Package go-pagination was designed to paginate simple RESTful APIs with GORM and Gin. It uses cursor-based strategy, that avoids many of the pitfalls of "offset–limit" pagination.
package models
import "github.com/rosberry/go-pagination"
type User struct {
ID uint
Name string
Role uint `json:"roleID" cursor:"roleID"`
}
func GetUsersList(role uint, paginator *pagination.Paginator) []User {
var users []User
q := db.DB.Model(&User{}).Where("role = ?", role)
err := paginator.Find(q, &users)
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
return nil
}
return users
}package controllers
import "github.com/rosberry/go-pagination"
type (
usersListResponse struct {
Result bool
Users []userData
Pagination *pagination.PageInfo
}
)
func UsersList(c *gin.Context) {
paginator, err := pagination.New(pagination.Options{
GinContext: c,
DB: models.GetDB(),
Model: &models.User{},
Limit: 5,
DefaultCursor: nil,
})
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
}
users := models.GetUsersList(0, paginator)
c.JSON(200, usersListResponse{
Result: true,
Users: usersListToData(users),
Pagination: paginator.PageInfo,
})
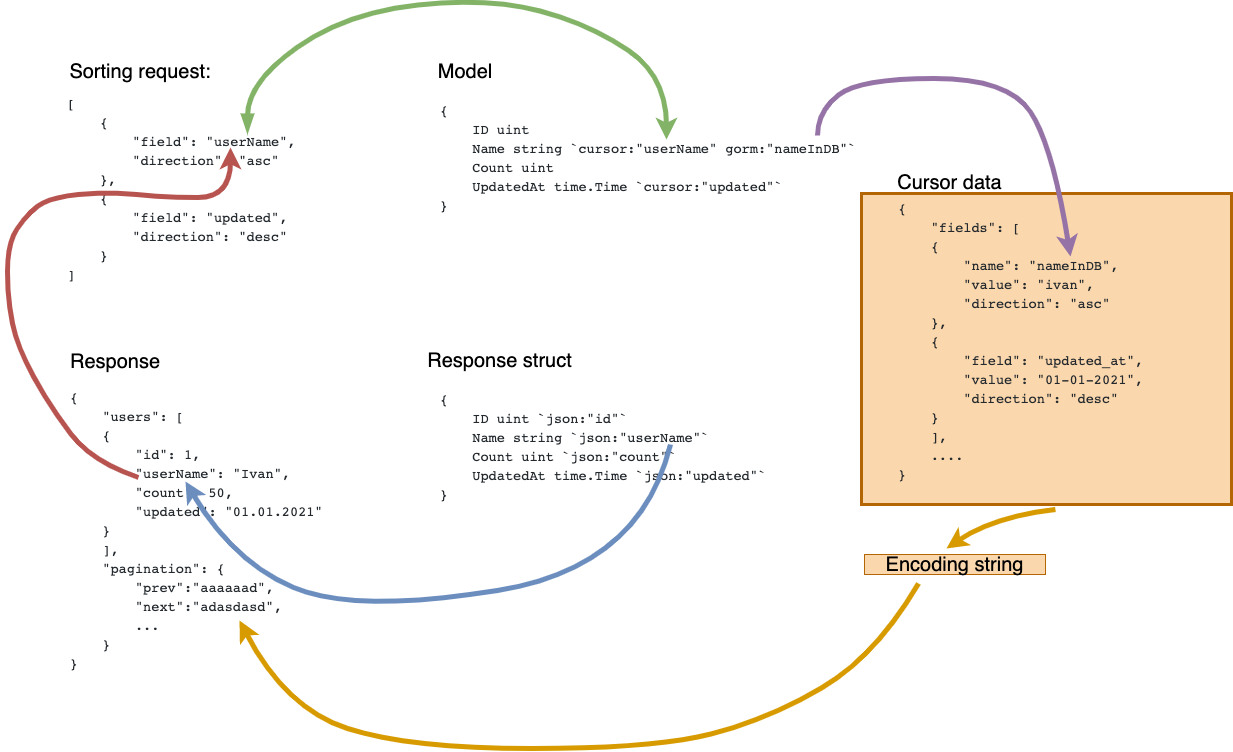
}If you want to get values in a special way, you can customize the functions to find the values you need.
You must implement functions RequestGetter type
type RequestGetter func(c *gin.Context) (query string)for example
func cursorGetter(c *gin.Context) (query string) {
cursorQuery := c.Request.Header.Get("customCursorFromHeader")
return cursorQuery
}
func sortingGetter(c *gin.Context) (query string) {
sortingQuery := c.Query("sort")
return sortingQuery
}and pass the functions as Options.CustomRequest (type RequestOptions) in pagination.New() function.
paginator, err := New(Options{
GinContext: c,
Limit: uint(limit),
DB: db,
Model: &Material{},
CustomRequest: &RequestOptions{
Cursor: func(c *gin.Context) (query string) {
cursorQuery := c.Request.Header.Get("customCursorFromHeader")
return cursorQuery
},
Sorting: func(c *gin.Context) (query string) {
sortingQuery := c.Query("sort")
return sortingQuery
},
},
})queryforcursor/after/before- base64 stringqueryforsorting- json string
Request:
GET /items
GET /items?sorting=%5B%7B%22field%22:%22id%22,%22direction%22:%22desc%22%7D%5D
Sorting query parameters is JSON:
[
{
"field": "Name",
"direction": "asc"
},
{
"field": "UpdatedAt",
"direction": "desc"
}
]
field name in query parameters should have name from response. If name in response is different from name in model - you need add tag cursor:"fieldName" in model
Response:
{
"result": true,
"data": {
},
"pagination": {
"hasPrev": false,
"hasNext": true,
"prev": "ew2YWxU0Cn01ZSI6ogICJID=",
"next": "ewogICJ2YWx1ZSI6IDU0Cn0=",
"totalRows": 10,
"rangeTruncated": true
}
}
Request next page:
GET /items?cursor=ew2YWxU0Cn01ZSI6ogICJID
Response (end):
{
"result": true,
"data": null,
"pagination:" null
}
You can use after/before params instead of cursor in request
GET /items?after=e2sdw2wO0WDwwW&before=sdqqwDsdDq2Pd1
The after parameter is typically sent by the client to get the next page, while before is used to get the prior page.
Clients MAY use the after and before parameters together on the same request. These are called “range pagination requests”, as the client is asking for all the results starting from immediately after the after cursor and continuing up until the before cursor.
For range pagination requests, the server uses a limit to determine the maximum page size. In other words, the page size used will depend on the value of the limit parameter or the maximum page size.
If the number of results that satisfy both the after and before constraints exceeds the used page size, the server responds with the same paginated data that it would have if the before parameter had not been provided. However, in this case the server MUST also add "rangeTruncated": true to the pagination metadata to indicate to the client that the paginated data does not contain all the results it requested.
This project is owned and maintained by Rosberry. We build mobile apps for users worldwide 🌏.
Check out our open source projects, read our blog or give us a high-five on 🐦 @rosberryapps.
This project is available under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for more info.