- Deployed App
- Introduction
- Repos
- Dev Team
- Technologies and Frameworks
- Local Deployment
- Testing and Test Coverage
- GraphQL
- Visit the deployed Rosetta app at http://rosetta-fe.herokuapp.com.
- Visit the interactive GraphiQL interface at http://rosetta-server.herokuapp.com/graphql.
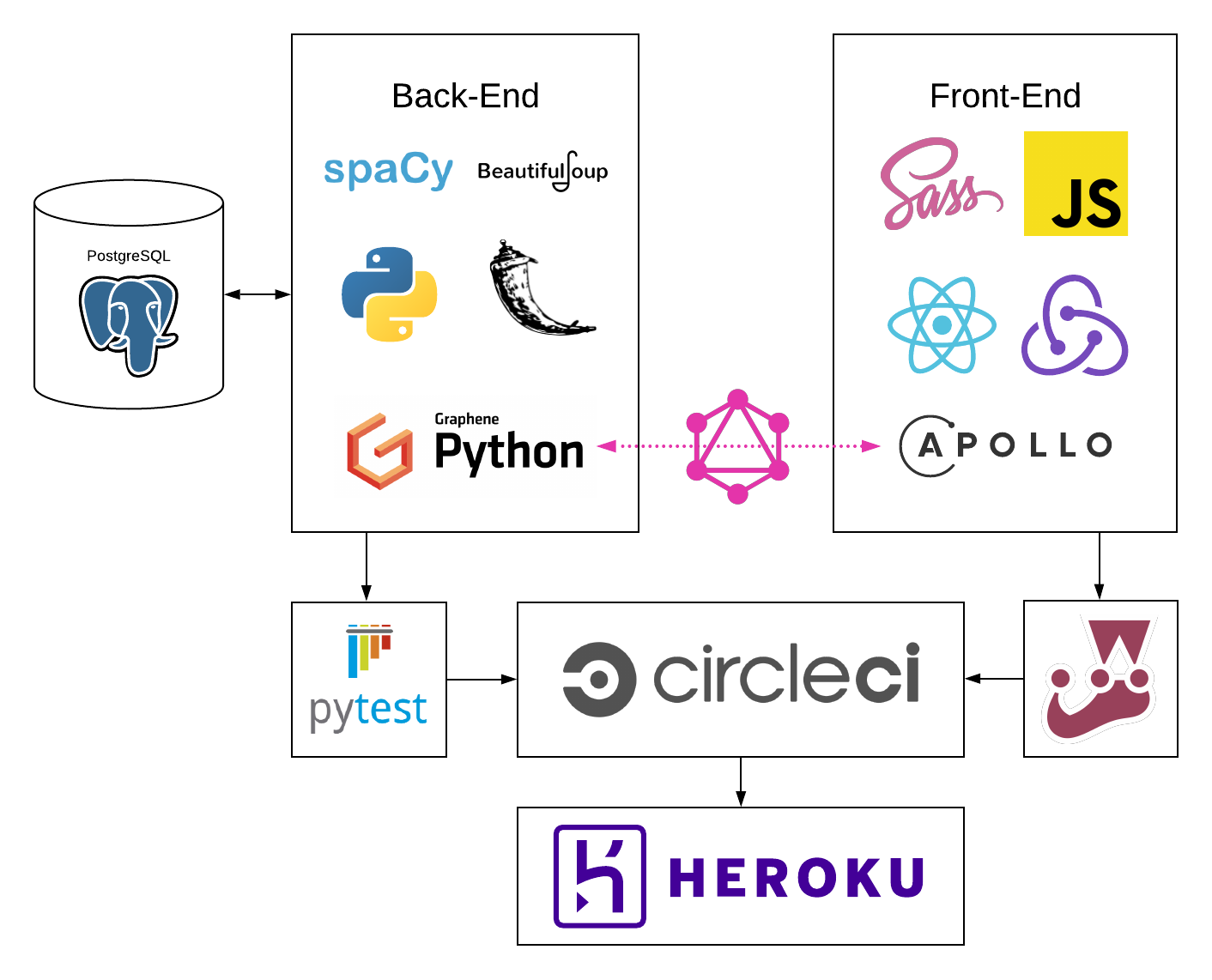
Rosetta is Google Translate for programming languages. It eases the process of learning new languages by translating a built-in function in a language you know into the closest equivalent in one you don’t. It does this by scraping official language docs using BeautifulSoup and comparing them using spaCy (a ML-powered natural language processing library) in the Python/Flask back-end, which the React/Redux front-end interacts with using Apollo Client and GraphQL.
This is the GitHub repo for Rosetta's back-end Flask micro-service. The repo for the React/Redux front-end can be found at https://github.com/rosetta-team/rosetta-fe.
Rosetta's dev team is:
- Alison Vermeil (GitHub, LinkedIn)
- Daniel Frampton (GitHub, LinkedIn)
- Josh O'Bannon (GitHub, LinkedIn)
- Matt Simon (GitHub, LinkedIn)
- Veronica Andrade (GitHub, LinkedIn)
- Back-End
- Language: Python
- Testing: Pytest
- Framework: Flask
- Database: PostgreSQL
- Database Interaction & ORM: SQLAlchemy
- Database Migrations: Alembic (via Flask-Migration wrapper)
- GraphQL Server: Graphene & Flask-GraphQL
- Web-Scraping: BeautifulSoup
- Machine Learning & Natural Language Processing: spaCy
- Front-End
- Language: JavaScript
- Framework: React/Redux
- Styling: Sass/SCSS
- GraphQL Client: Apollo Client
- Syntax Highlighting: Prism.js
- Testing: Jest & React Testing Library
- CI/CD
- Continuous Integration: CircleCI
- Deployment: Heroku
- Project Management
- Kanban & Sprint Planning: Github Project Boards
- Agile Planning & Retros: Miro
- Communication: Zoom & Slack
Both the back-end and front-end of the live Rosetta app are deployed on Heroku, but they can deployed locally by following the instructions below.
- Clone this repo to your local machine using SSH:
git clone git@github.com:rosetta-team/rosetta-be.git - Change the working directory to the repo directory:
cd rosetta-be - Install Pyenv with Homebrew
brew install pyenv - Add pyenv init to your shell profile (see instructions here under step 3)
- If using Bash, enter the following in your terminal:
echo -e 'if command -v pyenv 1>/dev/null 2>&1; then\n eval "$(pyenv init -)"\nfi' >> ~/.bash_profile - If using Zsh, use the following:
echo -e 'if command -v pyenv 1>/dev/null 2>&1; then\n eval "$(pyenv init -)"\nfi' >> ~/.zshrc
- If using Bash, enter the following in your terminal:
- Restart terminal to allow changes to take effect.
- Install Python 3.7.7 with Pyenv
pyenv install 3.7.7 - Set up virtual environment
python3 -m venv venv . venv/bin/activate - Upgrade Pip (or, if not made available by Python 3, install Pip)
pip install -U pip - Use Pip to install packages in requirements.txt:
pip install -r requirements.txt - Set environment variables:
export FLASK_APP=flaskr/app export FLASK_ENV=development
- Install PostgreSQL with Homebrew
brew install postgresql - Create database from terminal
- Open interactive PostgreSQL session:
psql - Enter SQL command to create empty database:
CREATE DATABASE rosetta_dev;
- Open interactive PostgreSQL session:
- Create a file named
.envin the/flaskrdirectory, and inside it add this line:DATABASE_URL = "postgresql://postgres:postgres@localhost:5432/rosetta_dev"
At this point you can populate your database from scratch by running the scripts below, but it's preferable to import this from an already populated database to avoid excessive hits to the official language docs.
This is possible by restoring the "dumpfile" contained in the root directory of the back-end repo. You can read instructions on how to do this in these official PostgreSQL docs, or simply run the following command while in the rosetta-be repo directory:
psql rosetta_dev < database_dump
This will recreate all the tables and relationships and data that would be created by the following scripts and migrations, and you can skip the rest of this section.
Alternatively, if you choose to populate the database from scratch, follow the instructions below. Note that, because these scripts rely upon web-scraping official documentation websites which may change without notice, these may cease to function as expected.
Run the Alembic migrations to add tables to database:
python flaskr/manage.py db upgrade
- If you run this subsequent times, you might encounter the error "Target database is not up to date," which means you are likely out of sync with the migrations. Run
python flaskr/manage.py db stamp headto set the current state of your database as "head," then re-attempt to rundb upgrade. - If you had to drop your DB in development, you might need to run
python flaskr/manage.py db migratebeforepython flaskr/manage.py db upgrade.
spaCy requires downloading an additional file to perform the natural language processing to create the weighted relevancy ratings. en_core_web_lg doesn't exist as a package in its own right on pypi.org or Anaconda, so you can't just pip install it by name. Instead, you must run the following command:
python -m spacy download en_core_web_lg
Afterwards, run the following scripts to populate the database:
python flaskr/manage.py get_ruby_array_methods
python flaskr/manage.py get_js_array_methods
python flaskr/relevancy_rating_generator.py
At this point your database should be populated.
If at any point something goes wrong and you need to reset a particular table, run the following commands:
- Enter the psql console:
psql - Connect with Rosetta database:
\c rosetta_dev - Clear tables:
TRUNCATE TABLE [table_name] RESTART IDENTITY CASCADE;
- To run server on
localhost:5000:flask run - To run Flask shell session with access to ORM:
python flaskr/manage.py shell
- Clone down the front-end repo:
git clone git@github.com:rosetta-team/rosetta-fe.git
- Change working directory to repo directory with
cd rosetta-fe - Run
npm install - Run
npm run devto get your development server running and compile the application. This will automatically open the website in your browser. - After running the server, to manually visit the website navigate to
localhost:3000in your browser.
To run back-end test suite:
pytest
To configure the included coverage module to run without additional arguments, as below, run the following (should only need to do so once):
coverage -m pytest
To run test coverage report:
coverage report
To generate HTML coverage report:
coverage html
To open generated HTML coverage report:
open html-cov/index.html
To run front-end test suite:
npm test
To run test suite with coverage report:
npm test -- --coverage --watchAll
After running coverage report, to open graphic interface version:
open coverage/lcov-report/index.html
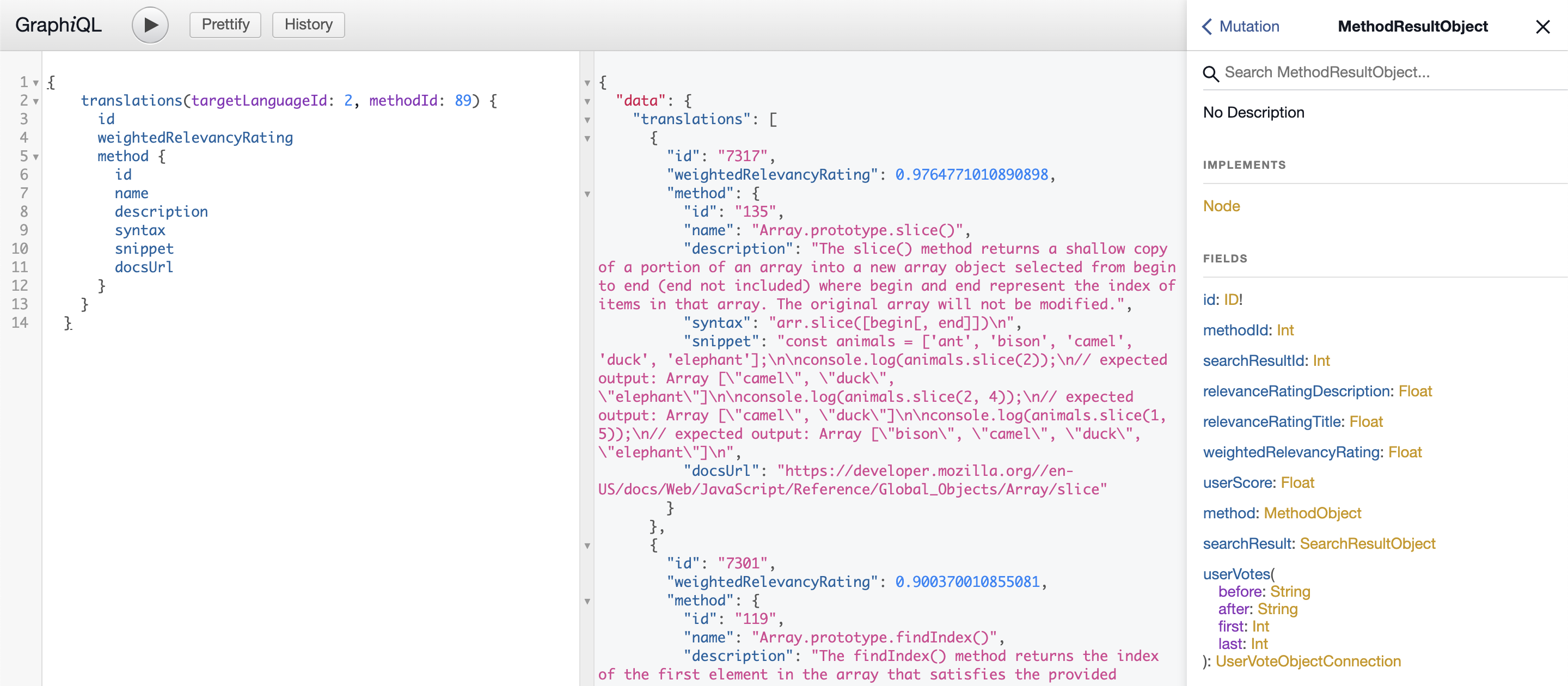
When running the back-end server locally, the interactive GraphiQL interface can be accessed at localhost:5000/graphql. There, you can run actual queries and mutations against the back-end and view the automated documentation of the schema and queries.
When sending a query to the server from elsewhere (such as Postman), send a POST request to localhost:5000/graphql with the query as the body.
This schema is non-exhaustive, and lists only the fields utilized by the front-end. For a complete reference of available GraphQL fields, use the GraphiQL interface and click "Docs" in the top-right corner to access the Documentation Explorer.
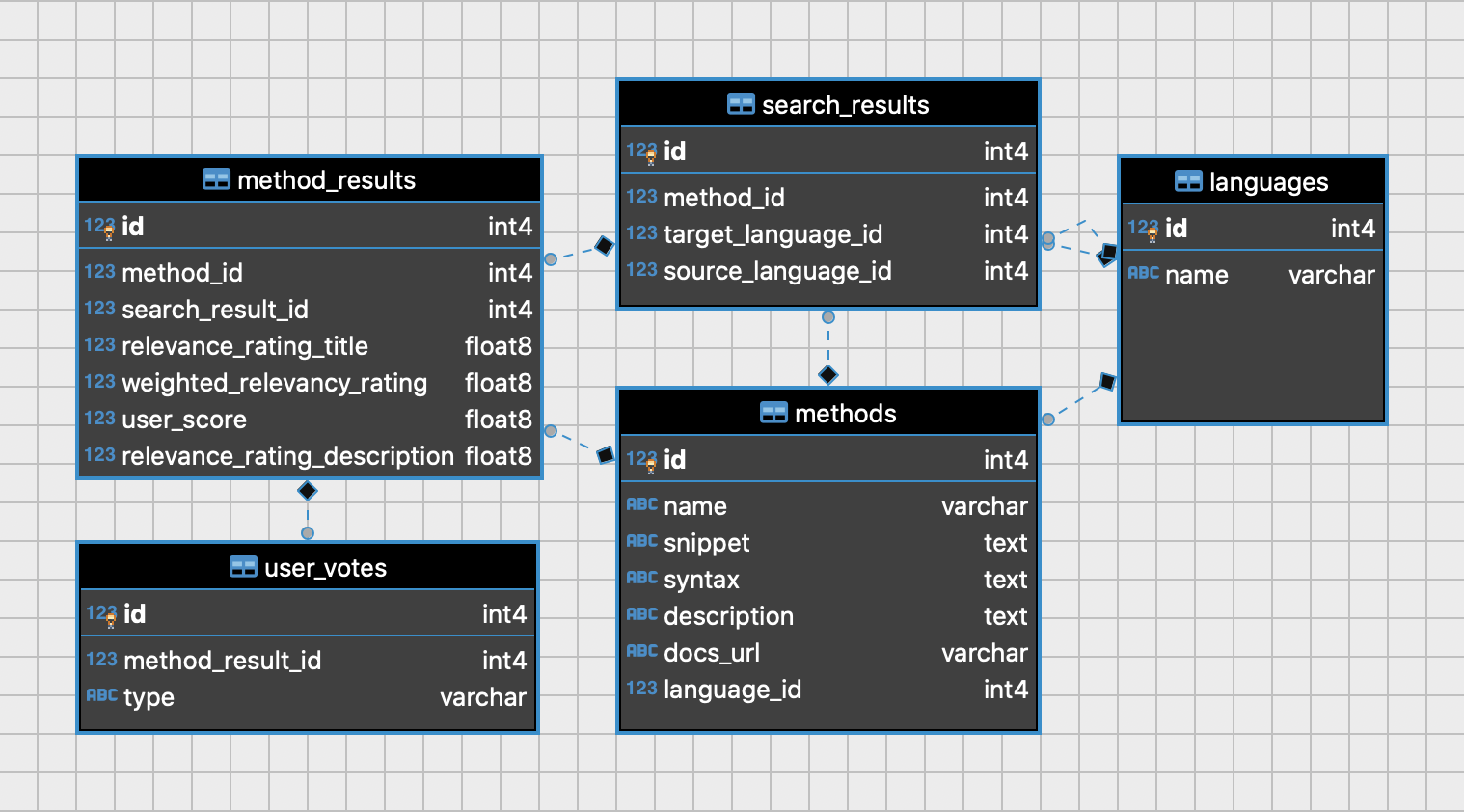
| Languages | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | ID! | Primary Key |
| name | String | Name of language |
| methods | [MethodObject] | Associated methods |
| Methods | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | ID! | Primary Key |
| language | LanguageObject | Associated language |
| name | String | Name of method/function |
| description | String | Description of method |
| snippet | String | Example code snippet |
| syntax | Text | Syntax of method usage |
| docsUrl | String | Source URL in official docs |
| MethodResults | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| id | ID! | Primary Key |
| weightedRelevancyRating | Float | Weighted similarity rating as number btw. 0-1 |
| method | MethodObject | Associated method |
Returns top 5 methods or functions in target language as compared to a given method, along with a relevancy rating generated by a machine learning and natural language process library weighted by user input.
- Example Input:
{ translations(targetLanguageId: 2, methodId: 89) { id weightedRelevancyRating method { id name description syntax snippet docsUrl } } } - Example Response:
{ "data": { "translations": [ { "id": "7317", "weightedRelevancyRating": 0.97647710108909, "method": { "id": "135", "name": "Array.prototype.slice()", "description": "The slice() method returns a shallow copy of a portion of an array into a new array object selected from begin to end (end not included) where begin and end represent the index of items in that array. The original array will not be modified.", "syntax": "arr.slice([begin[, end]])\n", "snippet": "const animals = ['ant', 'bison', 'camel', 'duck', 'elephant'];\n\nconsole.log(animals.slice(2));\n// expected output: Array [\"camel\", \"duck\", \"elephant\"]\n\nconsole.log(animals.slice(2, 4));\n// expected output: Array [\"camel\", \"duck\"]\n\nconsole.log(animals.slice(1, 5));\n// expected output: Array [\"bison\", \"camel\", \"duck\", \"elephant\"]\n", "docsUrl": "https://developer.mozilla.org//en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/slice" } }, { "id": "7301", "weightedRelevancyRating": 0.900370010855081, "method": { "id": "119", "name": "Array.prototype.findIndex()", "description": "The findIndex() method returns the index of the first element in the array that satisfies the provided testing function. Otherwise, it returns -1, indicating that no element passed the test.", "syntax": "arr.findIndex(callback( element[, index[, array]] )[, thisArg])\n", "snippet": "const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];\n\nconst isLargeNumber = (element) => element > 13;\n\nconsole.log(array1.findIndex(isLargeNumber));\n// expected output: 3\n", "docsUrl": "https://developer.mozilla.org//en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/findIndex" } }, { "id": "7307", "weightedRelevancyRating": 0.835100513965771, "method": { "id": "125", "name": "Array.prototype.join()", "description": "The join() method creates and returns a new string by concatenating all of the elements in an array (or an array-like object), separated by commas or a specified separator string. If the array has only one item, then that item will be returned without using the separator.", "syntax": "arr.join([separator])", "snippet": "const elements = ['Fire', 'Air', 'Water'];\n\nconsole.log(elements.join());\n// expected output: \"Fire,Air,Water\"\n\nconsole.log(elements.join(''));\n// expected output: \"FireAirWater\"\n\nconsole.log(elements.join('-'));\n// expected output: \"Fire-Air-Water\"\n", "docsUrl": "https://developer.mozilla.org//en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/join" } }, { "id": "7292", "weightedRelevancyRating": 0.834279735840426, "method": { "id": "111", "name": "Array.of()", "description": "The Array.of() method creates a new Array instance from a variable number of arguments, regardless of number or type of the arguments.", "syntax": "Array.of(element0[, element1[, ...[, elementN]]])", "snippet": "Array.of(7); // [7] \nArray.of(1, 2, 3); // [1, 2, 3]\n\nArray(7); // array of 7 empty slots\nArray(1, 2, 3); // [1, 2, 3]\n", "docsUrl": "https://developer.mozilla.org//en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/of" } }, { "id": "7291", "weightedRelevancyRating": 0.832082262294994, "method": { "id": "110", "name": "Array.isArray()", "description": "The Array.isArray() method determines whether the passed value is an Array.", "syntax": "Array.isArray(value)", "snippet": "Array.isArray([1, 2, 3]); // true\nArray.isArray({foo: 123}); // false\nArray.isArray('foobar'); // false\nArray.isArray(undefined); // false\n", "docsUrl": "https://developer.mozilla.org//en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/isArray" } } ] } }
Returns all languages in the database and (optionally) their associated methods and their attributes.
- Example Query:
{ allLanguages { id name methods { id name } } } - Example Response (abridged):
{ "data": { "allLanguages": [ { "id": "1", "name": "Ruby", "methods": [ { "id": "1", "name": "Array::[]" }, { "id": "2", "name": "Array::new" }, { "id": "3", "name": "Array::try_convert" }, { "id": "4", "name": "Array#&" }, { "id": "5", "name": "Array#*" }, // ... ] }, { "id": "2", "name": "JavaScript", "methods": [ { "id": "109", "name": "Array.from()" }, { "id": "110", "name": "Array.isArray()" }, { "id": "111", "name": "Array.of()" }, { "id": "112", "name": "Array.prototype.concat()" }, { "id": "113", "name": "Array.prototype.copyWithin()" }, // ... ] } ] } }
Creates a user vote record in the database associated with a particular method result, recalculates that result's user score and the overall weighted relevancy rating, and retrieves an updated top 5 results for the associated search.
- Example Mutation:
mutation {
createVote(methodResultId: 603, type: "down") {
id
weightedRelevancyRating
method {
id
name
syntax
snippet
description
docsUrl
}
}
}
- Example Response:
{ "data": { "translations": [ { "id": "7317", "weightedRelevancyRating": 0.97647710108909, "method": { "id": "135", "name": "Array.prototype.slice()", "description": "The slice() method returns a shallow copy of a portion of an array into a new array object selected from begin to end (end not included) where begin and end represent the index of items in that array. The original array will not be modified.", "syntax": "arr.slice([begin[, end]])\n", "snippet": "const animals = ['ant', 'bison', 'camel', 'duck', 'elephant'];\n\nconsole.log(animals.slice(2));\n// expected output: Array [\"camel\", \"duck\", \"elephant\"]\n\nconsole.log(animals.slice(2, 4));\n// expected output: Array [\"camel\", \"duck\"]\n\nconsole.log(animals.slice(1, 5));\n// expected output: Array [\"bison\", \"camel\", \"duck\", \"elephant\"]\n", "docsUrl": "https://developer.mozilla.org//en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/slice" } }, { "id": "7301", "weightedRelevancyRating": 0.900370010855081, "method": { "id": "119", "name": "Array.prototype.findIndex()", "description": "The findIndex() method returns the index of the first element in the array that satisfies the provided testing function. Otherwise, it returns -1, indicating that no element passed the test.", "syntax": "arr.findIndex(callback( element[, index[, array]] )[, thisArg])\n", "snippet": "const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];\n\nconst isLargeNumber = (element) => element > 13;\n\nconsole.log(array1.findIndex(isLargeNumber));\n// expected output: 3\n", "docsUrl": "https://developer.mozilla.org//en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/findIndex" } }, { "id": "7307", "weightedRelevancyRating": 0.835100513965771, "method": { "id": "125", "name": "Array.prototype.join()", "description": "The join() method creates and returns a new string by concatenating all of the elements in an array (or an array-like object), separated by commas or a specified separator string. If the array has only one item, then that item will be returned without using the separator.", "syntax": "arr.join([separator])", "snippet": "const elements = ['Fire', 'Air', 'Water'];\n\nconsole.log(elements.join());\n// expected output: \"Fire,Air,Water\"\n\nconsole.log(elements.join(''));\n// expected output: \"FireAirWater\"\n\nconsole.log(elements.join('-'));\n// expected output: \"Fire-Air-Water\"\n", "docsUrl": "https://developer.mozilla.org//en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/join" } }, { "id": "7292", "weightedRelevancyRating": 0.834279735840426, "method": { "id": "111", "name": "Array.of()", "description": "The Array.of() method creates a new Array instance from a variable number of arguments, regardless of number or type of the arguments.", "syntax": "Array.of(element0[, element1[, ...[, elementN]]])", "snippet": "Array.of(7); // [7] \nArray.of(1, 2, 3); // [1, 2, 3]\n\nArray(7); // array of 7 empty slots\nArray(1, 2, 3); // [1, 2, 3]\n", "docsUrl": "https://developer.mozilla.org//en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/of" } }, { "id": "7291", "weightedRelevancyRating": 0.832082262294994, "method": { "id": "110", "name": "Array.isArray()", "description": "The Array.isArray() method determines whether the passed value is an Array.", "syntax": "Array.isArray(value)", "snippet": "Array.isArray([1, 2, 3]); // true\nArray.isArray({foo: 123}); // false\nArray.isArray('foobar'); // false\nArray.isArray(undefined); // false\n", "docsUrl": "https://developer.mozilla.org//en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array/isArray" } } ] } }