C++ reference implementation of GENIVI SOTA OTA update client.
The client is intended to be installed on devices that wish to receive OTA updates from a GENIVI-compatible OTA server.
The client is responsible for:
-
Communicating with the OTA server
-
Authenticating using locally available device and user credentials
-
Reporting current software and hardware configuration to the server
-
Checking for any available updates for the device
-
Downloaded any available updates
-
Installing the updates on the system, or notifying other services of the availability of the downloaded file
-
Receiving or generating installation reports (success or failure) for attempts to install received software
-
Submitting installation reports to the server
The client maintains the integrity and confidentiality of the OTA update in transit, communicating with the server over a TLS link. The client can run either as a system service, periodically checking for updates, or can by triggered by other system interactions (for example on user request, or on receipt of a wake-up message from the OTA server).
This client, and the GENIVI SOTA project, is aligned with the Uptane security framework for software updates. Full details and whitepapers can be found on their site.
The following debian packages are used in the project:
-
asn1c
-
build-essential
-
clang (optional)
-
clang-format-3.8 (optional)
-
cmake (>= 3.5.1)
-
curl (>= 7.47)
-
doxygen (when building additional documentation)
-
graphviz (when building additional documentation)
-
lcov (when building for code coverage)
-
libarchive-dev
-
libboost-dev
-
libboost-filesystem-dev (>= 1.58.0)
-
libboost-log-dev (>= 1.58.0)
-
libboost-program-options-dev (>= 1.58.0)
-
libboost-random-dev (>= 1.58.0)
-
libboost-regex-dev (>= 1.58.0)
-
libboost-system-dev (>= 1.58.0)
-
libboost-thread-dev (>= 1.58.0)
-
libcurl4-openssl-dev (>= 7.47)
-
libdpkg-dev (when building with Debian packaging support)
-
libostree-dev (when building with OSTree support)
-
libpthread-stubs0-dev (>=0.3)
-
libsodium-dev
-
libsqlite3-dev
-
libssl-dev
-
libsystemd-dev (when building with systemd support)
-
libyaml-cpp-dev (>=0.5.2)
-
python3-dev (when building tests)
-
python3-openssl (when building tests)
-
python3-venv (when building tests)
-
valgrind
This project uses git submodules. To checkout the code:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/advancedtelematic/aktualizr
If you had an old checkout, forgot to include --recursive or need to update the submodules, run:
git submodule update --init --recursive
aktualizr is built using CMake. To setup your build directory:
mkdir build cd build cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug ..
You can then build the project from the build directory using Make:
make
You can also create a debian package:
make package
Before checking in code, the code linting checks should be run:
make qa
This will reformat all the code with clang-format and run clang-check and the test suite. Please follow the Google C++ Style Guide coding standard.
By default, the compilation and tests run in sequence and the output of failing tests is suppressed. To run in parallel, for example with eight threads, and print the output of failing tests, run this:
CTEST_OUTPUT_ON_FAILURE=1 CTEST_PARALLEL_LEVEL=8 make -j8 qa
To run the test suite:
make test
make qa will also run the test suite.
Some of the tests require provisioning credentials. For details of the credentials format, see credentials.adoc. Tests that require valid credentials are disabled by default. To enable them, set SOTA_PACKED_CREDENTIALS in the cmake GUI, by passing -DSOTA_PACKED_CREDENTIALS=… to cmake, or by editing CMakeCache.txt in the build directory.
The project can be configured to generate a code coverage report. First, create a CMake build directory for coverage builds, and invoke CMake with the -DBUILD_WITH_CODE_COVERAGE=ON flag:
mkdir build-coverage cd build-coverage cmake -DBUILD_WITH_CODE_COVERAGE=ON ..
Then use Make from the build-coverage directory to run the coverage report:
make coverage
The report will be output to the tests/coverage folder in your build-coverage directory.
A Dockerfile is provided to support building and testing the application without dependencies on your local environment. If you have a working docker client and docker server running on your machine, you can build a docker image with:
docker build -t advancedtelematic/aktualizr .
While the default Dockerfile image is usually the best one to use, you can select another one with the -f <Dockerfile> flag, e.g.:
docker build -t advancedtelematic/aktualizr -f Dockerfile.deb-stable .
Once your docker image is built, Aktualizr can be built and tested with:
docker run --rm -it advancedtelematic/aktualizr src/scripts/coverage.sh
The following command will get a shell to perform an interactive build, but note that your local working copy will not be synchronised with the Docker container. The recommended development workflow is perform local cmake builds, but passing -v $(pwd):/aktualizr-local to docker run is an alternative.
docker run --rm -it advancedtelematic/aktualizr
By default OpenEmbedded builds fixed versions of software from a VCS using bitbake recipes. When developing Aktualizr itself it is useful to have a quicker edit-compile-run cycle and access to a debugger. The following steps will use OpenEmbedded to create a cross-compilation environment, then build inside that.
-
Add the following to local.conf:
TOOLCHAIN_HOST_TASK_append = " nativesdk-cmake "
-
Build the SDK:
bitbake -c populate_sdk core-image-minimal
-
That will create a self-extracting installer that can be copied to your development machine. Install it by executing this script (or a similarly-named one, depending on your environment):
./tmp/deploy/sdk/poky-sota-glibc-x86_64-core-image-minimal-core2-64-toolchain-2.2.2.sh
-
Execute this script (or something similar, depending on where you installed it) to update the environment to point to the cross compilers:
. /opt/poky-sota/2.2.2/environment-setup-core2-64-poky-linux
You may want to verify that
which cmakereturns something like this:/opt/poky-sota/2.2.2/sysroots/x86_64-pokysdk-linux/usr/bin/cmake
-
Create a cmake build directory for this cross-compile:
mkdir build-cross cd build-cross cmake .. <options> make aktualizr
The compiled 'aktualizr' executable can be copied to the remote system and run.
Aktualizr can be debugged remotely by exposing a port from the VM to development machine (the --gdb option to the run-qemu-ota script in meta-updater does this), then:
gdbserver 0.0.0.0:2159 ./aktualizr --config /usr/lib/sota/sota.toml --loglevel 0
$ gdb aktualizr (gdb) target remote localhost:2159
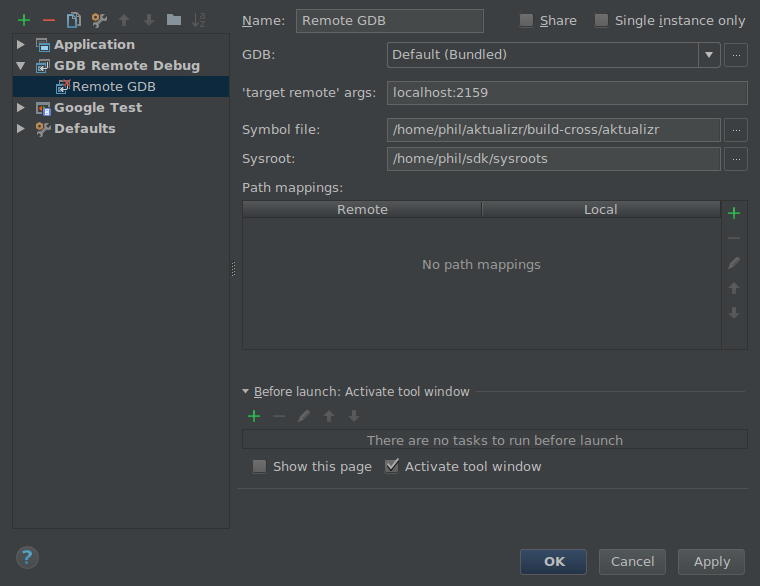
In CLion the remote debugger is configured as follows:
It is also possible to run it inside valgrind:
valgrind --vgdb=yes --vgdb-error=0 ./aktualizr --config /usr/lib/sota/sota.toml vgdb --port=2159
Then connect the debugger as usual.
Run the client and provide a yaml formatted configuration file using the commandline option -c or --config. The configuration file has to contain the OAuth2 server URL, the SOTA server URL, a valid clientID and according secret and a valid device UUID. See the example config file at config/config.yml.example. The client will use the clientID and according secret to get an OAuth2 token from the authorization server which is then used to send API requests to the SOTA server.
aktualizr -c <path/configfile>
This code is maintained by the team at ATS Advanced Telematic Systems GmbH. If you have questions about the project, please reach us through Github issues for this repository.
Complete contribution guidelines can be found in CONTRIBUTING.md.
This code is licensed under the Mozilla Public License 2.0, a copy of which can be found in this repository. All code is copyright ATS Advanced Telematic Systems GmbH, 2016-2018.