup sjtu_drone_bringup.launch.py
Note: Please replace <repository_url> and <your_api_key> with the actual repository URL and your OpenAI API key, respectively.
Simulation adapted from: https://github.com/NovoG93/sjtu_drone
@article{koubaa2023rosgpt,
title={ROSGPT: Next-Generation Human-Robot Interaction with ChatGPT and ROS},
author={Koubaa, Anis},
journal={Preprints.org},
year={2023},
volume={2023},
pages={2023040827},
doi={10.20944/preprints202304.0827.v2}
}
I am deeply appreciative of these individuals/teams for sharing their work to build on top of!