The objective of this script is to mine meaningful semantic connections between the notes in a given Obsidian vault. As a result the user receives a list of note titles that are recommended as new connection to a given note. The user can decide to form new edges basing on the recommendation.
Obsidian.md is an open source knowledge management software. As its creators describe it: "Obsidian is a powerful and extensible knowledge base that works on top of your
local folder of plain text files." The Obsidian allows for forward and back-links as a way of connection between notes. This approach results with a graph. It can be traversed by users in search of new meaningful connections. The quality of semantic edges in the graph is dictated by the judgement of the user.
If you want to learn more about the Obsidian, check: Obsidian.md
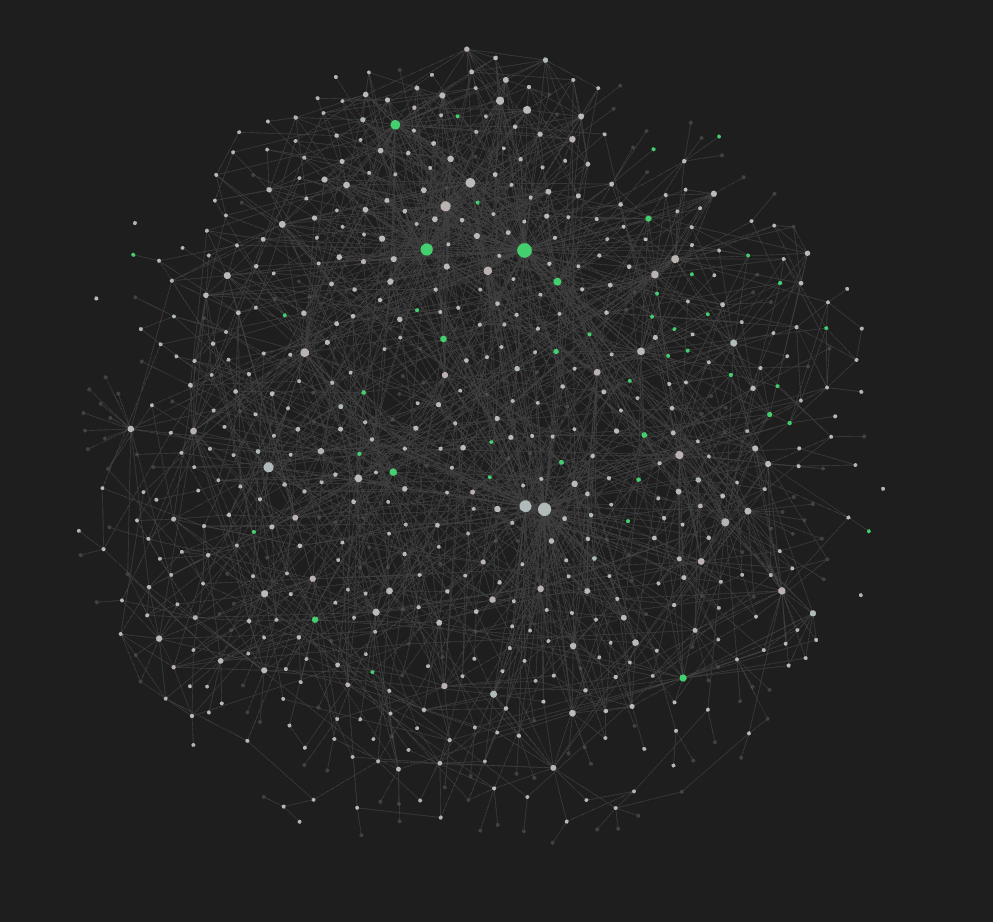
- An example of cluttered Obsidian graph (~500 notes)
The script employs method known as Bag of Words where each note is turned into a vector representation. Then, thanks to Nearest Neighbors algorithm, the script calculates the distance between the notes. This allows to return a list of notes that are the closest ones to a given master-note.
To use the script you need to have Python 3 installed on your machine as well as libraries specified in requirements.txt. All the commands here assume that you run them from the directory where vault_neighbors.py is saved.
This assumes you have Python 3 already installed on your machine. If not then the easiest way to do it is to use Anaconda distribution.
Instalation of required libraries from requirements.txt:
pip install -r requirements.txt
- The script logic lives in
vault_neighbors.py. Download it. - Three .txt files saved in the same location as .py file allow for more detailed parametrization. Each parameter value in these files should start a new line.
- In order for the script to work correctly you need to specify absolute path to your vault. You can do it under
nnpath.txt. The alternative is to provide it in the command line once prompted. nnignore.txtallows you to define directories within your vault that should be excluded from the analysis.nnpatterns.txtcontains regular expression patterns that script should employ to get rid of the non-meaningful phrases from your notes. As each vault is different, you probably should come up with your own list of patterns. You can also leave this file empty.
- In order for the script to work correctly you need to specify absolute path to your vault. You can do it under
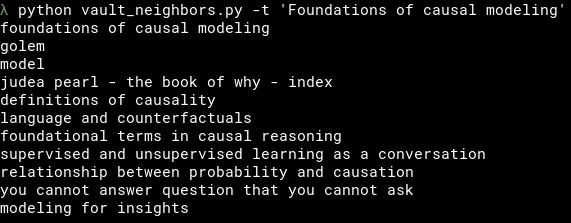
This will return you 10 nearest neighbors to a note which title was passed after -t argument:
python vault_neighbors.py -t 'title of the note'
You can control main parameters of the script like distance metric or number of recommendations with python script arguments.
Below is a screnshoot of the python notes_neighbors.py --help:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-e ENCODING, --encoding ENCODING
Set encoding for vault notes. Default utf-8
-de, --drop_empty Drop empty notes instead of filling them in with titles
-do, --drop_outlinks Dont take outlinks into the nearest neighbors analysis
-ip IGNORE_PATH, --ignore_path IGNORE_PATH
Set path to nnignore.txt file. Default ./nnignore.txt
-mt METRIC, --metric METRIC
Set distance metric for NN algorithm. Default 'cosine'. Available
metrics: jaccard, cosine.
-nn NEIGHBORS_NUMBER, --neighbors_number NEIGHBORS_NUMBER
Set nearest neighbors number the script should return. Default 10.
-pp PATTERN_PATH, --pattern_path PATTERN_PATH
Set path to nnpatterns.txt. Default ./nnpatterns.txt
-pk, --peek Show note content after it got processed by the script.
-t TITLE, --title TITLE
Pass full note title for which you want to get nearest neighbors
-v, --verbose Make script output more verbose
-vp VAULT_PATH, --vault_path VAULT_PATH
Set path to nnpath.txt. Default ./nnpath.txt
- The script has been tested Linux.
- It's performance was tested on a vault with ~500 notes:
1.73 s ± 79.8 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 1 loop each)
- User can look-up the note contents to see how it got processed by the script
- Accuracy metrics